1. Emergence of Two Power Blocs
- Books Name
- Education Vision Political Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Political Science
EMERGENCE OF TWO POWER BLOCS
Cuban Missile Crisis

- Cuba was an island closer to US but it was ruled by USSR
- Cuba got all aids from USSR
- Cuba was a communist government ruled country
- In April 1961, USSR’s president worried that US might invade Cuba and throw off President Fidel Castro (president of Cuba).
- So, the president of USSR -- Nikita Khrushchev made Cuba Military base and placed nuclear missiles at the coast of Cuba.
- US became a bit afraid because the place where the missiles was placed by USSR, many states of US were near to it and US could not afford to lose them.
- After 3 weeks US became aware of the missiles placed my USSR.
- President of US – John F. Kennedy.
- US And USSR were having many nuclear weapons with intensity of 10 – 1500, which could destroy the whole world.
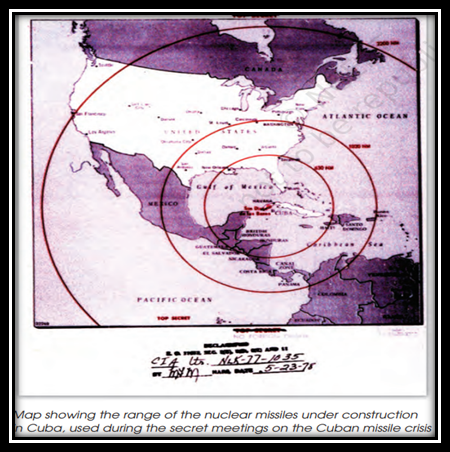
- US warned USSR, that If they say any missile approaching towards them, they will have to start the war.
- After the US made the statement USSR backed off and removed the missiles.
- And this war between US and USSR came to be known as CUBA MISSILE CRISIS because it created tension in the whole world.
- Cuba missile war was higher starting point of starting cold war.
The Cold War Rivalry
Reasons for Cold War between US and USSR
- Most important reason was their difference IDEOLOGIES as US favoured liberal,democracy and capitalism and USSR favoured socialism and communism.
- US wanted a multiparty or two-party dominance; USSR wanted one party dominance.
- Communism- Labours work for collective good, i.e., for govt and state.
- Capitalism- Refers to as individual gain, i.e., private gain.
- Alliance- a relationship based on similar interests.
COLD WAR
- It started after the end of World War II (1945).
- After the WW II ended US dropped 2 nuclear bombs to
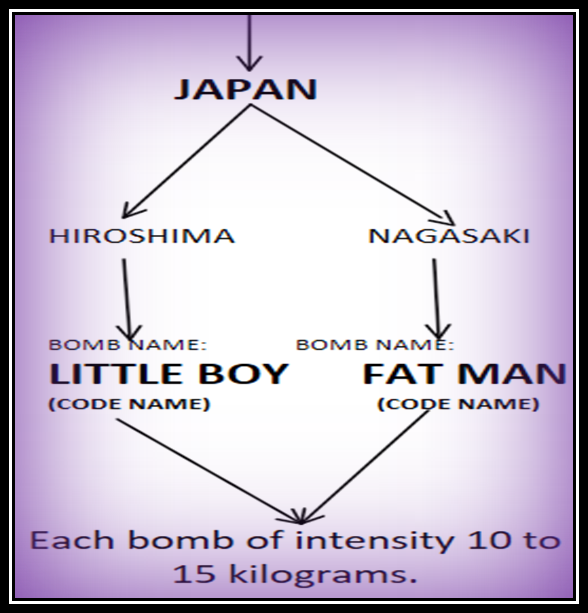
- And Japan surrendered.



