- Books Name
- SonikaAnandAcademy Mathmatics Book
- Publication
- SonikaAnandAcademy
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Mathmatics
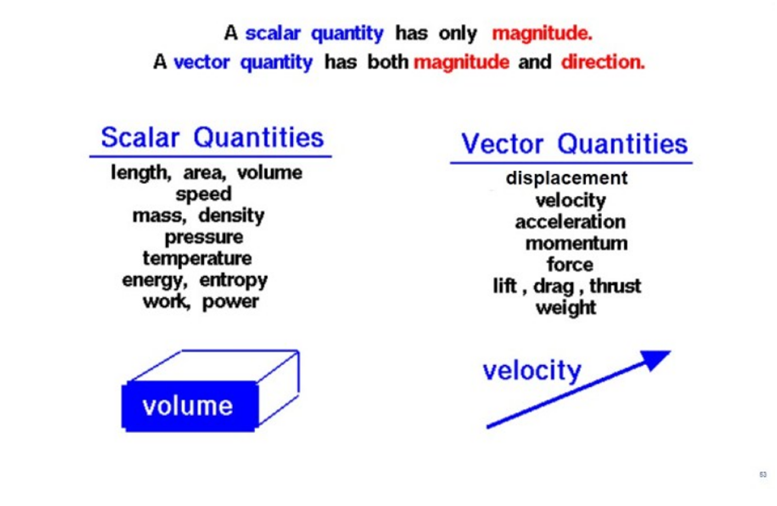
There are two types of physical quantities vector quantity and scalar quantity
Scalar quantity
The quantities which are the only magnitude are called scalar quantities for example time
Vector quantity
The physical quantities which have both direction and magnitude are called vector quantities for example velocity
How can we find the magnitude of a vector
Let A = 2i+3j+4k
Magnitude of vector = ✓2²+3²+4²
= ✓ 4+9+16 = ✓ 29
- Books Name
- Mathmatics Book Based on NCERT
- Publication
- KRISHNA PUBLICATIONS
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Chapter 10
Concepts of Vectors and scalars ,magnitude and direction of a vector :
The Physical quantity is either a vector or a scalar. These two categories can be distinguished from one another by their distinct definitions:
Scalars are Physical quantities that has magnitude but no particular direction is described as scalar.
Vectors are Physical quantities that are fully described by both a magnitude and a direction and also satisfy the triangle law of vector addition.
Examples of Scalar Quantities
Some examples of scalar include:
- Mass
- Speed
- Distance
- Time
- Area
- Volume
- Density
- Temperature
Examples of Vector Quantities
Examples of vector quantity include:
- Linear momentum
- Acceleration
- Displacement
- Momentum
- Angular velocity
- Force
- Electric field
- Polarization
![]()
Initial Points – The point A where from the vector ![]() starts is known as initial point.
starts is known as initial point.
Terminal Point – The point B, where it ends is said to be the terminal point.
Magnitude – The distance between initial point and terminal point of a vector is the
![]()
Position Vector – Consider a point p (x, y, z) in space. The vector ![]() with initial point, origin O and terminal point P, is called the position vector of P.
with initial point, origin O and terminal point P, is called the position vector of P.
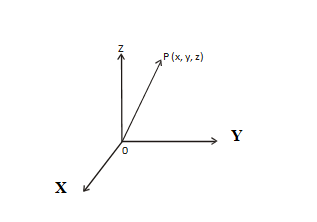

 SonikaAnandAcademy
SonikaAnandAcademy
