1. Solution of Two Linear Equations in Two Variables in Different Methods
- Books Name
- Rakhiedu Mathematics Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Mathmatics
3.1 INTRODUCTION
While solving the problems, in most cases, first we need to frame an equation. In this chapter, we learn how to frame and solve equations. There are given some methods to solve these equations. We will further study about word problems and application of simultaneous equations.
Equation: A statement in which two algebraic expressions are equal is known as equation.
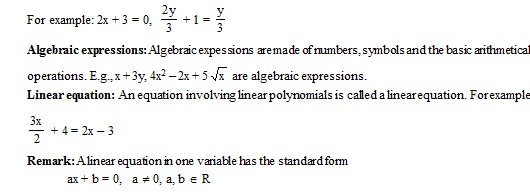
Solution (root) of a linear equation: The value of the variable which makes the two sides of the equation equal and satisfies the equation is called the solution of the equation.
Rules for solving an equation:
(i) The same number is added or subtracted to both sides of an equation, the resulting equation is equivalent to the first.
(ii) If both sides of an equation are multiplied by the same non-zero number the resulting equation is equivalent to the first.
Remark: Every linear equation in one variable has only one (unique) solution.
In this chapter we shall study about system of linear equation in two variables, solution of a system of linear equations in two variables.

3.3 algebraic methods of solving a pair of linear equations
There are four methods for solving a pair of linear equations
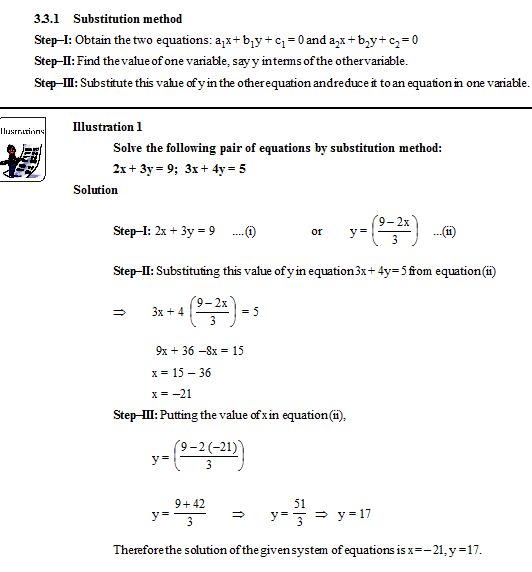
(i) Substitution method
(ii) Elimination method
(iii) Cross-multiplication method
(iv) Graphical Method
3.3.2 Elimination Method
Step–I: Obtain the two equations
Step–II: First multiply both the equations by some suitable non-zero constant to make the coefficient of one variable (either x or y) numerically equal.
Step–III: Add or subtract one equation from the other, then one variable gets eliminated.
Step–IV: Solve the equation in one variable.
Step–V: Substitute the value of x (or y) in any one of the given equations and find the value of another variable.
Geometric representation of different possibilities of solutions/inconsistency?
- Books Name
- Rakhiedu Mathematics Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Mathmatics
3.3 algebraic methods of solving a pair of linear equations
There are four methods for solving a pair of linear equations
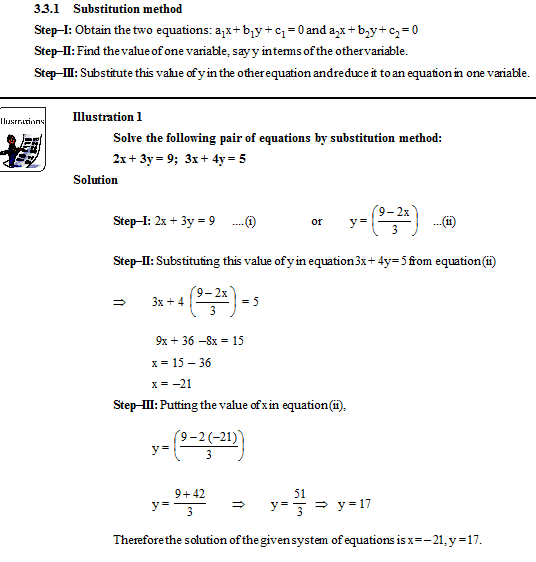
(i) Substitution method
(ii) Elimination method
(iii) Cross-multiplication method
(iv) Graphical Method
3.3.2 Elimination Method
Step–I: Obtain the two equations
Step–II: First multiply both the equations by some suitable non-zero constant to make the coefficient of one variable (either x or y) numerically equal.
Step–III: Add or subtract one equation from the other, then one variable gets eliminated.
Step–IV: Solve the equation in one variable.
Step–V: Substitute the value of x (or y) in any one of the given equations and find the value of another variable.


