- Books Name
- Science Made Easy Science Book
- Publication
- Science Made Easy
- Course
- CBSE Class 9
- Subject
- Science
Introduction
Anything which occupies space and has mass is called matter.
Matter can be divided in two categories.
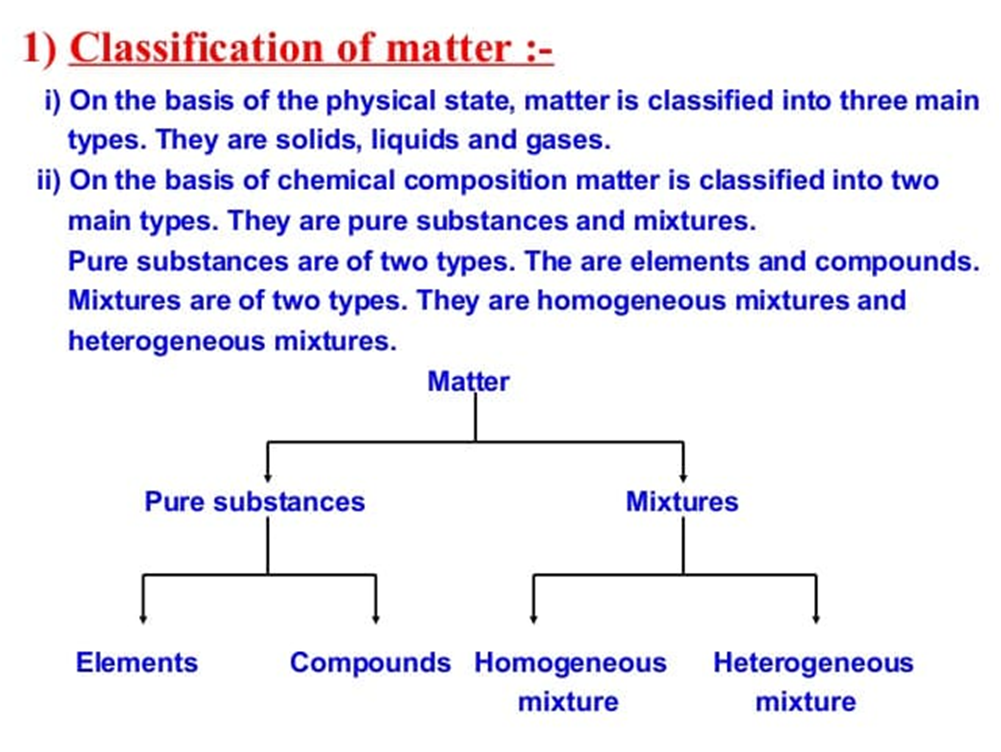
(i) Pure Substance: It consists of single types of particles which are same in their chemical nature.
(ii) Mixtures: Mixture consists of two or more particles.

Mixture and its types
Mixture consists of more than one kind of pure substances which can be separated by physical method.
Mixtures are of two types
(i) Homogeneous mixture
(ii) Heterogeneous mixture
(i) Homogeneous mixture: A mixture is said to be homogeneous if all the components of the
mixture are uniformly mixed and there are no boundaries of separation between them.
Ex: Sugar in water, etc.

(ii) Heterogeneous mixtures: A mixture is said to be heterogeneous if all the components of the
mixture are not uniformly mixed and there are visible boundaries of separation between them
Ex: Water and sand, Air etc.

