- Books Name
- Chemistry Class 10 NCERT based
- Publication
- Grow Career Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Chemistry
Effects of Oxidation Reactions in Everyday life: Corrosion and Rancidity.
Corrosion: The process of slow conversion of metals into their undesirable compounds due to their reaction with oxygen, water, acids, gases etc. present in the atmosphere is called Corrosion.

Example: Rusting of iron.
Corrosion of Copper: Copper objects lose their lustre and shine after some time because the surface of these objects acquires a green coating of basic copper carbonate, CuCO3.Cu(OH)2 when exposed to air.
Corrosion of Silver Metal: The surface of silver metal gets tarnished (becomes dull) on exposure to air, due to the formation of a coating of black silver sulphide(Ag2S) on its surface by the action of H2S gas present in the air.
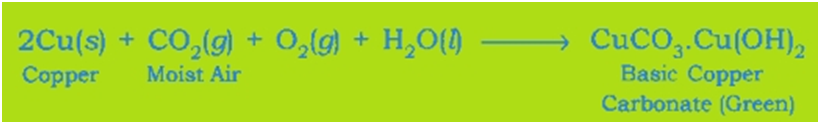

Rancidity: The taste and odour of food materials containing fat and oil changes when they are left exposed to air for a long time. This is called Rancidity. It is caused due to the oxidation of fat and oil present in food materials.
Methods to prevent rancidity:
By adding anti-oxidant.
Vacuum packing.
Replacing air by nitrogen.
Refrigeration of foodstuff.
A. Chemical Reaction: During the chemical reactions, the chemical composition of substances changes or make new substances are formed known as chemical reaction.
B. Chemical Equation: Chemical reactions can be written in chemical equation form which should always be balanced are know as chemical equation.
C. Types of Chemical Reactions:
Combination reaction: A single product is formed from two or more than two reactants.
2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
Decomposition reaction: A single reactant breaks down two or more then two products.
Thermal decomposition:
2Pb(NO2)2 → 2PbO + 4NO2 + O2
Electrolysis:
2H20 → 2H2 + O2
Photochemical reaction:
2AgBr → 2Ag + Br2
Displacement reaction: One element is displaced by another element.this format call di
Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu
Double displacement reaction: Exchange of ions between reactants.
AgNO3 + NaCl → AgCl + NaNO3
Redox reaction: Both oxidation and reduction take place simultaneously.
CuO + H2 → Cu + H2O
Exothermic reaction: A chemical reaction in which heat energy is evolved.
C + O2 → CO2 (g) + heat
Endothermic reaction: A chemical reaction in which heat energy is absorbed.
ZnCO3 + Heat → ZnO + CO2
5. Reduction: Reaction that shows the loss of oxygen or gain of hydrogen.
ZnO + C → Zn + CO
ZnO is reduced to Zn—reduction. C is oxidized to CO—Oxidation.
Effects of Oxidation Reactions in Our Daily Life:
Corrosion: It is an undesirable change that occurs in metals when they are attacked by moisture, air, acids and bases.
Example, Corrosion (rusting) of Iron: Fe2O3. nH2O (Hydrated iron oxide)
Rancidity: Undesirable change that takes place in oil containing food items due to the oxidation of fatty acids.
Preventive methods of rancidity: Adding antioxidants to the food materials, storing food in the airtight container, flushing out air with nitrogen gas and refrigeration
- Books Name
- Chemistry Book based on NCERT
- Publication
- PRIDE LEARNING PUBLICATION
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Chemistry
EFFORTS OF OXIDATION REACTIONS IN EVERYDAY LIFE
1) COROSION :- When a metal is exposd to moisture ,air, acid eyc. For some time , a layer of hydrated oxide, is formed which e weaknes the metal and hence metal is said to be corroded.
Example of corrosion are:-
- Rusting of iron .
- Black coating on silver
- Green coating on copper.
• Rusting of iron :- when iron is exposed to oxygen in the presence of moisture, reddish brown power is formed.
This is process is knon as rusting of iron.
• Method to prevent corrosion are:-
- Galvanization
- Electroplating
- By putting paints
2) RANCIDITY:- The oxidation of fats and oils when exposed to air is known as rancidity . due to rancidity, bad smell and bad taste of food occurs
Method of prevent rancidity are :-
- By adding antioxidants.
- Refrigeration.
- Replacing air by nitrogen.
- Keeping food in air tight containers.
• Chips manufactures fill bag of chips with nitrogen because it is non reactive gas and it prevent the chips from getting oxidized.

 Grow Career Publication
Grow Career Publication
 PRIDE LEARNING PUBLICATION
PRIDE LEARNING PUBLICATION