3.3.4 Graphical Method:
In graphical method, we draw the graph of both equations using same pair of horizontal and vertical lines called X-axis and Y-axis respectively. Coordinates of the point(s) of intersection of the two lines is/are the solution.
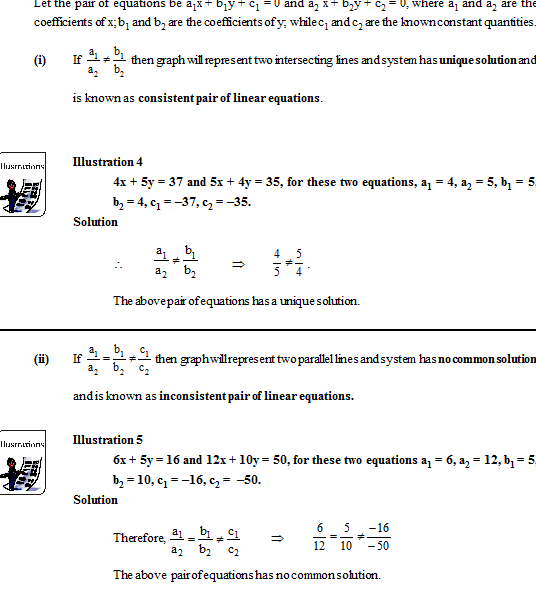
Nature of solutions:
When we try of solve a pair of equations we could arrive at three possible results. They are, having
(a) a unique solution
(b) an infinite number of solutions
(c) no solution
Algebraic conditions for number of solutions?
- Books Name
- Rakhiedu Mathematics Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Mathmatics
3.3 algebraic methods of solving a pair of linear equations
There are four methods for solving a pair of linear equations
(i) Substitution method
(ii) Elimination method
(iii) Cross-multiplication method
(iv) Graphical Method

3.3.2 Elimination Method
Step–I: Obtain the two equations
Step–II: First multiply both the equations by some suitable non-zero constant to make the coefficient of one variable (either x or y) numerically equal.
Step–III: Add or subtract one equation from the other, then one variable gets eliminated.
Step–IV: Solve the equation in one variable.
Step–V: Substitute the value of x (or y) in any one of the given equations and find the value of another variable.


3.3.4 Graphical Method:
In graphical method, we draw the graph of both equations using same pair of horizontal and vertical lines called X-axis and Y-axis respectively. Coordinates of the point(s) of intersection of the two lines is/are the solution.
Nature of solutions:
When we try of solve a pair of equations we could arrive at three possible results. They are, having
(a) a unique solution
(b) an infinite number of solutions
(c) no solution

Solution of a pair of linear equations in two variables algebraically - by substitution, by elimination and by cross multiplication method?
- Books Name
- Rakhiedu Mathematics Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Mathmatics
3.6 Solution of a system of a pair of equations reducible to the system of a pair of linear equations in two variables
By using the suitable substitution or simplification first we convert the given system into the system of a pair of linear equations in two variables. Then after using any algebraic or graphical method we solve the system.
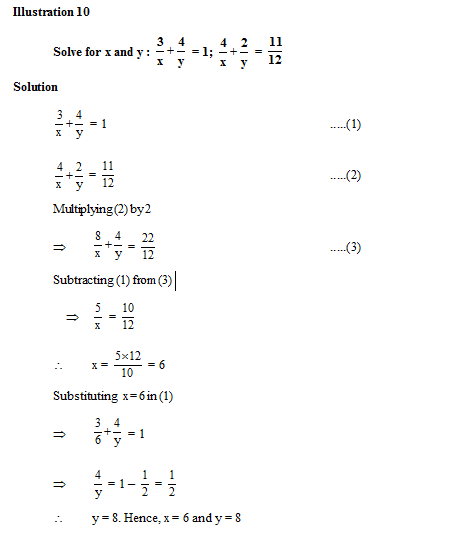

 Pragati
Pragati
