- Books Name
- Psychology Book Class-12
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Psychology
Stress and the Immune System
- Stress can cause illness by impairing the workings of the immune system which guards the body against attackers, both from within and outside.
- Psychoneuroimmunology focuses on the links between the mind, the brain and the immune system. It studies the effects of stress on the immune system.
- Working of immune system:
- The white blood cells (leucocytes) within the immune system identify and destroy foreign bodies (antigens) such as viruses.
- Leads to the production of antibodies.
- Several kinds of WBCs:
- T cells destroy invaders and T helper cells increase immunological activity. It is these T helper cells that are attacked by HIV (Human Immuno Deficiency Virus), the virus causing AIDS (Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome).
- B cells produce antibodies.
- Natural killer cells are involved in the fight against both viruses and tumors.
- Stress can affect natural killer cell cytotoxicity which is of major importance in the defense against various infections and cancer, therefore reduced levels of natural cell cytotoxity have been found in people who are highly stressed.
- Immune functioning is better in individuals receiving social support.
- Changes in the immune system will have more effect on health among those whose immune systems are already weakened.
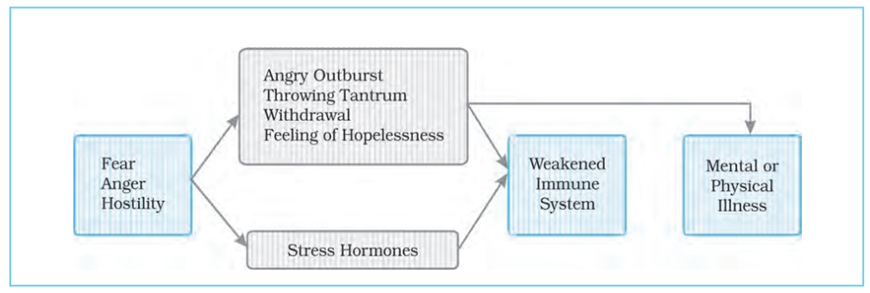
- Psychological stress is accompanied by negative emotions and associated behaviors, including depression, hostility, anger and aggression.
- Negative emotion states are of particular concern to the study of effects of stress on health.
- The incidence of psychological disorders, such as panic attacks and obsessive behavior increases with the build up of long-term stress.
- Worries can reach such a level that they surface as a frightening, painful physical sensation, which can be mistaken for a heart attack.
- People under prolonged stress are more prone to irrational fears, mood swings and phobias and may experience fits of depression, anger and irritability.
- These negative emotions appear to be related to the function of the immune system.
- Negative moods have been associated with poorer health outcomes.
- Feelings of hopelessness leads to/ causes worsening of disease, increased risk of injury and death due to various causes.

 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