LOGIC OF DETERRENCE:
Means if both countries fought together then It will be difficult to announce winner because both have extreme nuclear power and both can destroy each other.
---- No one will be winner
---- NO political gain
--- No economic gain
And that is why both the countries decided to adopt LOGIC OF DETERRENCE.
Military feature of Cold War:
If two countries have logic of deterrence the then they avoid war so countries have to stay rational and responsible, i.e., that is maintaining good relations and taking care of nuclear weapo
Emergence of Two Power Blocs
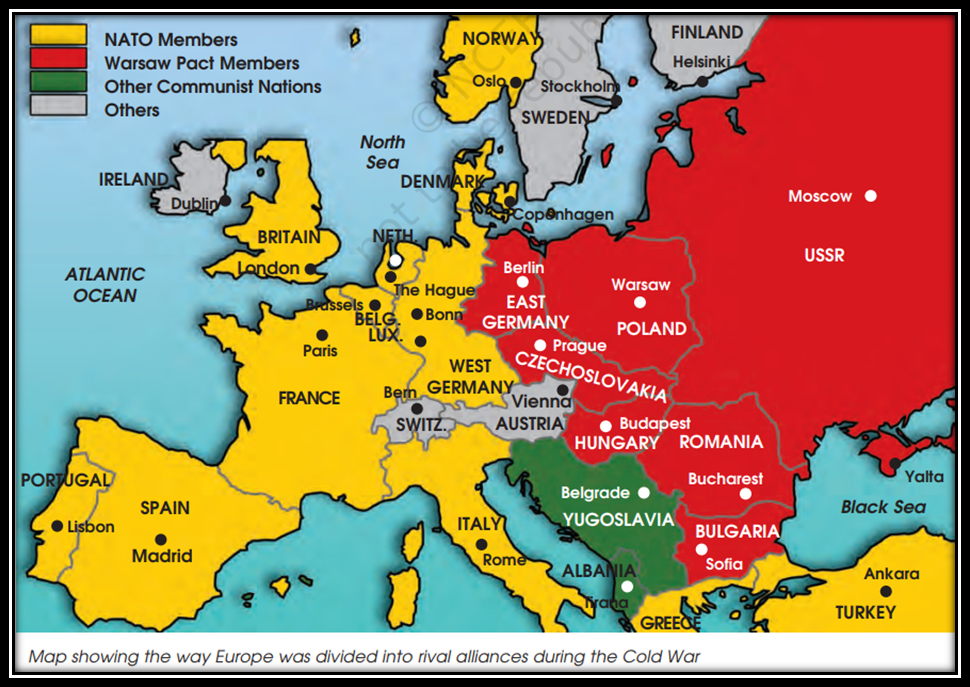
- The two superpowers i.e., the US and USSR wanted to expand their influence on the rest of the world.
- While expanding to the other states USSR and US promised of protection, weapons and economic aid against the state’s local rivals, mostly regional neighbours.
- The first division took place in Europe. Most countries of Western Europe sided with the US and were known as 'Western alliance’.
- The Western alliance formed itself into an organisation known as North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO). It came into existence in April, 1949 with twelve states namely Belgium, Canada, Denmark, France, Iceland, Italy, Luxemburg, Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, US and UK.
- The NATO declared that armed attack on any one of them in Europe or North America would be regarded as an attack on all of them.
- In East and South East Asia and in West Asia (Middle East), the United States built an alliance system called the South-East Asian Treaty Organisation (SEATO) and the Central Treaty Organisation (CENTO).
- The countries of the Eastern Europe joined the USSR and came to be known as ‘Eastern Alliance’
- The Eastern alliance, also known as the Warsaw Pact, was led by the USSR was established in 1955. Its principle function was to counter NATO's forces in Europe.
- Communist China quarrelled with the USSR towards the late 1950s and in 1969 they fought a brief war over a territorial dispute.
- The other important development was the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM), which gave newly independent countries a way of staying out of the alliances.
- The smaller countries were of more help to the superpowers because they were the means to gain vital resources such as oil and minerals; locations to spy each other and to launch weapons.
Arenas of The Cold War
- US and USSR were having cold war but they did not have war in their territory they used do wars in Alliance states.
- Arenas: Area where wars occurred or threated to occur between alliances system but did not cross limits ad there was no nuclear war.
- Cold war was also responsible for many shooting wars such as:
- Korean War (1950 – 1953) – Jawahar Lal Nehru, the key leader of NAM helped negotiate/end war between the two Korea’s.
- Afghanistan War (1979 – 1989)
- Vietnam War (1954-1975)
- Cuban Missile Crisis
- Berlin (1948-1949)
- Congo War (early 1960’s) – UN Secretary-General mediated/stopped the war.
- US and USSR always had fear of war so they used to stay ready by: -
- Stocking arms and ammunitions in huge quantity
- Collecting nuclear weapons
- Military setup
- USSR thought what if someone tries to start a war intentionally/ some soldiers fires a missile intentionally to start a war.
- Therefore, they decided to collaborate in eliminating/limiting certain nuclear weapons and “Arms Control” was introduced.
- They signed 3 treaties/ agreement –
- Limiter Test Ban Treaty (LTBT) -1963
- Nuclear Non- Proliferation Treaty (NPT)- 1968
- The Anti- Ballistic Missile Treaty

2. Non-Aligned Movement(NAM)
- Books Name
- Education Vision Political Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Political Science
NON-ALIGNED MOVEMENT (NAM)
Countries which did not want to become the alliance of US and USSR, wanted to stay out from war and got independence with very difficult at their time.

