1. European Union Integration
- Books Name
- Education Vision Political Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Political Science
European Union
- After Second World War Europe’s economy became worst, USA introduced “Marshall Plan”
- Marshall Plan (1948):
- Under the Marshall Plan, the organization for European Economic Cooperation was the established in 1948 it was made to help the western European states.
- The Organisation for European Economic Co-operation (OEEC) became a forum where the western European states began to cooperate on trade and economic issues.
- The Council of Europe was introduced in 1949, for political cooperation.
- Then European Economic Community was formed in 1957, then European Parliament was formed
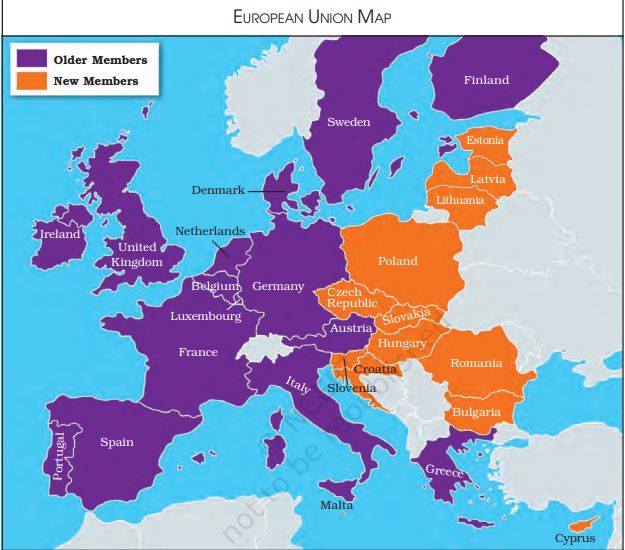
- After the disintegration of USSR, European countries got confused at whether they should join USA or remain with USSR so therefore they formed European Union in 1992
- Did this to cooperate with foreign policy that is no war and peace everywhere.
- And decided to use common currency in European Union i.e., EURO
- European Union started behaving like nation state i.e., country
- It could not make its own constitution so it made its own flag, anthem, founding date, and currency.
- European Union had only a few members in the starting but soon it started to expand.
- EU has good economic, political and diplomatic, and military influence.
- The EU is the world’s second biggest economy with GDP of more than $17 trillion in the 2016 which is next to the United States of America.
- The EU possess a threat to the dominance US dollar.
- European Union’s share of world trade is much larger than that of the United states.
- European Union has influence over Africa, Asia and World Trade Organization (WTO) because of its economic power.
- European Union has influence over UN Security Council because Britain and France (countries in EU) are 2 permanent members of UN.
- The European Union also includes several non- permanent members of the UNSC, which enables European Union to influence some US policies such as the current US position on Iran’s nuclear program.
- Militarily, the EU’s combined armed forces are the second largest in the world.
- Its total spending on defense is second after the US.
- 2 EU member states, Britain and France, have nuclear arsenals of the approximately 550 nuclear warheads.
- It is also the world’s second most important source of the space and communication technology.
- As European Union is a supranational organization it is able to intervene in economic, political and social areas.
- European Union’s member states have their own Foreign Relations and different policies that are often at odds with each other.
- This limits the ability of the European Union to act in matters of the Foreign Relations and defense.
- Britain’s former Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher, kept the UK out of the European market.
- Denmark and Sweden have resisted the Maastricht treaty and adoption of the euro.

2. Association of South East Asian Nations
- Books Name
- Education Vision Political Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Political Science
ASSOCIATION OF SOUTH EAST ASIAN NATIONS(ASEAN)
- Association of South East Asian Nations.
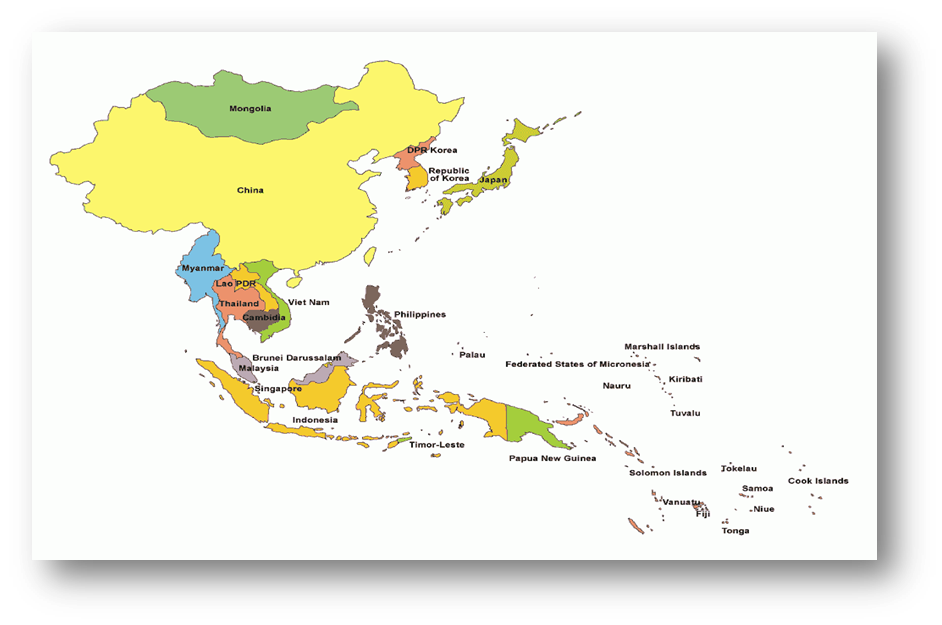
- ASEAN was established in 1967 by signing of Bangkok Declaration, by 5 countries of the region, namely:
 Indonesia
Indonesia - Malaysia
- Philippines
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Later South East Asia region joined, namely:
- Brunei Darussalam
- Lao PDR
- Myanmar (Burma)
- Vietnam
- Cambodia
joined making total count to 10.
- The objectives of ASEAN were to accelerate economic growth and through that ‘social progress and cultural development’ and promote regional peace and stability based on the rule of law and the principles of the United Nations Charter.
- After the Second World War, when the war ended Asia confronted problems of nation building, ravages of poverty and economic backwardness and the pressure to align with great power and therefore for informal corporation interaction ASEAN was formed.
- ASEAN countries celebrate a day known as “ASEAN WAY” in which these countries do not talk about any war, it is informal and cooperative talk.
- Its aim is to achieve sovereignty.
- In 2003, ASEAN decided to evolve like European Union, so established ASEAN community also known as the 3 pillars, namely:
- The ASEAN Security Community
- The ASEAN Economic Community
- The ASEAN Socio-Cultural Community
- ASEAN Security Community
- It was made because, if there was a dispute among neighboring countries regarding territory, they solve it by talking politely without any war.

