Tissues
Introduction
• Living organisms in this world comprise of cells.
• There are unicellular as well as multicellular organisms present in this world.
• In unicellular organisms, the only single cell is capable of performing several functions such as Respiration, Digestion and Clearing of the cell.
• In multicellular organisms, there is a division of labour. There are different types as well as groups of cells that perform different functions in a multicellular organism.
• Cells form groups cells that need to perform a single task often group together.
• This grouping of cells together to perform a function efficiently is called a Tissue. For Example, Muscles and Blood.
• The tissue cells have the same structure and they perform the same function.
Plant Tissues
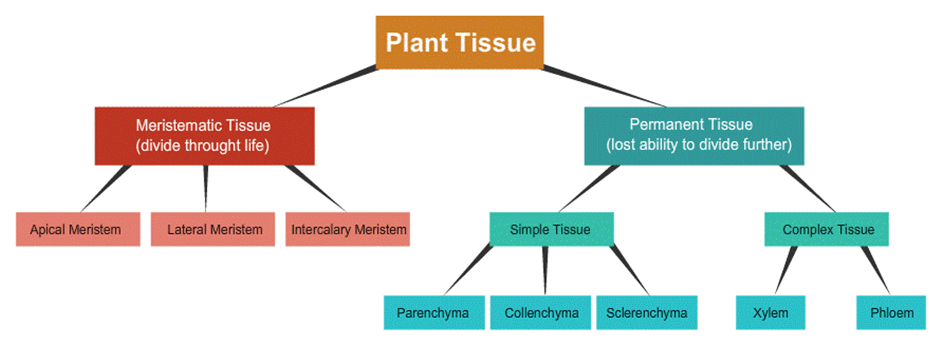
Types of Plant Tissues
Meristematic Tissue
• Only certain parts of a plant tend to grow. The tissues located in such parts are called meristematic tissues.
• They have the capability to divide themselves and form new tissues. They have thin cell wall made of cellulose. Also have dense nucleus and cytoplasm but lack vacuoles.
• They can further we classify differently based on the areas of the plants where they are located -
o Apical
o Lateral
o Intercalary
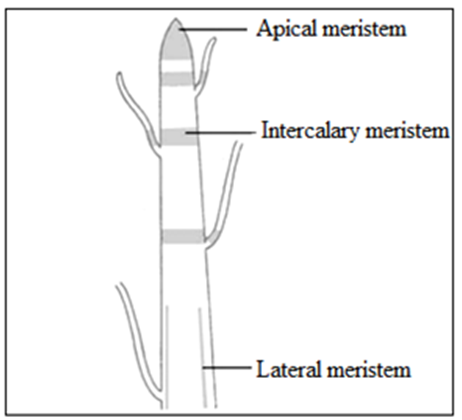
Location of meristematic tissue
|
Apical Meristem |
Lateral Meristem |
Intercalary Meristem |
|
|
|
Why there are no vacuoles in the intercalary meristem?
- Vacuoles are responsible for storage of food in water. The intercalary tissues do not store them. They are rather responsible for manufacturing them.
- Moreover, vacuoles contain sap which provides rigidity to a cell. This property of vacuoles may not allow the intercalary tissues to divide and manufacture new cells. Hence vacuoles are not present in them.
- Books Name
- Yash Tyagi Coaching Science Book
- Publication
- ACERISE INDIA
- Course
- CBSE Class 9
- Subject
- Science
Chapter-2
Tissues
Introduction and Plant Tissues
Introduction
As you all know that we have a complex body organization starting from cellular level to a well-developed individual. If we look at the hierarchy of organization we see that:
Cells → Tissue→ organ→ organ system→ organism
As far as cells are concerned, we have studied that cells are structural and functional units of life. The cells, when formed, undergo the process of differentiation according to the functions that they will perform. The cells that have the same structure, features and perform the same functions form a particular type of tissue. Let us start with the chapter where we will learn all about it.
