Kingdom Animalia
Basic Characteristics of the Animalia Kingdom
1. Animals are eukaryotic, multicellular organisms that lack a cell wall.
2. They are heterotrophs therefore they rely on others for food.
3. They have a growth pattern. The adult animals have a specific shape and size.
4. Most of the organisms have well-defined organ systems such as Respiratory System, Digestion System and so on.
5. Most of the animals can move. They aren’t stationary as Plants.
6. Animals have a nervous system which is why they are able to respond to an external stimulus.
Animals are classified on the basis of differences in their body type and design. The body cavity or coelom in animals contains the organs. Based on the presence of body cavity animals can be categorized as:
1. Coelomate – They have true body cavity called Coelom
2. Pseudocoelomate – It means false cavity. They have a body cavity which is filled with fluid
3. Acoelomate – They have no body cavity at all.
1. Phylum - Porifera
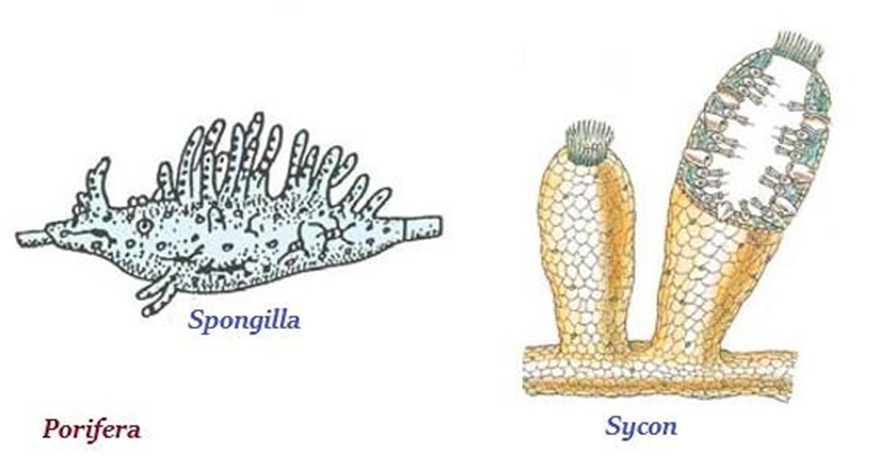
Phylum- Porifera
• Level of Organization – Cells are present
• Symmetry – Asymmetrical
• Segmentation – No segments
• Body Cavity/ Coelom – No
• Presence of Organs – No
• Examples – Sycon, Spongilla, Euspongia
• Other Characteristics-
o They cannot move and are attached to a support.
o They have pores in their body
o These pores form a Canal system through which water and food circulate in the body and waste is removed.
o They have a skeleton made of spongin protein and calcium carbonate – hard covering on them
2.Phylum - Coelentrata
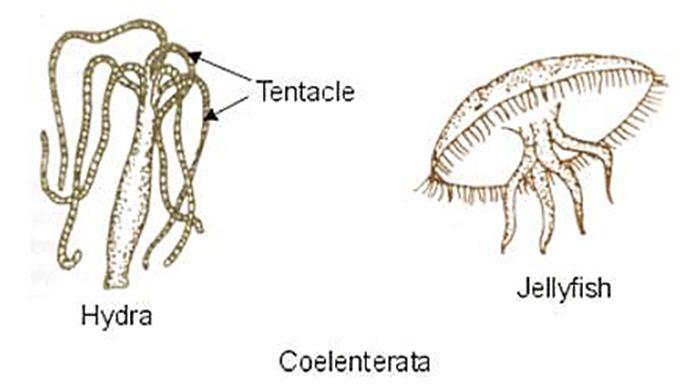
Phylum- Coelenterata
• Level of Organization – Tissues, Cells have two layers – so called as Diploblastic Organism
• Symmetry – Radial
• Segmentation – No segments
• Body Cavity/ Coelom – No
• Presence of Organs – No
• Examples – Aurelia (Jelly fish) and Adamsia (Sea Anemone)
• Other Characteristics –
o Some of them live in colonies - They are physically attached to each other such as Corals
o Some of them live solitary such as Hydra
3.Phylum - Platyhelminthes
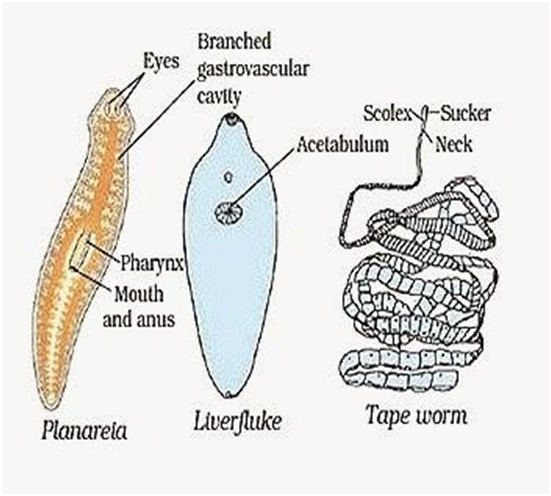
Phylum Platyhelminthes
• Level of Organization – Organs, The cells have three layers – so are called Triploblastic
• Symmetry – Bilaterally Symmetrical - Left half of the body is identical to the right half
• Segmentation – No segments
• Body Cavity/ Coelom – No so called as Acoelomates
• Presence of Organs – Yes
• Examples – Taenia solium (Tapeworm), Fasciola hepatica (Liver Fluke)
• Other Characteristics -
o They have a flat body and thus are called Flatworms
o They can be Free-living like Planaria or parasitic.
