- Books Name
- Vision classes Accountancy Book
- Publication
- Vision classes
- Course
- CBSE Class 11
- Subject
- Accountancy
Accounting Equation:
The accounting equation is the basic element of the balance sheet and the primary principle of accounting. It helps the company to prepare a balance sheet and see if the entire enterprise’s asset is equal to its liabilities and stockholder equity. It is the base of the double-entry accounting system.
Double-entry accounting is a system that ensures that accounting and transaction equation should be equal as it affects both sides. Any change in the asset account, there should be a change in related liability and stockholder’s equity account. While performing journal entries accounting equation should be kept in mind.
Total Assets =Total Liabilities
OR
Total Assets = Internal Liabilities + External Liabilities
OR
Total Assets = Capital + Liabilities
Examples of accounting equation
1) Ram started business with cash rs.10000
Assets (cash+) = liabilities (capital+) +10000 = +10000
Its mean assets increase and liabilities also increase same amount so result will be same
2) mohan purchase good with cash rs.1000
Assets (stock+) asset (cash-) =liabilities +1000 -1000
3) Goods sold to shyam on credit for rs.5000
Assets (stock-) assets (debtors+) = lia. (No change)
4) Furniture purchase for cash rs.25000
Assets (furniture+) assets (cash) = lia. (No change)
5) Paid rent rs.500
Assets (cash-) = liabilities (capital-)
6) Received commission rs.400
Assets (cash+) = lia. (Capital+)
Multiple effect entries
Goods sold on credit (cost price rs.30000) for Rs. 40000
Assets (stock-) assets (debtors+) = lia. (capital+)
-30000 + 40000 = + 10000
Classification of Transactions Following are the nine basic transactions:
1. Increase in assets with corresponding increase in capital.
2. Increase in assets with corresponding increase in liabilities.
3. Decrease in assets with corresponding decrease in capital.
4. Decrease in assets with corresponding decrease in liabilities.
5. Increase and decrease in assets.
6. Increase and decrease in liabilities
7. Increase and decrease in capital
8. Increase in liabilities and decrease in capital
9. Increase in capital and decrease in liabilities.
Example :
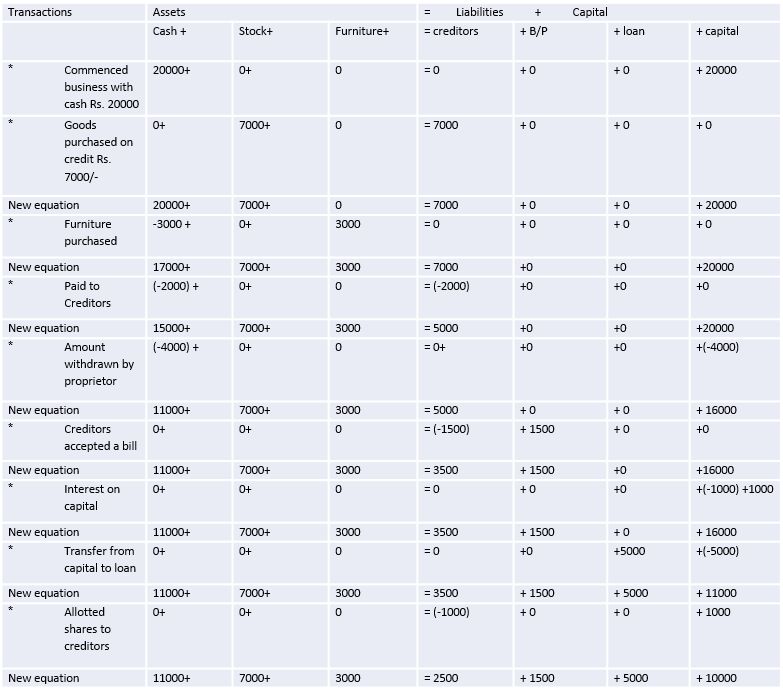
Show the effect of the following business transactions on assets, liabilities and capital through accounting equations:
1. Commenced business with cash 20,000
2. Goods purchased on credit 7,000
3. Furniture purchased 3,000
4. paid to creditors 2,000
5. Amount withdrawn by the proprietor 4,000
6. Creditors accepted a bill for payment 1,500
7. Interest on capital 1,000
8. Transfer from capital to loan 5,000
9. Allotted shares to creditors 1,000
Solution:
Important note
Assets = Liabilities +Capital
Assets are equal to the sum total of Liabilities and Capital
Question for Practice:
Prepare Accounting equation on the basis of following information:
(1) Sohan started business with cash =80,000
Machinery =10,000
And stock =10,000
(2) Interest on the above capital was allowed @10%
(3) Money withdrew from the business for his personal use10, 000
(4) Interest on drawings 500
(5) Depreciation charged on machinery 2,000

 Vision classes
Vision classes
