- Books Name
- Chemistry Class 10 NCERT based
- Publication
- Grow Career Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Chemistry
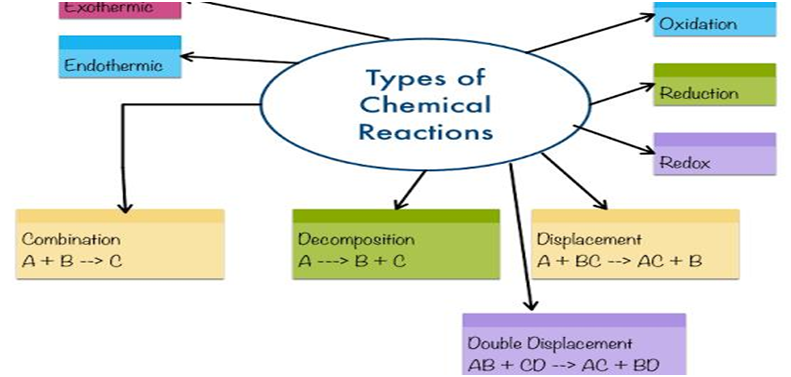
Types of Chemical Reactions: Combination Reaction, Decomposition Reaction, Displacement Reaction, Double Displacement Reaction, Neutralization Reactions, Exothermic – Endothermic Reactions and Oxidation-Reduction Reactions.
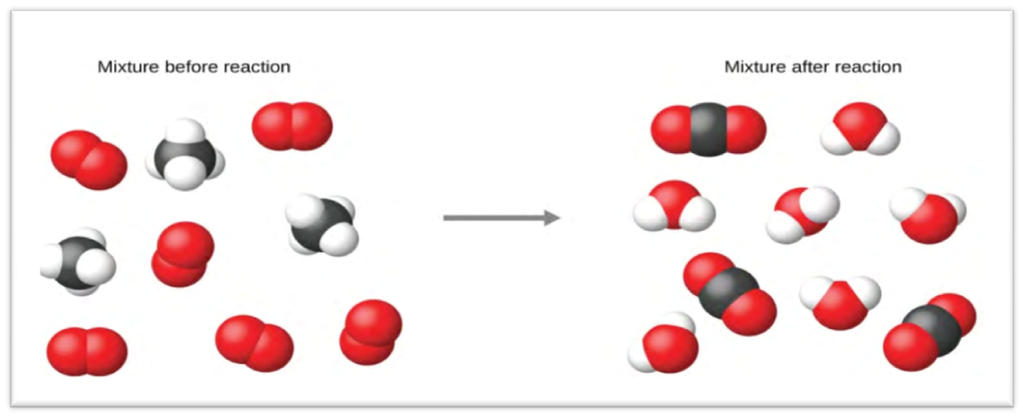
A. Combination or Synthesis Reactions:
The reactions in which two or more chemicals combine to generate a single new compound.
Types of Combination reactions:
I. Combination of two elements to form a compound
● Burning of hydrogen in air or oxygen to produce water.
H²(hydrogen) + O²( oxygen) → H²O(water) + O²( oxygen)
II. Combination Reactions involving an Element and a Compound
● Burning of carbon monoxide in oxygen to form carbon dioxide.
2CO (carbon monoxide) + O2(Oxygen) → 2CO2(Carbon dioxide)
III. Combination Reactions involving Two Compounds
● Combination of ammonia and hydrogen chloride to produce ammonium chloride.
NH³( Ammonia) + HCl(Hydrogen chloride) → NH⁴Cl³( Ammonium chloride)
B . Decomposition Reaction: Reactions in which one compound decomposes in two or more compounds or elements are known as Decomposition Reaction. A decomposition reaction is just the opposite of combination reaction.
A general decomposition reaction can be represented as follows :
AB → A + B
Examples:
When calcium carbonate is heated, it decomposes into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide.
CaCO3(s) heat−→− CaO(s) + CO2(g)
Calcium carbonate → Calcium oxide + Carbon dioxide
When ferric hydroxide is heated, it decomposes into ferric oxide and water
2Fe(OH)3(s) △→ Fe2O3(s) + 3H2O(l)
Thermal Decomposition: The decomposition of a substance on heating is known as Thermal Decomposition.
