1. What was the Soviet System?
- Books Name
- Education Vision Political Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Political Science
END OF BIPOLARITY
- Bipolar: Two poles i.e., 2 superpowers
- Bipolar World ended and Unipolar world started.
- Berlin (i.e., Germany) was divided in 2 parts. East Berlin and West Berlin by the construction of Wall in 1961
- Division led because of difference in ideologies. West Berlin supported Capitalism and East Berlin followed Communism.
- 9th November 1989 wall between West and East Berlin was broken and everyone united and adopted Capitalism.
- It was remarkable in the world history and Unipolar World started.
- Many collapses like this happened and USSR disintegrated.
- US became the superpower.
WHAT WAS THE SOVIET SYSTEM?
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) came into being after Russian Revolution in 1917.
1. Soviet Union POLITICAL SYSTEM:
- COMMUNISM:
- Economy was planned and controlled by government.
- One party dominance and no opposition
- Communist party in USSR
- East Europe was part of USSR and followed same ideology of communism. And this group of countries was called the Second World or the “socialist bloc”.
- The military alliance (Warsaw Pact) held them together.
- The USSR was the leader of bloc.
2. The soviet economy was very developed than the rest of the world except US. Features being:
- Had complex communication network, vast energy resources including oil and minerals.
- Transport sector which connected its remotest areas with efficiency.
- It had domestic consumer industry that produced everything from pins to cars, though their quality did not match to the quality of western countries.
- Ensured minimum standard of living, all the basic amenities were provided by government.
- No unemployment.
- State ownership was dominant
3. Problems of USSR or in USSR:
- It was very bureaucratic and authoritarian i.e., strict rules and regulation imposed on citizens

- No Democracy
- No freedom of speech, people expressed their opinions through jokes and cartoons.
- Communist party had tight control over institutions and was unaccountable to people of USSR.
- And such institutions which needed reforms were ignored by government.
- The communist party refused to recognize the urge of people in 15 different republics (Russia + 14 states) that formed the Soviet Union.
- On papers 15 republics together constituted the USSR, but in reality, Russia dominated everything and people of other regions felt suppressed/ neglected.
4. In arms race USSR managed to match the US but USSR lagged behind from US in:
- Technology
- Infrastructure
- Fulfilling the political or economic aspirations of citizens.
- USSR invaded Afghanistan in 1979 because of which the USSR’s system weakened.
- Wages continued to grow but productivity and technology got far behind.
- Which led to shortage in customer goods.
- Food imports increased.
- And in the late 1970’s the Soviet economy became stagnant.
2. Gorbachev and the Disintegration of the USSR
- Books Name
- Education Vision Political Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Political Science
GORBACHEV AND THE DISINTEGRATION OF USSR
- Mikhail Gorbachev the General Secretary of Communist party (USSR) in 1985.
- He brought reform in the USSR.
- He wanted to know the citizens of USSR and also wanted to be fully updated about the technological revolutions taking place in the West.
- He wanted to normalize the relationships with the west and democratize and reform the USSR.
- But this brought some effects which neither he nor anyone else anticipated:
- East European countries started protesting against their own government and USSR for democracy to be established. And one by one communist regimes started collapsing.
- At the same time economic system was of the USSR weakened which hastened the disintegration.
- Gorbachev initiated political and economic reforms and democratization within the country but the reforms were opposed by the leaders withing the Communist party.
- And the leaders of communist party started a coup in 1991.
- People now tasted the freedom and did not want to live in the old style.
- Boris Yeltsin became the national hero as he won the election in Republic Russia and opposed the coup.
- Eastern Europe demanded independence and Central Asian republics wanted to remain with Soviet Federations.
- In 1991, Russia, Ukraine and Belarus, the three major republics of USSR declared that USSR has disbanded.
- Capitalism and democracy were adopted for post- Soviet republics.
- USSR disintegrated, all states separated from Warsaw Pact and “Commonwealth of Independent States” (CIS) was introduced and this was a surprise for Central Asia republics.
- After disintegration Russia inherited the Soviet seat in the UN security Council.
- Russia accepted all the international treaties of Soviet Union.
- Only nuclear state was Russia and carried out some nuclear disarmament measures with the US.
- Old USSR buried and Russia was accepted as the successor state.
Why Did the Soviet Union Disintegrate?
- Weakness of the USSR’s economic and political institutions led to the disintegration:
1. Economic Weakness:
- The e
 conomic stagnation leading to severe consumer shortages of goods and services. As a result, the public was not satisfied and started doubting and asking questions openly, which was later followed by protests.
conomic stagnation leading to severe consumer shortages of goods and services. As a result, the public was not satisfied and started doubting and asking questions openly, which was later followed by protests. - Reasons of weak and stagnated economy:
- USSR used to spend money and resources in maintaining a nuclear and military arsenal.
