- Books Name
- Chemistry Book based on NCERT
- Publication
- PRIDE LEARNING PUBLICATION
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Chemistry
Nature of carbon compounds.
Catenation:- The property of elements to form long chains or rings by self linking of their own atoms through covalentbonds is called catenation. These compounds may have long, branched chains of carbon atoms may be linked by single, double or triple bound. The extent of catenation depends upon the strength of the bounds between the atoms involved in catenation.
Saturated and unsaturated compounds
- Compounds of carbon which are linked by only single bonds between carbon atoms are called saturated compounds.
For example, C - C
Carbon atom linked together with single bound.
But the valencies of each carbon atom remain unsatisfied , so each carbon atom is bonded to 3 hydrogen atoms:-
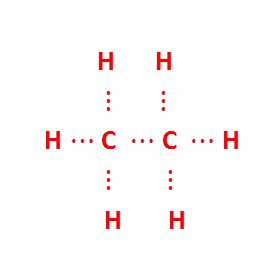
atom is bonded to 3 hydrogen atoms:-
Electron dot structure of ethane
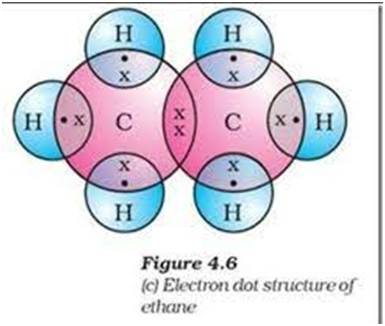
Compounds of carbon having double or triple bounds between their carbon atoms are called unsaturated compounds.
For example,
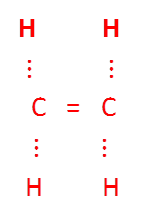
.To satisfy the valency , carbon form double bond.
Strength of compound
The bonds that carbon forms with other elements are very strong, so these compounds because very stable. Carbon form strong bonds is due to its small size. Nucleus hold shaired pair of electrons strougly.
Chains , branches and rings,
Straight chain compounds: the compounds which conatin straight chain of carbon atom e.g butane (
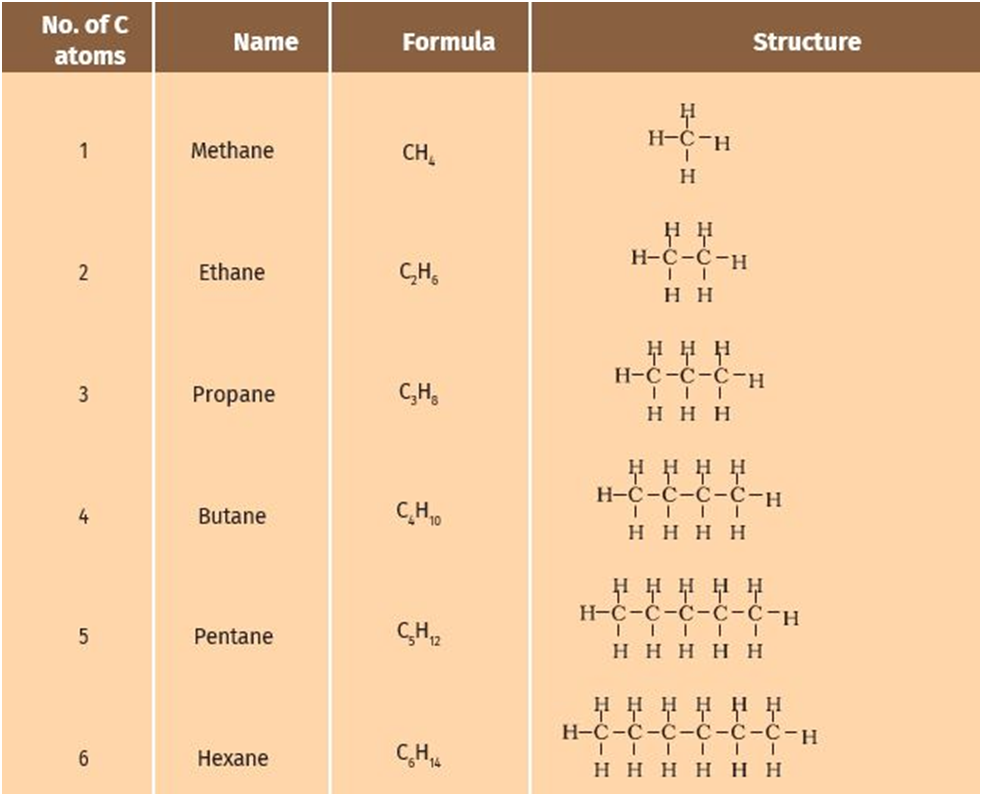
Branched chain compounds: Those compounds which are branched.
E.g. ISO- butane (
Ring compounds:- they are also known as closd chain compounds.
Cyclic compounds are called ring coumpounds.