Example: 2Pb(NO3)2(s) heat−→− 2PbO(s) + 4NO2(g) + O2(g)
Electrolytic Decomposition: Reactions in which compounds decompose into simpler compounds because of passing of electricity, are known as Electrolytic Decomposition. This is also known as Electrolysis.
Example: When electricity is passed in water, it decomposes into hydrogen and oxygen.
2H2O(l) Undefined control sequence \xrightarrow 2H2(g) + O2(g)
Photolysis or Photo Decomposition Reaction: Reactions in which a compound decomposes because of sunlight are known as Photolysis or Photo Decomposition Reaction.
Example: When silver chloride is put in sunlight, it decomposes into silver metal and chlorine gas.
2AgCl(s) (white) Sunlight−→−−−−− 2Ag(s) (grey) + Cl2(g)
Photographic paper has a coat of silver chloride, which turns into grey when exposed to sunlight. It happens because silver chloride is colourless while silver is a grey metal.
C. Displacement Reaction: The chemical reactions in which a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from a compound is known as Displacement Reactions. Displacement reactions are also known as Substitution Reaction or Single Displacement/ replacement reactions.
A general displacement reaction can be represented by using a chemical equation as follows :
A + BC → AC + B
Displacement reaction takes place only when ‘A’ is more reactive than B. If ‘B’ is more reactive than ‘A’, then ‘A’ will not displace ‘C’ from ‘BC’ and reaction will not be taking place.
Examples:
When zinc reacts with hydrochloric acid, it gives hydrogen gas and zinc chloride.
Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
When zinc reacts with copper sulphate, it forms zinc sulphate and copper metal.
Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
D. Double Displacement Reaction: Reactions in which ions are exchanged between two reactants forming new compounds are called Double Displacement Reactions.
AB + CD → AC + BD
Examples:
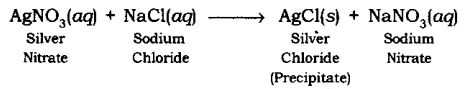
When the solution of barium chloride reacts with the solution of sodium sulphate, white precipitate of barium sulphate is formed along with sodium chloride.
BaCl2(aq) + Na2SO4(aq) → BaSO4(s) (Precipitate) + 2NaCl(aq)
When sodium hydroxide (a base) reacts with hydrochloric acid, sodium chloride and water are formed.
NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
Note: Double Displacement Reaction, in which precipitate is formed, is also known as precipitation reaction. Neutralisation reactions are also examples of double displacement reaction.
Precipitation Reaction: The reaction in which precipitate is formed by the mixing of the aqueous solution of two salts is called Precipitation Reaction.
Example:
Neutralization Reaction: The reaction in which an acid reacts with a base to form salt and water by an exchange of ions is called Neutralization Reaction.
Example:
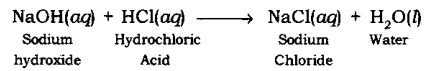
E. Oxidation and Reduction Reactions:
Oxidation: Addition of oxygen or non-metallic element or removal of hydrogen or metallic element from a compound is known as Oxidation.
Elements or compounds in which oxygen or non-metallic element is added or hydrogen or metallic element is removed are called to be Oxidized.
Reduction: Addition of hydrogen or metallic element or removal of oxygen or non-metallic element from a compound is called Reduction.
The compound or element which goes under reduction in called to be Reduced.
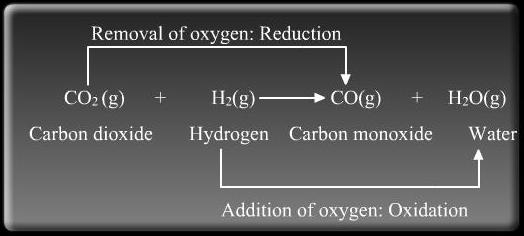
Oxidation and Reduction take place together. For example
Oxidizing agent:
- The substance which gives oxygen for oxidation is called an Oxidizing agent.