- Spend money in development of satellite states in Eastern Europe and within USSR (basically in 5 Central Asian republics).
- People gained knowledge about the technological advancement in the West and started comparing.
2. Political Weakness:
- Communist party was ruling over 70 years and became authoritarian and was not accountable to people.
- Corruption started at high rate; government could not stop/reduce it.
- The people did not know about the functioning about the government/ political system i.e., lack of transparency between people and the government.
- Party bureaucrats gained privileges than ordinary citizens.
- People did not identify with the system and with the rulers and the government lost popular backing.
- Even after reforms of Gorbachev were introduced and promised to deal with the problems, USSR disintegrated. Why?
3. There were sections of society which believed that Gorbachev should have moved much faster, and he was disappointed and impatient with his methods.
4. Communist party had a opposite view and concerns, they felt that their power and privileges were eroding and Gorbachev was moving very fast.
- Therefore, Gorbachev lost support on all sides and divided the public opinion. People who were with him were disillusioned and felt he did not defend his own policies.
- The final and most immediate cause for the disintegration for USSR:
5. The rise of nationalism and the desire for sovereignty within various republics including Russia and the Baltic Republics (Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania), Ukraine, Georgia, and others.
2.Consequences of Disintegration
- There were many consequences of disintegration, but for now we will talk about only three:
1) End of Cold War Confrontation and Ideology Dispute
- The ideological dispute over whether the socialist system would beat the capitalist system was not an issue any more.
- As a result, the end of confrontation demanded an end to his arms race and a possible new peace.
2) Power relations in World Politics Changed:
- Two possibilities were there:
(i) Unipolar world- Only one republic will be dominant
(ii) Multipolar world- No one country will be dominant.
- But after Cold War US became the dominant republic and became unipolar.
- Capitalistic ideology was followed internationally.
- Institutions like World Bank and International Monetary Fund became powerful advisors and other countries took loan from them for developing.
- Now, the best way to organize the political life was liberal democracy.
3) Emergence of New Countries:
- The end of Cold War led to the emergence of many new countries.
- Baltic and east European states became part of NATO.
- Central Asian countries continued close ties with Russia and also established ties with the west, the US, China and others.
- All the new countries had their own independent aspirations and choices.
3. Shock Therapy in Post-Communist Regimes
- Books Name
- Education Vision Political Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Political Science
SHOCK THERAPY IN POST-COMMUNIST REGIMES
- The collapse of communism was followed in most of these countries by a painful process of transition from an authoritarian socialist system to a democratic capitalist system.
- The model of transition in Russia, Central Asia and east Europe that was influenced by the World Bank and the IMF came to be known as ‘shock therapy’.
- Shock therapy varied in intensity and speed amongst the former second world countries, but its direction and features were quite similar.
- Features of Shock Therapy:
- Each of these countries was required to make a total shift to a capitalist economy, which meant rooting out completely any structures evolved during the Soviet period.

- Private ownership became the dominant pattern.
- Privatisation of state assets and corporate ownership patterns were to be immediately brought in.
- Collective farms were to be replaced by private farming and capitalism in agriculture.
- Shock Therapy also changed the external orientation of these economics:
- Development was now envisaged (to bring) through more trade, and thus a sudden and complete switch to free trade was essential.
- The free trade regime and foreign direct investment (FDI) were to be the main engines of change. Also involved:
- Foreign investment
- Financial Opening/de-regularisation
- Currency Convertibility
- Finally, the transition also involved a break-up of the existing trade alliances among the countries of the Soviet bloc:
- The states were to adopt the western eco system(capitalism).
- The Western capitalist states now became the leaders and thus guided and controlled the development of the region through various agencies and organisations.
Consequences of Shock Therapy
Bad results are:
- Largest – Garage sale
- 90 % of the state-owned industries were to put upon sales to private individual companies.
- Virtual disappearance of entire industries happened, they were undervalued and sold through auction at thrown away prices.
- All citizens were given vouchers to participate in sales, but many sold it in black market for extra money.
- De- regulation of currency
- The value of Russian currency “ruble” decreased.
- The rate of inflation was so high that people lost all they savings.
- The collective farm system disintegrated leaving people without food security and Russia, started to import food.
- In 1999 the GDP of Russia was less than that of the previous year
- Social-Welfare Declined
- The withdrawal of government subsidies pushed large sections of the people into poverty. Basic needs weren’t fulfilled now.
- The middle classes were pushed to the periphery of society, and the academic and intellectual manpower disintegrated or migrated.
- Mafia Emergence
- Many economics activities controlled by Mafia’s.
- Privatisation led to new disparities.
- Post-Soviet states, Russia, was now divided as rich and poor regions.
