- Books Name
- Psychology Book Class-12
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Psychology
Promoting Positive Health and Well-being
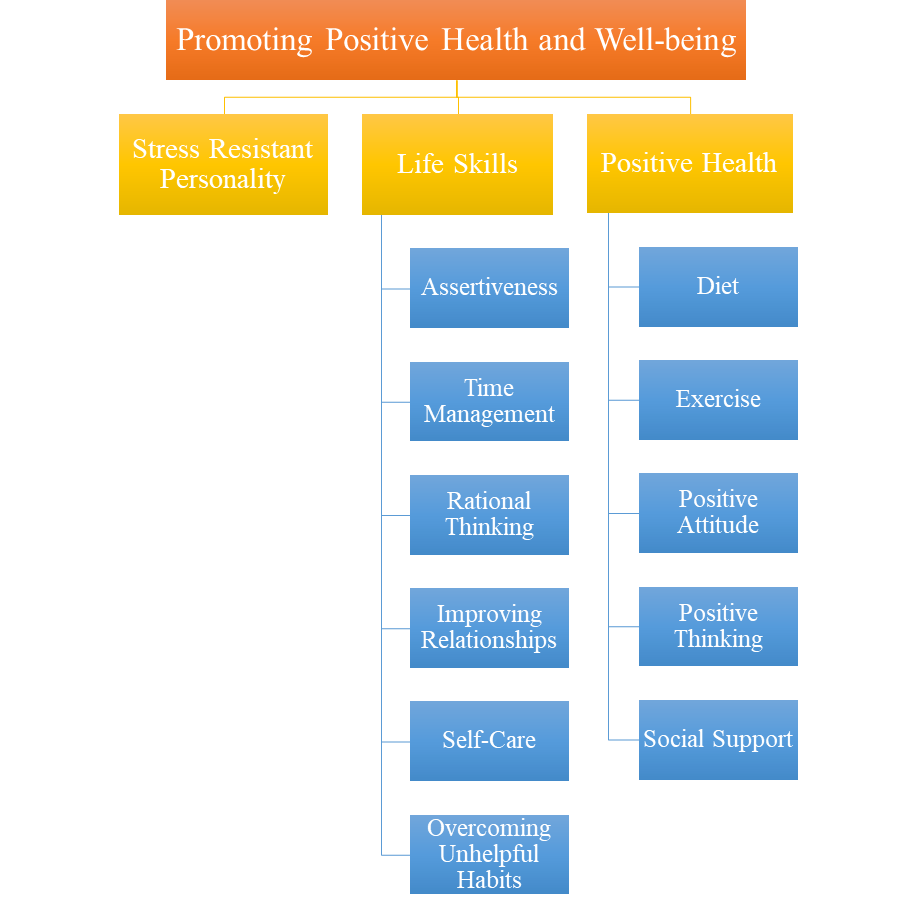
Stress Resistant Personality
- Kobasa have shown that people with high levels of stress but low levels of illness share 3 characteristics, which are referred to as the personality traits of ‘hardiness’
- Hardiness is a set of belief about oneself, the world and how they interact.
- It consists of ‘3 C’s’:
- Commitment - A sense of personal commitment to what you are doing. For instance, commitment to work, family, hobbies, social life.
- Control - A sense of control over your life.
- Challenge - A feeling of challenge i.e., they see changes in life as normal and positive rather than as a threat.
Life Skills
- Life skills are abilities for adaptive and positive behavior that enable individuals to deal effectively with the demands and challenges of everyday life.
- Our ability to cope depends on how well we are prepared to deal with and counterbalance everyday demands, and keep equilibrium in our lives.
- Can be learned as well as improved upon.
- Some of the like skills are:
a) Assertiveness
- A behavior or skill that helps to communicate, clearly and confidently, our feelings, needs, wants, and thoughts.
- Ability:
- to say ‘no’ to a request.
- to state an opinion without being self-conscious.
- to express emotions (love, anger, etc.) openly.
- An assertive person:
- feels confident
- has high self-esteem
- has a solid sense of own identity
b)Time Management
- The way we spend our time determines the quality of our life.
- Learning how to plan time and delegate can help to relieve the pressure.
- Major way to reduce time stress is to change one’s perception of time.
- Central principle of time management is to spend your time doing the things that you value or that help you to achieve your goals.
- It depends on being realistic about what you know and that you must do it within a certain time period, knowing what you want to do, and organizing your life to achieve a balance between the two.
c) Rational Thinking
- Many stress-related problems occur as a result of distorted thinking.
- The way we think and the way we feel are closely connected.
- When we are stressed, we have an inbuilt selective bias to attend to negative thoughts and images from the past, which affects our perception of the present and the future.
- Principles of rational thinking are:
- Challenging your distorted thinking and irrational beliefs.
- Driving out potentially intrusive negative anxiety-provoking thoughts.
- Making positive statements.
d) Improving Relationships
- Key to a sound lasting relationship is communication.