Is Matter around us pure
Introduction
When we talk about pure, it means that all the constituent particles of that substance are the same in their chemical nature. A pure substance consists of a single type of a particles. What is the type of pure substances?
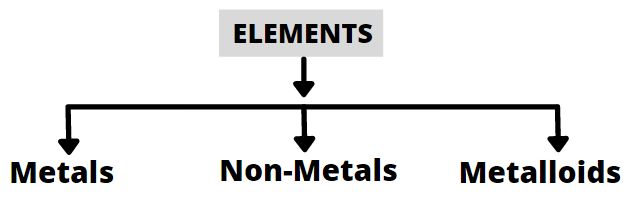
- Elements
- Robert Boyle A was the first scientist to use the term element in 1661.
- Antoine Laurent Lavoisier (1743–94), a French chemist, was the first to establish an experimentally useful definition of an element.
- Elements can be normally divided into metals, non – metals and metalloids.
Metals
- Metals usually show some or all of the following properties:
- They have a lustre (shine).
- They conduct heat and electricity.
- They are ductile (can be drawn into wires).
- They are malleable (can be hammered into thin sheets).
- They are sonorous (make a ringing sound when hit).
# Examples of metals are gold, silver, copper, iron, sodium, potassium etc.
# Mercury is the only metal that is liquid at room temperature.
Non metals
- Non – metals usually show some or all of the following properties:
- They are poor conductors of heat and electricity.
- They are not lustrous, sonorous or malleable.
# Examples of non – metals are hydrogen. oxygen, iodine, carbon (coal, coke). bromine, chlorine etc.
Metalloids
- Metallaoids have intermediate properties between of metals and non – metals.
# Examples are boron, silicon, germanium etc.
Mixture and compound
| Mixture | Compound |
| 1. Elements or compounds are simple calling so new substance is formed. Compound | 1. Substances Are Reated Together with each other to make a new substance. |
| 2. Elements do not combine in a fixed ratio. | 2. Compositions the the component is Fixed i.e. , They combine together in a fixed ratio according to their masses. |
| 3. A mixture shows the properties of its components | 3. compound does not show the Properties of component elements. |
| 4. Components can be easily separated by any mechanical method which is suitable. | 4. components can not be separated from each other by simple mechanical methods. |
- Books Name
- Yash Tyagi Coaching Science Book
- Publication
- ACERISE INDIA
- Course
- CBSE Class 9
- Subject
- Science
Chapter-2
Is Matter around us Pure
Is Matter around us Pure Introduction
We come across different substances like water that we drink; salt that we add in food for taste, milk that we drink as it provides us with calcium and other minerals, soaps that we use to wash clothes, paint that we use to colour walls and so on. These substances have different nature, different properties. They can be pure or there can be some impurities in them. Let us see what do we understand by the words pure or impure substance[12]
We come across different substances like water that we drink; salt that we add in food for taste, milk that we drink as it provides us with calcium and other minerals, soaps that we use to wash clothes, paint that we use to colour walls and so on. These substances have different nature, different properties. They can be pure or there can be some impurities in them. Let us see what do we understand by the words pure or impure substances[15]
We come across different substances like water that we drink; salt that we add in food for taste, milk that we drink as it provides us with calcium and other minerals, soaps that we use to wash clothes, paint that we use to colour walls and so on. These substances have different nature, different properties. They can be pure or there can be some impurities in them. Let us see what do we understand by the words pure or impure substances[20]
Pure substance
They are substances that are made up of a single type of particle. But there are certain characteristics that determine the purity of a substance. Let us see what all properties they possess.
Characteristics of a pure substance are as follows
1. They all have a uniform composition (homogeneous).
2. They can not be separated into their constituents.
3. They have fixed melting and boiling points.
4. They always have the same characteristic properties.
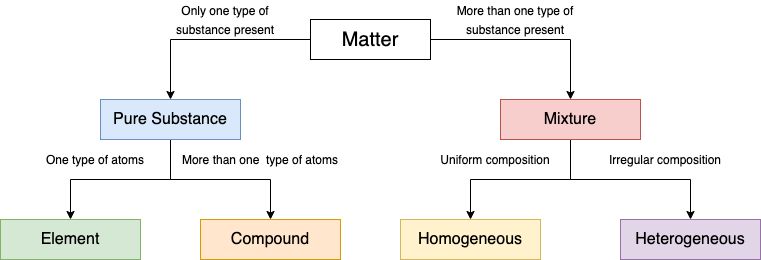
Two categories of substances fall under pure substance. They are as follows
1. Elements
2. Compounds
Element
As we know, an atom is the smallest particle that may or may not exist independently. These atoms unite together and form an element. This element can exist independently but it can not be broken into atoms as they are not visible. About 118 elements are known so far and still many discoveries are in the pipeline. Elements can be prepared artificially in lab, also by transmutation process. The elements having atomic number more than 92 are manmade and are called transuranic elements. An element is defined as a substance that can not be broken into simpler substances as it is formed of atoms and atoms can not be seen.
The characteristics of elements are as follows
1. They are made up of atoms
2. The physical & chemical properties of an element are due to the arrangement of atoms.
3. They can occur in nature in free or combined form.
4. They can be prepared artificially by nuclear reaction.
5. They can be solids, liquids (only 3) or gases (11) at normal room temperature.
Metals
In daily routine, we use a lot of substances that fall in this category like the vehicles which are usually made up of iron, furniture, utensils and many more. Let us see their properties. Those substances which have a tendency to lose electrons and form positively charged species, that is cation are called metals.
Na – 1e- → Na+ (cation)
2, 8, 1 2, 8
Physical properties of metals are as follows
- They are malleable like Al(aluminum), Ag(silver) [ except alkali metals that is Na,K,Li etc]
- They are ductile like Al, Ag, etc.
- They are lustrous (except – Hg(mercury), Cs(cesium), Ga (gallium)) .
- They are hard (except Na & K ).
- They are good conductors of heat & electricity.
- They have high melting and boiling points [except Na, k, Ca they have low boiling and melting point] .
- They are Sonorous (that is when hit, they produce a sound).