- Economic inequality between people started increasing at a high rate.
- Ignorance of Democratic Institution
- Construction of democratic institutions weren’t given much importance.
- As the constitution of countries were drafted in hurry, President was given high powers.
- In Central Asia, the presidents had great powers, and several of them became very authoritarian.
- The presidents of Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan appointed themselves to power for first ten years and then extended it for another ten years, not allowing any opposition to take place.
- No Judicial Culture
- A judicial culture and independence of the judiciary was yet to be established in most of these countries.
- Countries started reviving in 2000, as most of the countries were oil, gas and mineral rich countries.
- Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, Russia, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan were major oil and gas producers and exported them for money.
- Other countries on their territories got rent for the oil pipelines passing through them.
2.Tensions and Conflicts
- Most of the former Soviet Republics are prone to conflicts, and many have had civil wars and insurgencies, growing involvement of outside powers complicate the situations.
- Chechnya and Dagestan [Russian Republics]- had violent secessionist and movements.
- Moscow’s method of dealing with Chechen rebels and indiscriminate military bombing had led to many human right violations but have failed to deter the aspirations for independence.
- Tajikistan witnessed a civil war that went on for 10 years till 2001.
- The region as a whole has many sectarian conflicts.
- In Azerbaijan’s province of Nagorno-Karabakh, some locals Armenian’s wanted to secede and join Armenia.
- In Georgia, two provinces demanded independence which later turned out to be civil war.
- Countries and provinces are fighting over river waters, which makes ordinary citizens life difficult.
- The Central Asian Republics has areas with vast hydrocarbons resources, at the same time it has become a zone of competition between outside powers and oil companies.
- Region which next to Russia, China, Afghanistan, Pakistan and Close to West Asia, US wanted the military base in that region and paid to all Central Asian States to hire bases, and to allow airplanes to fly over their territories during the war in Afghanistan and Iraq. (After 11 September 2001)
- In easter Europe, Czechoslovakia divided themselves into two independent countries. i.e., the Czechs and the Slovaks.
- After 1991, Balkan republics of Yugoslavia was broken into independent provinces like Croatia, Slovenia and Bosnia and Herzegovina etc.
- Serbs opposed this, and a massacre of non-Serb Bosnians followed.
- The NATO intervention and the bombing of Yugoslavia followed the inter-ethnic civil war.
- Russia perceives these countries to be “Near Abroad” and tells these countries should be under their influence.
- China has interest because of oil resources and settling around borders to conduct trade.
3.India And Post-Communist Countries

- India has good relations with all states but it is stronger with Russia.
- India’s relations with Russia are an important aspect of India’s foreign policy.
- It is popular in history
- Russian people keep names after Bollywood actors.
- Bollywood song are popular in Russia and many post- Soviet countries.
- India and Russia share a vision of multipolar world order.
- More than 80 bilateral agreements have been signed between India and Russia as a part of Indo-Russia strategic Agreement of 2001.
- India has benefits with relationship, which being on:
- Kashmir Issue
- Energy supply (oil crisis)
- Sharing information on international terrorism
- Access to Central Asia
- Balancing relationships with China
- Military hardware’s from Russia
- Russia is important for India’s nuclear energy plans. Ex- Russia gave cryogenic rocket to India when we needed it.
4. Middle East Crisis
- Books Name
- Education Vision Political Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Political Science
MIDDLE EAST CRISIS
5. Democratic Politics and Democratization
- Books Name
- Education Vision Political Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Political Science
DEMOCRATIC POLITICS AND DEMOCRATIZATION