- ASEAN sign several agreements in which the member states promise to maintain peace, stay neutral, always cooperate, non-interference and respect for the national differences and sovereign rights.
- The ASEAN regional forum, it was established in 1994, this organization carries out coordination of security and foreign policy
- ASEAN Economic Community
- Its objective is to create a common market and production base within ASEAN states and to aid social and economic development in the region.
- It has focused on creating a Free Trade Area (FTA) for investment, labor, and services.
- ASEAN community it’s also interested in resolving the old economic disputes.
- The US and China have already moved fast to negotiate FTAs with ASEAN.
- ASEAN has sorted out 2 biggest disputes that is,
- Cambodian conflict,
- the East Timor crisis
- The Cultural Economic Strength
- Attractive partners for trade of India and China.
- During the Cold War years Indian foreign policy did not pay adequate attention to ASEAN, but now it has signed trade agreements with 3 ASEAN members, Malaysia, Singapore and Thailand.
- The ASEAN- India FTA came into effect in 2010.
The reason for ASEAN being powerful is that they, interact and corporate with each other.

3. The Rise of the Chinese Company
- Books Name
- Education Vision Political Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Political Science
THE RISE OF THE CHINESE ECONOMY

- Chinese Economy started rising in 1978. It is predicted that by 2040 it will day overtake U.S. as the world’s largest economy.
- In 1949 People’s Republic of China started, in which China adopted USSR’s ideology that is communism and cancelled USA’s ideology that is capitalism (As China was weak at that time). So, they chose Soviet model under the leadership of Mao.
- China became an isolated country (no relation with other countries) , Decreased imports because it was short on foreign exchange.
- Economic Context – Aid from USSR
- Economic growth was increasing but population growth was also increasing which was not in balance of economic growth.
- USSR crisis (disintegration) because of which China suffered.
- Industrial Production was not growing fast enough, international trade was minimal and per capita income was very low.
- In 1972 (Leader) Premier Zhou Enlai proposed to end the isolation.
- Then in 1972 China started its relations with US
- PM of china i.e., Zhou Enlai proposed the ‘four modernizations’ in 1973, in which he told they will increase:
- Industry
- Agriculture
- Military Power
- Science and Technology
- In 1978, leader i.e., Deng Xiaoping announced the “open door” policy i.e., China opened its doors for foreign trade and investments.
- China adopted privatization i.e., Market Economy –(no shock therapy).
- They slowly started moving towards capitalism
- 1992- privatization of Agriculture
- 1998 – Privatization of Industries.
- Trade barriers were eliminated only in Special Economic Zones (SEZs) where foreign investor could set up enterprises.
- Trade started and tariffs were removed/reduced. Foreign direct investment increased.
- China became the most important destination for foreign direct investment (FDI).
- In 2001, China became part of World Trade Organization (WTO).
- As the economy rose China still faced problems like:
- Unemployment with almost 100 million people looking for job.
- Environmental Degradation rose high
- Corruption rate also increased
- Rise in economic inequality between rural and urban residents and coastal and inland provinces.
- China is a permanent member of UN.
- China started having issues with ASEAN, Japan, the US and Russia.
4. INDIA-CHINA Relations
- Books Name
- Education Vision Political Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Political Science
India-China Relations

- India and China were great powers of Asia before the advent of Western Imperialism.
- In 20th Century, both nations confronted each other, they had some difficulty evolving a foreign policy to deal with each other.
- For a brief while, the slogan of ‘ Hindi-Chini bhai-bhai’ was popular.
- A military conflict over a border dispute between the two countries marred the hope.
- China and India have been in conflict in 1950 over Tibet issue.
- And also, in border conflicts in 1962 principally in Arunachal Pradesh and Ladakh.
- Diplomatic relations of both countries were downgraded until 1976.
- Slowly the relations of both the countries started improving, when the China’s political leadership changed in mid to late 1970’s.
- 1981- Steps were taken to resolve the border issues.
- 1988- Rajiv Gandhi visited China, since then both governments have taken measures to contain conflict and maintain ‘peace and tranquility’ on the border.
- 1999 – trade between both countries have increased from 30 percent
- Bilateral trade between India and China has increased from $338 million in 1992 to more than $84 billion in 2017.
- At global level both the countries have adopted similar policies in international economic situation like WTO.
- India’s nuclear test of 1998, justified on the grounds of a threat from China, and did not stop greater interaction.
- There is a positive relation between the two countries.

 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
