Kingdom Plantae
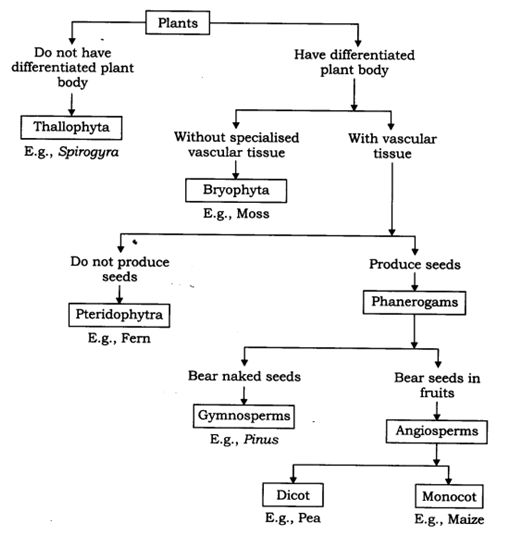
Plant Kingdom
• Components of Plants – whether they are distinct or not
• Presence of Special Tissues in plants for the transportation of food and water
• Presence of Seeds – whether the seeds are present inside the fruits or not.
Classification of plants on the ability to produce seeds -
• Cryptogams – These plants do not have well developed reproductive organs. The organs cannot be seen clearly as well and appear as if they are hidden. Example are Thallophyte, Bryophyta and Pteridophyte.
• Phanerogams – These plants have well developed reproductive organs hence they can produce seeds. They are further classified as the ones which have seeds hidden inside fruits or not - Gymnosperms and Angiosperms
|
Criteria |
Thallophyta |
Bryophyta |
Pteridophyta |
|
Components of plants |
No distinct components. Undifferentiated Body |
Little differentiated body. Distinct components are present as leaves and stem |
Distinct components are present as roots, leaves and stem |
|
Presence of special tissues- Vascular tissue |
No |
No |
Yes |
|
Presence of seeds |
No |
No |
No |
|
Found in |
Aquatic environment, snow |
First terrestrial plants but but need water for sexual reproduction. So called as Amphibian of plant kingdom. |
Terrestrial or dry areas |
|
Example |
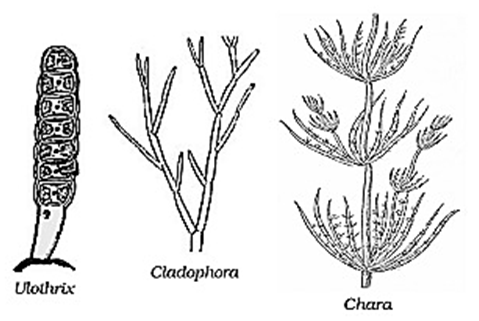
Spirogyra, Ulothrix, Volvox |
Moss and liverworts |
Ferns |
|
|
Gymnosperms |
Angiosperms |
|
The ability to produce seeds |
Naked seeds |
Seeds develop in an organ which then turns into the fruit |
|
Existence |
Exist for long time periods, Evergreen |
Grow for varied time periods |
|
Type |
Woody, No flowers |
Flowering plants |
|
Meaning |
Gymno – naked |
Angio – Covered |
|
Sperm – seeds |
Sperma – seeds |
|
|
Example |
Pines, Deodar |
Mustard, Maize |
What are Cotyledons?
The seed leaves in Angiosperms are called Cotyledons. They turn green on the germination of the seeds. Angiosperms can be divided into two types on the basis of the presence of cotyledons in them-
- Monocotyledons or monocots
- Dicotyledons or Dicots
|
Criteria |
Monocotyledons or Monocots |
Dicotyledons or Dicots |
|
Cotyledons (Seed Leaves) |
Single Cotyledon |
Two Cotyledons |
|
Leaves |
Long leaves, with parallel veins |
Broad leaves with network of veins |
|
Roots |
Fibrous |
Long taproot |
|
Floral Parts |
Multiples of three |
Multiples of four or five |
|
Example |
Corn, Wheat, Grass |
Rose, Sunflower, Lily |

 Vaishnav Publication
Vaishnav Publication
