The Nervous Tissue
- How do we react to stimuli?
This is becaus e of the nervous tissues present in our body. They are capable of transmitting information quickly from the brain to different parts of the body and vice-versa.
- Therefore, nervous tissues are found in nerves, brain, and spinal cord.
- The Nervous tissue is made up of cells called the Nerve Cells or Neurons.
- These neurons connect together to form the nerves of our body.
Structure of a Neuron
-
- It is an elongated cell with a Cell Body that consists of some branch-like structure called Dendrites.
- There is a Nucleus present in the centre of the cell body.
- The Nerve Endings of the cell are connected with the cell body via Axon.
- A nerve cell can be up to 1 m long.
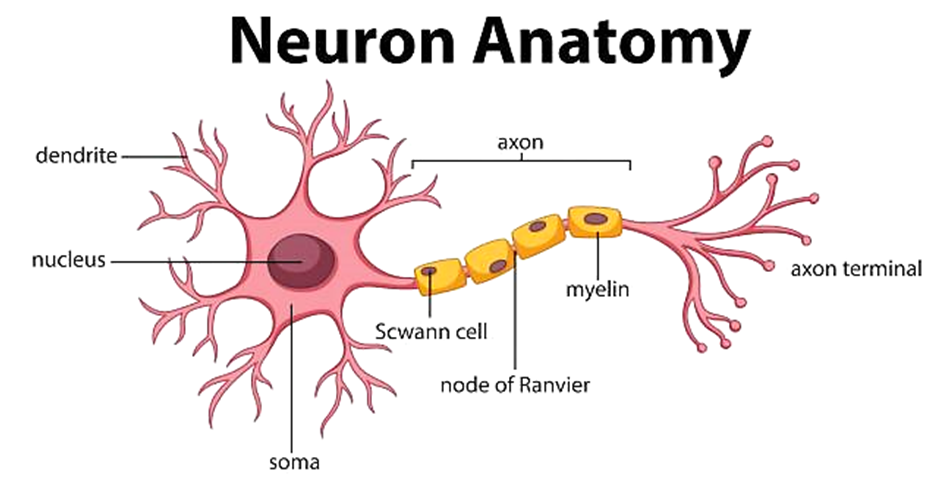
Structure of Neuron
1.Dendrites
- They are tree-like extensions (highly-branched) at the beginning of a neuron.
- They increase the surface area of the neuron.
- They receive chemical signals from different neurons of the body.
- They then convert these chemical signals into electrical signals and pass them to the neuron cell body.
- A neuron can have a single dendrite or multiple dendrites
2. Cell Body
- Also called Soma.
- The main function of the cell body and nucleus of the neuron is to maintain the functionality of the cell.
- It does not play an active role in the transmission of the signal.
- It produces proteins that are required by different parts of the neuron to work properly.
- It contains different cell organelles such as mitochondria, Golgi apparatus etc that perform various functions of the cell.
3. Axon
- Neurons have one axon in general.
- It is a long structure that connects the cell body to the terminals and it also connects with other neurons, cells and organs of the body through nerve terminals.
- It allows in fast transmission of signals. The larger the diameter of the axon the faster it will transmit signals.
- It is covered with a special insulating substance called myelin. It helps in rapid transmission of signals.

 ACERISE INDIA
ACERISE INDIA
 Vaishnav Publication
Vaishnav Publication