Chemical Properties of metals are as follows
1. Reaction with oxygen
Metals react with oxygen to form oxides.
M + O2 → Metal oxides
All Metal oxides are basic in nature i.e. they turn red litmus blue but some metal oxides are amphoteric in nature (that is, they have acidic & basic nature) like Al2O3 (aluminum oxide) & ZnO (zinc oxide).
2. Reaction with dilute acids
Metals react with dilute acids to form a salt and H2 gas.
M + HX → MX + H2
Example: Na + HCl → NaCl + H2
The hydrogen gas, when comes in contact with air, burns with a popping sound.
Non-Metals
Non – Metals are those elements that always gain electrons and form anions (negatively – charged ions).
Example: Cl + e- → Cl- anion
2, 8, 7 2, 8, 8
Physical properties of non – metals are as follows
- They are liquid or gases (only one exists in liquid form – that is Bromine) except C, S, P, I that are solids.
- They are non – malleable and non – ductile because to make wires or sheets, we need to hammer them, but as they are brittle, they break.
- They are bad conductors of heat and electricity (like graphite).
- They have low melting and boiling point (except B, C which have high melting and boiling points).
- They are non sonorous.
- They are non lustrous (except graphite and iodine).

Chemical properties of non – metals are as follows
1. Reaction with oxygen
Non – metals react with O2 to form Non Metal oxide with respective formula as given below:
N + O2 → non metal oxide
They are acidic in nature and turn blue litmus red.
2. Reaction with dilute acids
Non metals do not react with die acids as they do not have sufficient electrons.
Metalloids
They are those which have properties similar to metals and non-metals. Few elements exist as Noble gases. They are those which are stable elements as they have a stable configuration and generally exist free in nature as they do not need to combine with other elements because they have a stable electronic configuration. The noble gases are He (helium), Ne (neon), Ar (Argon), Kr (krypton), Xe (xenon) and radon.

Compounds
We use so many compounds like salt, water, fertilizers, etc. Let us learn about their properties. They are formed when 2 or more elements combine in a fixed whole number ratio. Example: H2O (water), NaCl (sodium chloride), etc.

Characteristics of compounds are as follows
- They are homogenous.
- The properties of a compound are entirely different from its constituents.
- The constituents can not be separated by physical methods.
- They have fixed properties like Melting point and Boiling point.
- The formation of compound is accompanied by energy changes.

 Science Made Easy
Science Made Easy
 ACERISE INDIA
ACERISE INDIA