Countries which were in NAM: -
- Yugoslavia – Josip Broz Tito
- India – Jawahar Lal Nehru
- Indonesia – Sukarno
- Egypt – Gamal Abdel Nasser
- Ghana – Kwame Nakrumah
It was initiative by 5 countries for forming a 3rd world.
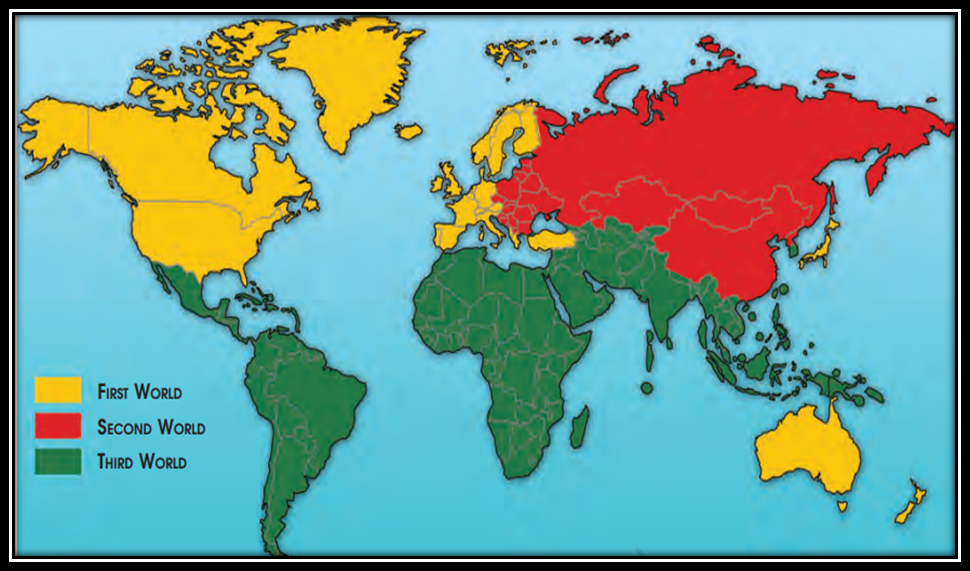
1. Challenge to Bipolarity
- NAM came to challenge US and USSR.

- Newly decolonised countries of Asia, Africa and Latin America were offered a option by NAM to not join any of the alliances and they were included to NAM.
- 1st NAM summit was held in 1961 in Belgrade and was attended by 25 states.
- Latest meeting i.e., 18th summit was held in 2019 at Azerbaijan and was attended by 120 member states and 17 observer countries.
- NAM was mainly founded by 3 leaders – Josip Broz Tito (Yugoslavia), Jawahar Lal Nehru (India) and Gamal Abdel Nasser (Egypt). And were further strongly supported by Sukarno (Indonesia) and Kwame Nkrumah (Ghana).

- NAM was defined by 2 Principles which they did not follow:
- Isolation: Remaining aloof from world affairs.
- Neutrality: Staying out of war or not taking any position in war
2. New International Economic Order
- NAM was a mediator between US and USSR but it had its own challenges and Problems:
1. Many countries in NAM came in the category of LDC’s (least developed country), as they were newly decolonised at that time. So, important challenge for NAM was to become economically developed.
2.Development was important because if not then NAM countries would have to been dependent on other rich countries for their needs.
- The idea of NEW INTERNATION ECONOMIC ORDER (NIEO) :
-
- UNCTAD (The United Nations Conference on Trade and Development) brought out a report in 1972.
- Report name/entitled - “Towards a New Trade Policy for Development”
4 reforms of Global trading system were discussed in the Report:
- Give the LDCs control over their natural resources exploited by the western countries,
- Obtain access to Western markets so that the LDC’s could sell their products and, therefore, make a trade more beneficial for poorer countries.
- Reduce the cost of technologies from western countries, and
- Provide the LDC’s with a greater role in international economic situations.
-
- For NAM countries economic issues became important.
-
- In the first summit NAM did not give much importance to economic issue but from mid-1970’s NUM started giving importance to it.
-
- NAM become an economic pressure group in 1970’s.
-
- By 1980’s the reforms started fading/ western countries stopped following it.
-
- And by 1980’s all the western countries united and started opposing the reforms by NIEO
3.India and The Cold War
- The responses of India towards Cold War were in two folds:
- Staying away from alliances i.e., not becoming part of USA or USSR.
- Raising voice against newly decolonized countries becoming part of the alliances, because the they become free from the British rule just at that time.
- India’s Policy:
- India’s policy was neither naïve nor passive.

- Non – Alignment was not the policy of “Fleeing Away”
- In fact, India played a big role in softening the cold war rivalries.
- India played a major role reducing the differences between alliances thus preventing it from escalating in a full-scale ware.
- Indian leaders and diplomats used to often communicate to the rivals to mediate the issue, such as in Korean War.
- Most importantly, India also involved and activated regional and international organizations which were not the part of alliances, to soften the situation.
- Nehru also reposed a great faith in “a genuine commonwealth of free and cooperating nations” that would play a positive role in softening, if not ending the war.
- Therefore, we can say India played big role in the war.
The Non-Alignment Policy also benefited India directly in two ways:
- It allowed India to take international decisions and stances that served India its interests rather than the interests of super powers and their allies.
- India had the power to balance one super-power against the other. If India felt ignored or unduly pressurised by one super-power, it tilted towards the other. Therefore, no alliance system could take India for granted or bully it.
India’s Policy of Non-Alignment was often criticized on a number of counts.
Two of them were:
1. UNPRINCIPLED:
India’s NAM was called unprincipled because, in the name of serving personal interests India never used to take a firm stand on the international issues.
2. INCONSISTENT:
India was inconsistent as it often used to take contradictory postures, because India signed Treaty of Friendship with USSR in August 1971 and some people saw it as joining USSR.
Indian Government reply to the criticism was that India needed diplomatic and military support during Bangladesh crisis and that never stopped India from having good relations with US.


 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