- This consists of 3 essential skills:
- Listening to what the other person is saying.
- Expressing how you feel and what you think.
- Accepting the other person’s opinions and feelings, even if they are different from your own.
- Also requires us to avoid misplaced jealousy and sulking behavior.
e) Self-care
- If we keep ourselves healthy, fit and relaxed, we are better prepared physically and emotionally to tackle the stresses of everyday life.
- Our breathing patterns reflects our state of mind and emotions.
- When we are stressed or anxious, we tend towards rapid and shallow breathing from high in the chest, with frequent sighs.
- When we are relaxed, breathing is slow, stomach-centered breathing from the diaphragm i.e. a dome like muscle between the chest and the abdominal cavity.
- Environmental stresses can all exert an influence on our mood.
- These have a noticeable effect on our ability to cope with stress and well-being.
f) Overcoming Unhelpful Habits
Such as perfectionism, avoidance, procrastination, etc. are strategies that help to cope in the short-term but make one more vulnerable to stress.
- Perfectionists are persons who have to get everything just right.
- They have difficult in varying standards according to factors such as time available, consequences of not being able to stop work, and the effort needed.
- More likely to feel tense
- Find it difficult to relax
- Critical of self and others
- May become inclined to avoid challenges
- Avoidance is to put the issue under the carpet and refuse to accept or face it.
- Procrastination means putting off what we know we need to do.
- People who procrastinate are deliberately avoiding confronting their fears of failure or rejection.
Positive Health
Health is a state of complete physical, mental, social and spiritual well-being, and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity.
Positive health comprises the following:
- A healthy body
- High quality of personal relationships
- A sense of purpose in life
- Self-regard
- Mastery of life’s tasks
- Resilience to stress, trauma and change
Following act as stress buffers and facilitate positive health:
a) Diet
- A balanced diet can:
- Lift one’s mood
- Give more energy
- Feed muscles
- Improve circulation
- Prevent illness
- Strengthen the immune system
- Make one feel better to cope with stresses of life
- The key to healthy living is to eat three main meals a day and eat a varied well-balanced diet.
- One’s activity level, genetic makeup, climate and health history determines the amount of nutrition one needs.
- What people eat, and how much do they weigh involve behavioral processes.
- Some people are able to maintain a healthy diet and weight while others become obese.
- When we are stressed, we seek ‘comfort foods’ (high in fats, salts and sugars).
b) Exercise
- Positive relationship between physical fitness and health.
- Lifestyle change with the widest popular approval.
- Regular exercise plays an important role in managing weight and stress
- Has a positive effect on reducing tension, anxiety and depression.
- Physical exercise that are essential for good health are stretching exercises such as yogic asanas and aerobic exercises such as jogging, cycling, swimming etc.
- Stretching exercises have a calming effect.
- Aerobic exercises increase the arousal level of the body.
- Health benefits of exercise work as a stress buffer.
- Fitness permits individuals to maintain general mental and physical well-being even in the face of the negative life events.
c) Positive Attitude
- Positive health and well-being can be realized by having a positive attitude.
- Factors leading to a positive attitude are:
- Having a fairly accurate perception of reality.
- A sense of purpose in life and responsibility.
- Acceptance and tolerance for different viewpoint of others
- Taking credit for success and accepting blame for failure.
- Being open to new ideas
- Having a sense of humor with the ability to laugh at oneself.
- These factors help us to remain centered, and see things in a proper perspective.
d) Positive Thinking
- Helps significantly in reducing and coping with stress.
- Optimism i.e. the inclination to expect favorable life outcomes, has been linked to psychological and physical well-being.
- Optimists tend to:
- assume that adversity can be handled successfully.
- use more problem-focused coping strategies whereas,
- Pessimists tend to:
- anticipate disasters
- ignore the problem or the source of stress
- use strategies such as giving up the goal with which stress is interfering or denying that stress exists.
e) Social Support
- The existence and availability of people on whom we can rely upon, people who let us know that they care about, value, and love us.
- Someone who believes that she/he belongs to a social network of communication and mutual obligation experiences social support.
- Perceived support i.e., the quality of social support, is positively related to health and wellbeing.
- Social network i.e., the quantity of social support, is unrelated to well-being, as it is very time-consuming and demanding to maintain a large social network.
- Social support can help to provide protection against stress.
- During times of stress, one may experience sadness, anxiety and loss of self-esteem.
- People with high levels of social support from family and friends may experience less stress when they confront a stressful experience, and they may cope with it more successfully.
- Social support may be in the form of:
- Tangible support or assistance involving material aid such as money, goods, services etc.
- Family and friends also provide informational support about stressful events.
- Supportive friends and family provide emotional support by reassuring the individual that she/he is loved, valued and cared for.
- Social support effectively reduces psychological distress such as depression, anxiety during times of stress.
- Social support is positively related to psychological well-being.
- Social support leads to mental health benefits for both the giver and the receiver.

 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