E.g. cyclohexane (
Cyclopropane (
Hydrocarbons :- All those compounds which contain only carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbon. The saturated hydrocarbon which contain single bond are called alkanes. The unsaturated hydro carbons which contain one or more double bonds are called alkanes those containing one or more triple bounds are called alkynes.
Functional group:- The atoms or group of atoms which determine the properties of a copmpond is known as functional group.
E.g. –Cl , -Br ( choro/ bromo alkane
-OH (alcohol)
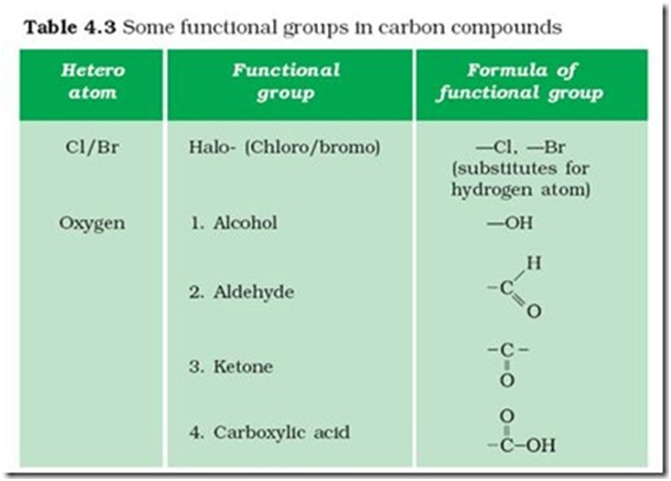
Homologous series :- A series of compounds in which the same functional group substitutes hydrogen ina carbon chain is called a homologous series. E.g , C
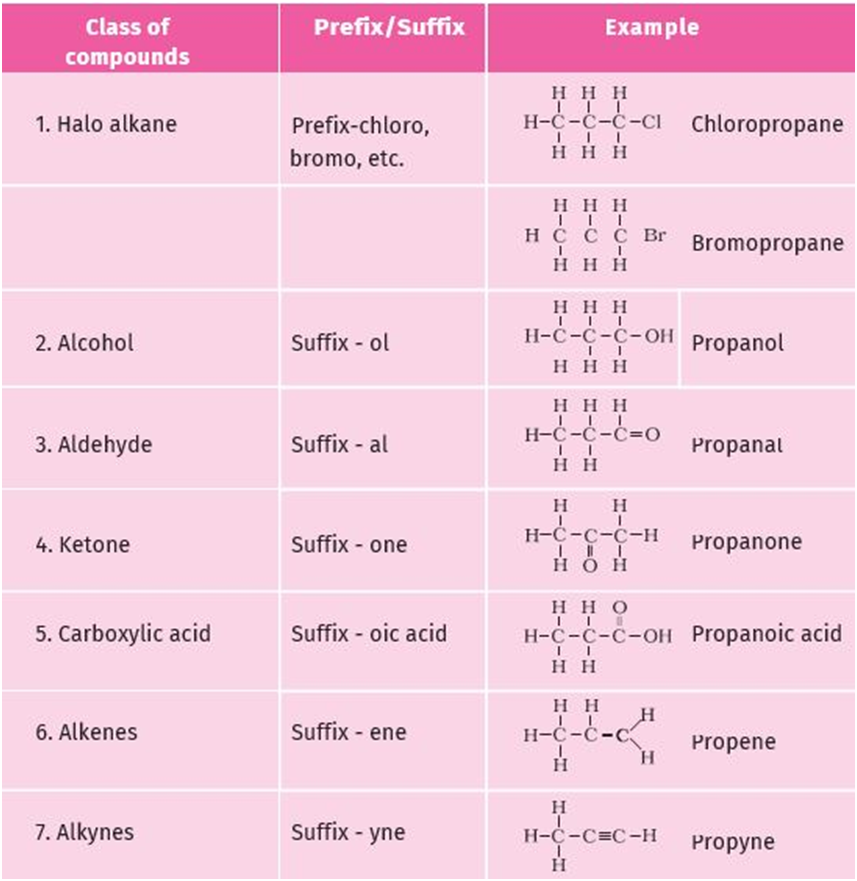
Nomenclature :- For naming organic compounds based on their structures, are followed by UPSC rules.
IUPAC name of an organic compounds consists of 3 parts –
- Prefix :- in case functional group is present , it is indicated in the name of the compound with either as a prefix or as a suffix.
- Word root :- A word root indicates the nature of basic carbon skeleton.
- Suffix :- while adding the suffix to the word rrot, the terminal ‘e’ of carbon chain is removed . if the carbon chain is unsaturated , then final ‘are’ is substituted by ‘en and yne’ respectively for double and triple bonds.

 Grow Career Publication
Grow Career Publication
 PRIDE LEARNING PUBLICATION
PRIDE LEARNING PUBLICATION