- The substance which removes hydrogen is also called an Oxidizing agent.
Reducing agent:
- The substance which gives hydrogen for reduction is called a Reducing agent.
- The substance which removes oxygen is also called a Reducing agent.
The reaction in which oxidation and reduction both take place simultaneously is called Redox reaction.
When copper oxide is heated with hydrogen, then copper metal and hydrogen are formed.
CuO + H2 → Cu + H2O
(i) In this reaction, CuO is changing into Cu. Oxygen is being removed from copper oxide. Removal of oxygen from a substance is called Reduction, so copper oxide is being reduced to copper.
(ii) In this reaction, H2 is changing to H2O. Oxygen is being added to hydrogen. Addition of oxygen to a substance is called Oxidation, so hydrogen is being oxidised to water.
- The substance which gets oxidised is the reducing agent.
- The substance which gets reduced is the oxidizing agent
F. Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions:
Exothermic Reaction: Reaction which produces energy is called Exothermic Reaction. Most of the decomposition reactions are exothermic.
Example:
Respiration is a decomposition reaction in which energy is released.
![]()
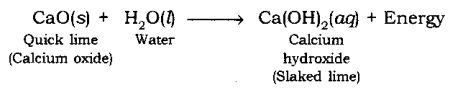
When quick lime (CaO) is added to water, it releases energy.
Endothermic Reaction: A chemical reaction in which heat energy is absorbed is called Endothermic Reaction.
Example: Decomposition of calcium carbonate.

- Books Name
- Chemistry Book based on NCERT
- Publication
- PRIDE LEARNING PUBLICATION
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Chemistry
TYPE OF CHEMICAL REACTION
There are five type of chemical reactions.
COMBINATION REACTION:- The reaction in which two or more reaction combine to form a single product is called combination reaction They are represented by equation of the following term.
Reactant product
For Example :-
Burning of coal
C(s) +
(carbon) (oxygen) (carbon dioxide)
Formation of water
2
(Hydrogen) (oxygen) (Water)
Formation of slaked line
CaO (s) +
(calcium oxide) (water) (calcium Hydroxide)/ slaked lime
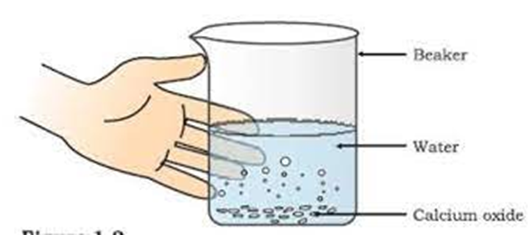
Formation of slaked lime by the reaction of calcium oxide with water.
DECOMPOSITION REACTION :- The reaction I which single compound breaks down to simpler product is called decomposition reaction. They are represented by equation of the following term .
AB
(i) Thermat decomposition :- when decomposition is carried out by heating.
For example
(i) 2 Fe S
(Ferrous sulphate ) (Ferric Oxide)
Green colour Red brown colour
(ii) CaC
(calcium carbonate) ( calcium oxide ) (Carbon dioxide ) Limestone quick lime
(iii) 2Pb (N
(Lead nitrate ) (lead oxide) (Nitrogen dioxide) oxygen
Brown fumes
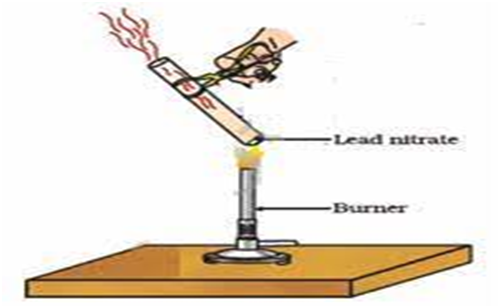
Heating of lead nitrate and emission of nitrogen dioxide
ELECTRONIC DECOMPOSITION :- When decomposition is carried out by passing electricity .