4. Phylum- Nematode
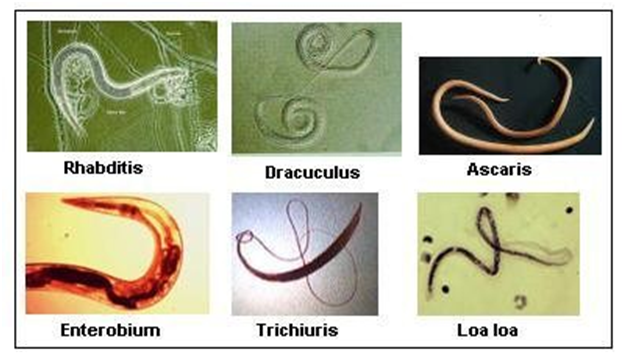
Phylum Nematoda
• Level of Organization – Tissues so are called Triploblastic
• Symmetry – Bilaterally Symmetrical - Left half of the body is identical to the right half
• Segmentation – No segments
• Body Cavity/ Coelom - False body cavity so called as Pseudocoelomates
• Presence of Organs – Organ System Level Organisation
• Examples – Parasitic worms and worms in the intestine
• Other Characteristics–
o They are called as Round Worms.
o Sexual dimorphism visible - Female and male worms are distinct.
- 5. Phylum Annelida
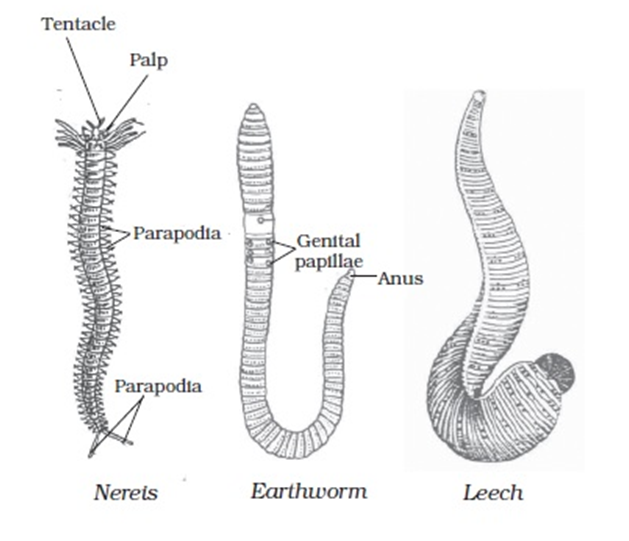
Phylum Annelida
• Level of Organization – Organ system level, the cells have three layers so called Triploblastic
• Symmetry – Bilaterally Symmetrical
• True Segmentation – Present (organs can be identified separately)
• Body Cavity/ Coelom – True body cavity so called as Coelomates
• Presence of Organs – Definite organs
• Examples – Leech, Earthworms
• Other Characteristics –
o They are found in freshwater and marine water.
o They have closed Circulatory system.
6. Phylum Arthropoda

Phylum Arthropoda
• Level of Organization – Organ systems
• Symmetry – Bilaterally symmetrical
• Segmentation – Present (organs can be identified separately)
• Body Cavity/ Coelom – True body cavity
• Presence of Organs – Definite organs
• Examples – Prawns and butterflies
• Other Characteristics
o They have jointed legs
o They have an open circulatory system – There are no well-defined blood vessels
o They have chitinous exoskeleton
7. Phylum - Mollusca
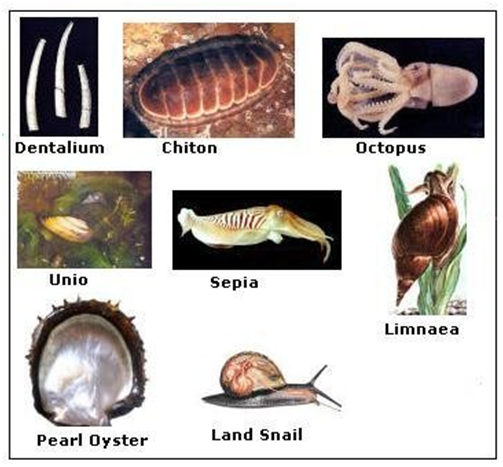
Phylum Mollusca
• Level of Organization – Organ systems, the cells have three layers– called Triploblastic
• Symmetry – Bilaterally symmetrical
• Segmentation – Little segmentation
• Body Cavity/ Coelom – Reduced
• Presence of Organs – Definite organs
• Examples – Snails
• Other Characteristics
o Body is divided into head, Visceral Mass and Muscular Foot.
o Some of the molluscs have hard external shell like that of Snails and some have internal reduced shell like that in Octopus.
o They have an open circulatory system
o There is a kidney-like organ for excretion

 Vaishnav Publication
Vaishnav Publication