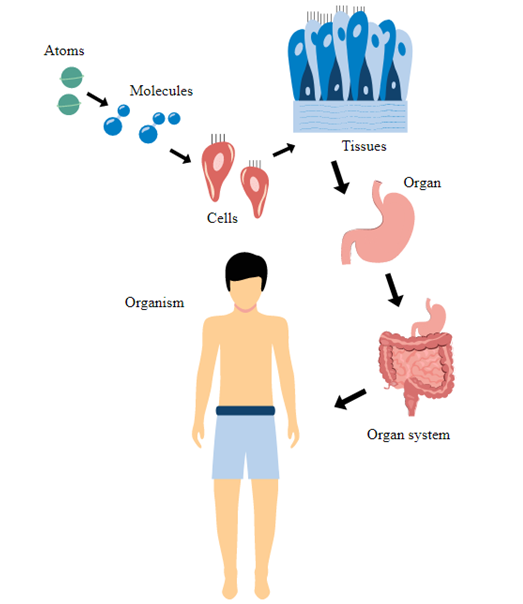
The cells which are specialized in a function are grouped together and form a particular type of tissue. We have different tissues in our body that performs different functions like:
1. They play the role of protection.
2. They help in control and coordination.
3. They help in transportation.
4. They act as insulators.
5. Many more functions are performed.
Let us learn about Plant tissue
Types of plant tissues
They are classified into mainly two types as given below
- Meristematic tissue
- Permanent tissue
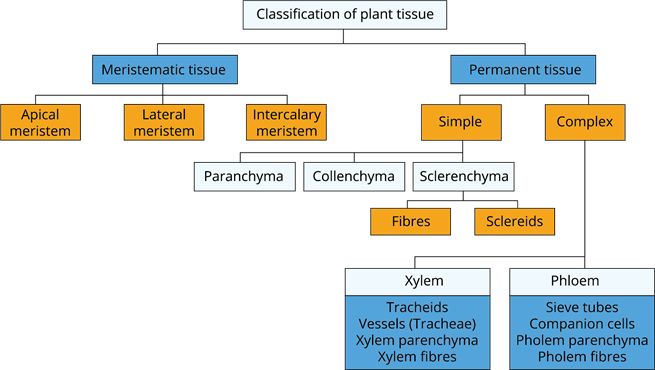
Meristematic tissue and its types
You all have seen that plants have a tendency to grow and keep growing throughout their life. This is because of certain cells in it that keep on dividing and they are called meristematic cells. Let us learn about them. They are formed of cells that have the ability to divide continuously throughout their life and help in increasing the length and girth of the plant.
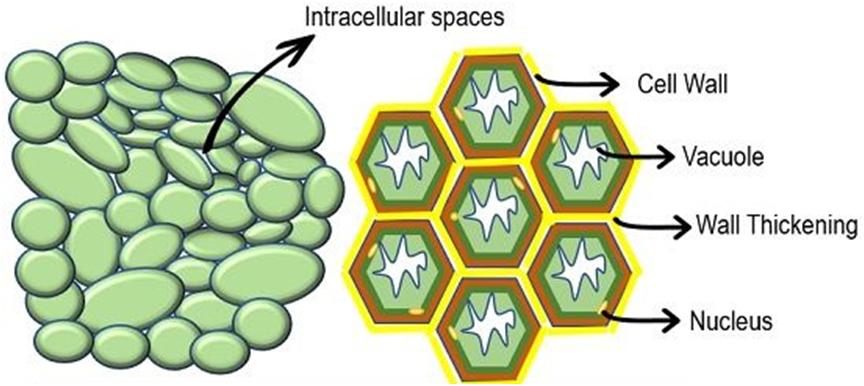
Characteristics of meristematic cells
- They have thin cellulose cell walls.
- The meristematic cells may be spherical, oval, polygonal or rectangular in shape. The meristermatic cells are compactly arranged.
- Each meristematic cell contains dense or abundant cytoplasm and a single large nucleus.
- The meristematic cells contain few vacuoles or no vacuoles at all.
Occurrence
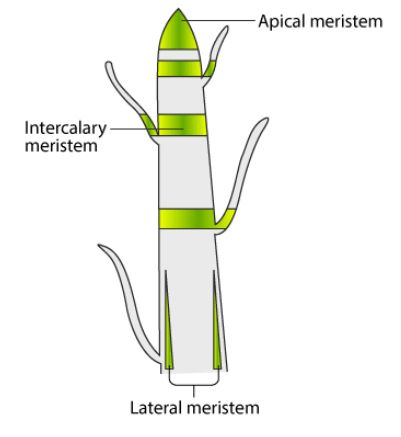
According to their position in the plant, meristems are of three types:
- Apical meristem
- Lateral meristem
- Intercalary meristem
Apical meristems
- It is present at the growing tip of stems and roots. It is at shoot apex and root apex.
- Its function is to increase the height of the plant.
Lateral meristems
- These are found beneath the bark (called cork cambium).
- The function is to help increase in diameter.
Intercalary meristems
- It is located at the base of leaves or at internodes.
- Its function is to increase the number of branches.

 Vaishnav Publication
Vaishnav Publication
 ACERISE INDIA
ACERISE INDIA