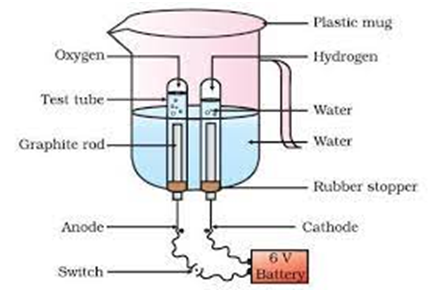
For Example:- (i) Electrolysis of water.
Electric current
2
(Water) (Hydrogen) (Oxygen)
Electrolysis of water is done as follows:-
When decomposition is carried out in presence of sunlight .
For Example:-
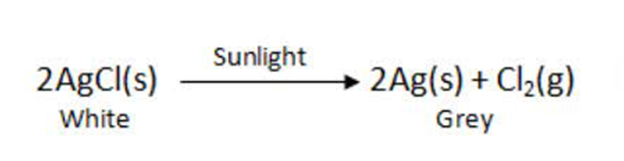
This is why silver chloride turns grey in sunlight because of the decomposition of silver chloride into silvers and chloride by light.
This reaction is used in black and write Photography.
DISPLACEMENT REACTION :- This reaction in which more reactive element displace less reative element from its salt solution is called displacement reaction . they aare represented by equation of the following term.
A + BC
For example :-
(i) Fe (s) + CuS
(Iron ) (copper Sulphate) ( iron Sulphate) ( Copper)
Fe is more reactive than therefore iron (Fe) has displaced copper (Cu) from copper sulphate solution.
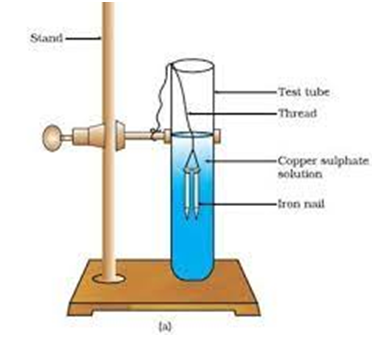
Iron nails dipped in copper sulphate solution.
(ii) Zn(s) + CuS
(Zinc) (copper sulphate) ( Zinc sulphate ) copper
Zinc is more reactive than copper , therefore it displace copper from copper sulphate solution.
(iii) Pb (s) + CuC
(Lead) (copper chloride) ( lead chloride) copper
Lead is more reactive elements than copper, therefore it displaces copper from copper chloride solution.
DOUBLE DISPLACEMENT REACTIVE :- The reaction in which the reactant ions exchange to form new products is called double displacement reaction . they are represented by equation of the following term.
AB + CD
For Example :-
N
(sodium sulphate) (barium chloride) (barium sulphate) (sodium chloride)
White precipitate of BaS
OXIDATION AND REDUCTION :-
OXIDATION
(i) The addition of oxygen to reactant
(ii) the removal of hydrogen from reactant
For Example :-
2 Cu +
(Copper) (oxygen) (copper oxide )
Black substance
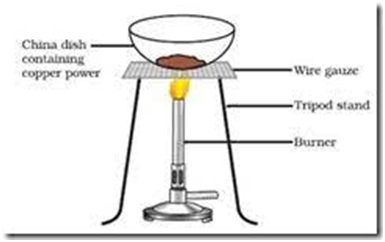
Oxidation of copper to copper oxide
Reduction : - (i) the addition of hydrogen to reactant
(ii) the removal of oxygen from a reactant.
Redox Reactions :- The reaction on written one substance gets oxidisied and other get reduced is known as redox reaction
For example :-
CuO +
In this reaction CuO is reduced to Cu and
ZnO + C
Here, C is oxidized to CO because oxygen is being added and ZnO IS REDUCED TO Zn because O is being removed.
NOTE :
* If a substance loses oxygen during a reactant , it is said to be reduced.
ENDETHERMIC REACTION:- Reaction in which energy is absorded are known as endothermic reaction.
For example :-
CaC
FXOTHERMIC REACTION :- Reaction in which heat is released along with formation of products.
For Example,
C

 Grow Career Publication
Grow Career Publication
 PRIDE LEARNING PUBLICATION
PRIDE LEARNING PUBLICATION