1.Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS)
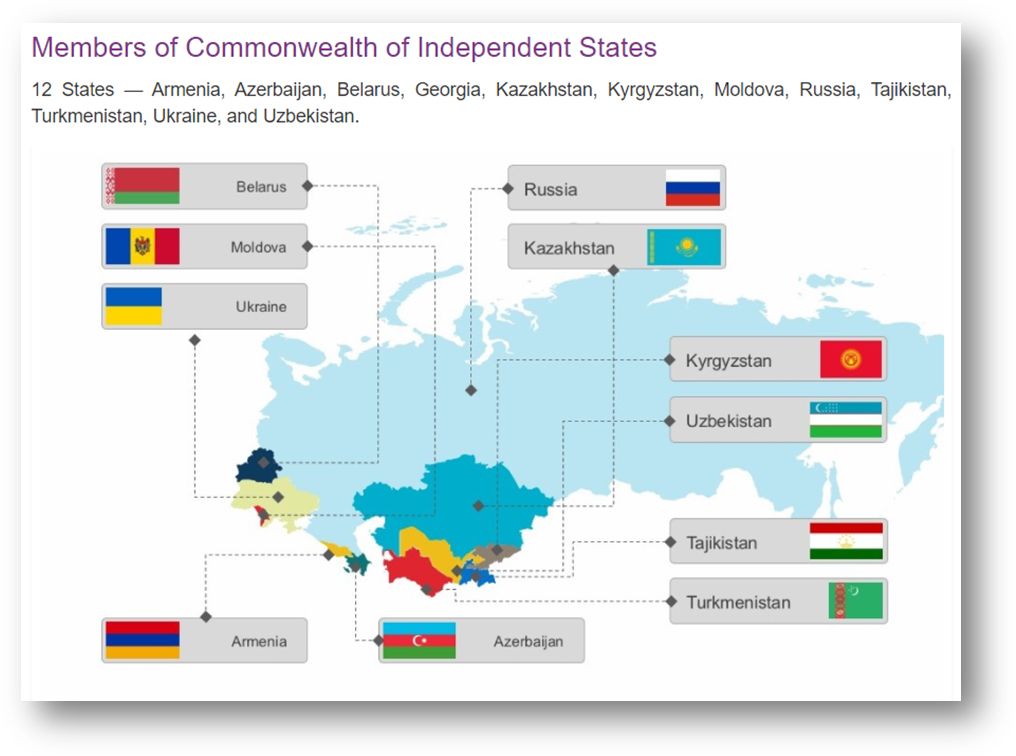
- CIS -> Commonwealth of Independent states
- Established on: 8th December 1991
- History:
In December 1991, Russia, Belarus and Ukraine formed a regional organization known as intergovernmental commonwealth of independent states (CIS), later on joined by Armenia, Kazakhstan, Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, Moldova and Kyrgyzstan.
↓
The objective of the formation of CIS was to cooperate on political, economic, environmental and other issues.
- Features and functions of CIS:
- The CIS has its headquarters at Minsk, Belarus,
- An Executive Director heads the CIS.
- The CIS is not a successor country to the Soviet Union. The CIS is an organization or alliance of independent countries.
- The Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) meets periodically on a rotating basis at the capitals of the Member Countries.
- The CIS performs its activities based on the CIS Charter which was signed in 1993 in order to set up various institutions of the CIS and their rules and functions.
- It also mentions that the Commonwealth of Independent States shall serve in developing and strengthening trust, mutual understanding, friendship, Inter-ethnic accord and cooperation between the member states.
2.Arab Spring

- The 21st century witnessed emergence of new developments for democracies and democratization in West Asian countries, one such event is characterized as Arab Spring that began in 2009.
- Located in Tunisia, the Arab Spring took its roots where the struggle against corruption, unemployment and poverty was started by the public which turned into a political movement because the people considered the existing problems as outcome of autocratic dictatorship.
- The demand for democracy that started in Tunisia spread throughout the Muslim-dominated Arab countries in West Asia.
- Hosni Mubarak, who had been in power in Egypt since 1979, also collapsed as a result of the massive democratic protests.
- In addition, the influence of Arab Spring could also be seen in Yemen, Bahrain, Libya and Syria where similar protests by the people led to democratic awakening throughout the region.
- Causes of Arab Spring were
1. Economic Causes
- The economic condition of the Middle East countries was very much deteriorating. The people were suffering from food crisis and low standard of living. Level of unemployment was increasing.
2. Social Causes
- The people did not have the social freedom to move freely or to express their opinions in the public. The government of dictator had the absolute rule over the whole society.
3. Corruption
- In Middle East countries the corruption was at its height during this this time. The business elites collaborated with the regime to exploit the masses
4. Rebellion
- Within a month of the downfall of Tunisian dictatorship in 2011, the protests spread to almost every Arab country, as people revolted, though with varying intensity, but the media helped to a great extent to give further encouragement to the rebellion.
5.Sudden cause
- The death of Mohammed Bouazizi, the street hawker of Tunisia led the inhabitants of Arab states to go against the despotic rulers. He committed the self-immolation as a protest in December, 2010, when his goods were taken away and he was humiliated at the hands of a female municipal officer.
- Result of Arab Spring:
6. Removal of Authoritarian rulers from Tunisia, Libya and Egypt-
- Most of the Middle Eastern countries were being ruled by the authoritarian rulers. Many of them ruled for decades so, after the revolt these despotic rulers were being removed from their thrones.
7. Political and Social Rights
- The rulers of Oman, Saudi Arabia, Morocco and Bahrain granted social and economic rights to their citizens.
8. Development of Public Political Sphere
- Arab Springs marked the formation of a public political sphere where common masses could discuss politics openly in the public places.
9. Emergence of democracy
- The revolt was a successful attempt at bringing democratic ideals in the Middle Eastern countries. The people got freedom from all the despotic shackles after long drawn war against it.

 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
