- Books Name
- Class 6 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Science
Water cycle
Water Cycle
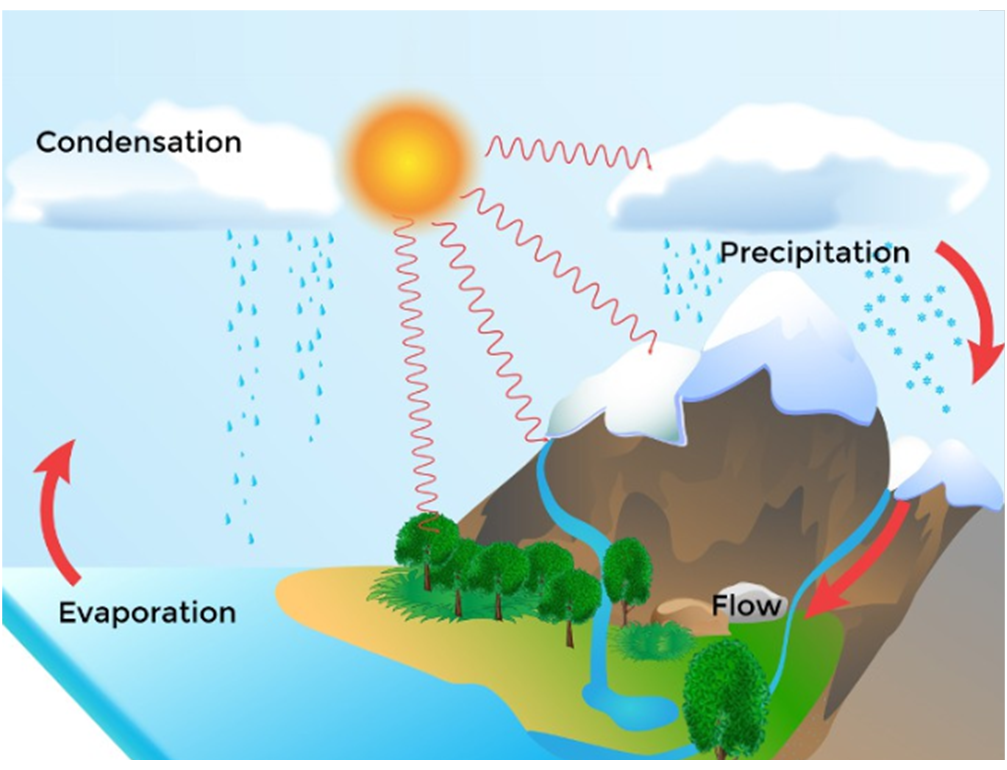
Water cycle can be defined as the process through which water gets evaporated from open surfaces like oceans and seas, gets condensed as it rises in the cool atmosphere and ultimately pours down as rain (precipitation) back into oceans, lakes, rivers and ponds.
To know how these rivers, get their water from we need to study a little about the water cycle and the processes of evaporation and condensation.
Evaporation: The process of conversion of water into its gaseous state i.e. vapours is known as evaporation.
Condensation: The process of conversion of vapours into water is referred to as condensation.
Transpiration: The process of evaporation of water from the surface of the leaves into the atmosphere is defined as the process of transpiration. In this manner, plants also contribute to the water cycle.

- The water cycle is the circulation of water through the process of evaporation or condensation as rain or snowfall.
- The water cycle is like a ring.
- In nature, the water cycle takes place from sea to land and back to sea again.
- It is through the process of water cycle that we are able to make use of the ocean water.
- Ocean water is saline in nature and hence cannot be used directly.
- When it gets evaporated, it leaves behind the salts and forms clouds.
- As the warm air from these surfaces rises into the cold air of the atmosphere, saturation and condensation occur to form tiny droplets of water which result in cloud formation.
- These clouds then lead to rainfall and snow which deposit in lakes, wells and ponds is then used by us to satisfy our needs. Apart of this rainwater gets absorbed by the soil, some of it gets evaporated while the rest seeps in the ground and becomes another source of water for us in the form of groundwater.
- Handpumps, wells and even lakes draw water from groundwater. The water cycle is a continuous process
In this process, the water on the earth changes into three different states of matter:
- Solid
- Liquid
- Gas
The complete process of the water cycle involves the following process:
1. Evaporation :

- The process of changing water to its vapour form is known as evaporation.
- Evaporation takes place from open surfaces of water all the time—day and night.
- Evaporation of water takes place continuously from oceans, rivers, lakes, wells and soil. Oceans, seas, rivers, lakes, ponds and wells together are often known as water bodies.
- During the daytime, sunlight falls on the water in oceans, rivers, lakes. The fields, roads, rooftops and other land areas also receive sunlight. The sunlight also carries heat with it. As a result, water from oceans, rivers, lakes and the soil, and other land areas gets continuously changed into vapour.
- Thus, water vapour gets continuously added to the air due to evaporation.
2. Condensation :

- The process of conversion of vapour into liquid form of water is called condensation.
- The process of condensation is opposite to evaporation.
- Cloud formation: The climate close to the earth’s surface is warm. It gets cooled as one goes up in the atmosphere. Water vapour being lighter rises in the atmosphere. At the upper layer of the atmosphere, where the temperature is lower, the vapour gets condensed into tiny water droplets and forms clouds.
3. Precipitation :

- Clouds carry small droplets of water in them. It may so happen that many droplets of water come together to form larger-sized drops of water. Such drops of water may become so heavy that they begin to fall. The falling of water drops is called precipitation.
- Rain: If the water during precipitation remains liquid till it reaches the surface of the earth, we have rained.
- Hail/Snow: Sometimes precipitation may be in the form of hail or snow. Water in hail or snow is in its frozen or solid form.
- Dew: Many times, especially during winter nights, the air near the surface becomes quite cool. As a result, the water vapour present in it condenses to form water droplets. These water droplets appear as dew.

 Param Publication
Param Publication
 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
