- Books Name
- Psychology Book Class-12
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Psychology
Coping with Stress
- It is how we cope with stress and not the stress one experiences that influences our psychological well-being, social functioning and health.
- Coping is a dynamic situation-specific reaction to stress. It is a set of concrete responses to stressful situations or events that are intended to resolve the problem and reduce stress.
- The way we cope with stress often depends on rigid deep-seated beliefs, based on experience.
- People who cope poorly with stress have an impaired immune response and diminished activity of natural killer cells.
- Endler and Parker gave the following coping strategies:
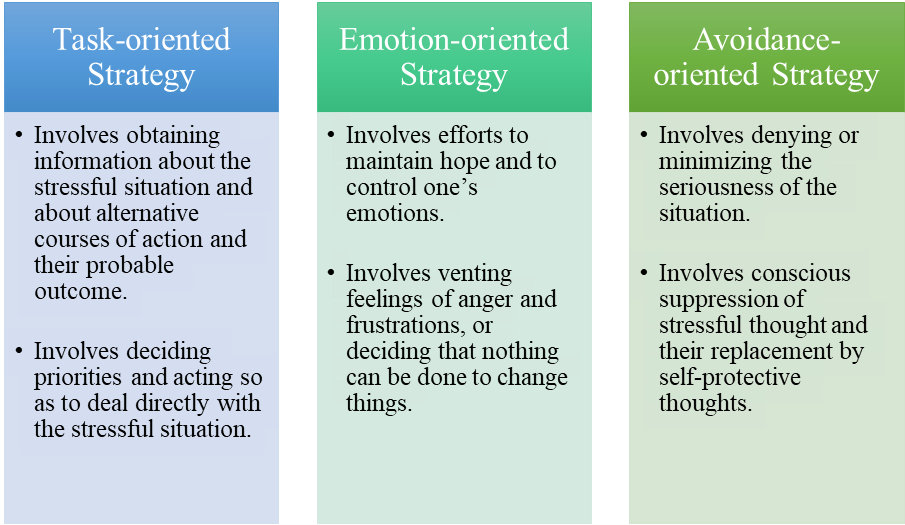
- Lazarus and Folkman have conceptualized coping as a dynamic process rather than an individual trait.
Coping refers to constantly changing cognitive and behavioral efforts to master, reduce or tolerate the internal or external demands that are created by the stressful transaction.
Coping serves to allow the individual to manage on alter a problem and regulate the emotional response to that problem.
According to them, coping responses can be divided into two types of responses:
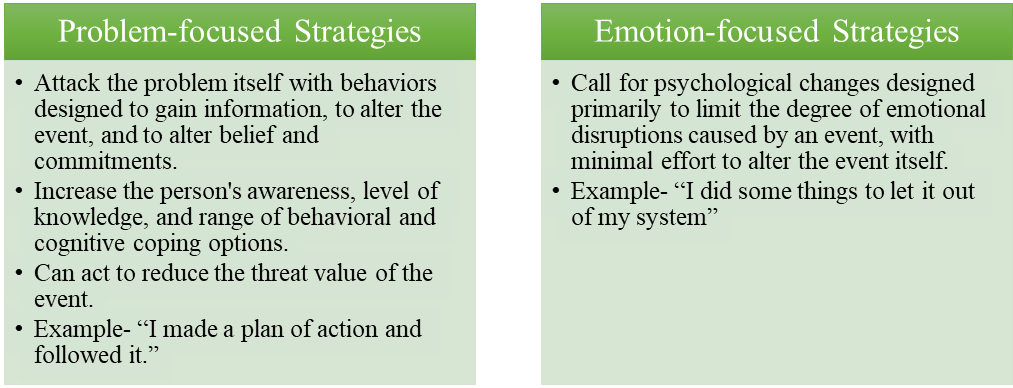
Stress management techniques
Relaxation Techniques
- An active skill that reduces symptoms of stress and decreases the incidence of illnesses such as high blood pressure and heart disease.
- Usually relaxation starts from the lower part of the body and progresses up to the facial muscles in such a way that the whole body is relaxed.
- Deep breathing is used along with muscle relaxation to calm the mind and relate the body.
Meditation Procedures
- The yogic method of meditation consists of a sequence of learned techniques for refocusing of attention that brings about an altered state of consciousness.
- Involves such a thorough concentration that the meditator becomes unaware of any outside stimulation and reaches a different state of consciousness.
Biofeedback
- A procedure to monitor and reduce the physiological aspects of stress by providing feedback about current physiological activity and is often accompanied by relaxation training.
- Biofeedback training involves 3 stages:
- Developing an awareness of the particular physiological response.
- Learning ways of controlling that physiological response in quiet conditions.
- Transferring that control into the conditions of everyday life.
Creative Visualization
- An effective technique for dealing with stress
- A subjective experience that uses imagery and imagination.
- Before visualizing one must set oneself a realistic goal; helps build confidence.
- Easier to visualize if one’s mind is quiet, body relaxed, and eyes are closed.
- Reduces the risk of interference from unhidden thoughts.
- Provides the creative energy for turning an imagined scene into reality.
Cognitive Behavioral Techniques
- Aim to inoculate people against stress.
- Stress inoculation training is one effective method developed by Meichenbaum.
- The essence of this approach is to replace negative and irrational thoughts with positive and rational ones.
- There are 3 main phases in this:
- Assessment involves discussing the nature of the problem and seeing it from the viewpoint of the person/client.
- Stress reduction involves learning the techniques of reducing stress such as relaxation and self-instruction.
- Application and follow-through involves applying or following the stress reduction techniques.
Exercise
- Can provide an active outlet for the physiological arousal experienced in response to stress.
- Improves the efficiency of the heart.
- Enhances the function of the lungs
- Maintains good circulation
- Lowers blood pressure
- Reduces fat in the blood
- Improves the body’s immune system
- Swimming, walking, running, cycling, skipping etc. help to reduce stress.
- Must practice these exercises at least four times a week for 30 mins at a time.
- Each session must have a warm-up, exercise and cool down phases.

 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
