- Books Name
- CBSE Class 7 Social Science Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 7
- Subject
- Social Science
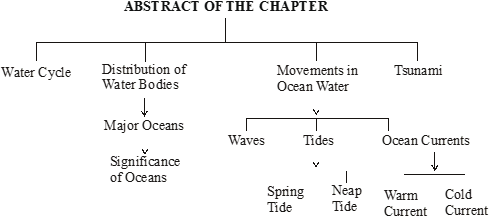
* INTRODUCTION
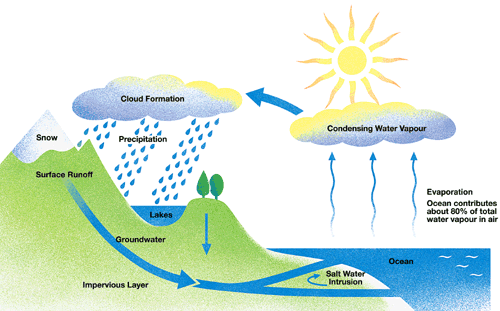
Our earth is like a terrarium. The same water that existed centuries ago still exists today. Water is found in abundance on the earth. It covers about three forth of the earth surface as such the earth appears blue from space and hence called a blue planet.
The major sources of fresh water are the rivers, ponds, springs and glaciers. The ocean bodies and the seas contain salty water. The water of the oceans is salty or saline as it contains large amount of dissolved salts. Most of the salt is sodium chloride or the common table salt that we eat.
* Water Cycle
The sun’s heat causes evaporation of water vapour. When the water vapour cools down, it condenses and forms clouds. From there it may fall on the land or sea in the form of rain, snow or sleet.
The process by which water continually changes its form and circulates between oceans, atmosphere and land is known as the Water Cycle
* Distribution of Water Bodies
We all know that three-fourth of the earth surface is covered by water. About 97% of the earth's total water is in oceans and sea. It is salty and unsuitable for consumption. Another two percent water is contained in Ice-caps and glaciers. Only one percent is fresh water which is available and is suitable for human use.
Distribution of water bodies
Oceans : 97.3 - Saline water
Ice-caps : 02.0
Ground water : 0.68
Fresh water lakes : 0.009
Atmosphere : 0.0019
Rivers : 0.0001
Inland seas and salt lakes : 0.009
100.00
* Major Water Bodies
There are four major oceans on the Earth They are:
Pacific Ocean
This is the largest ocean. It is roughly triangular. It covers nearly 1/3 of the Earth’s surface. The average depth of this ocean is 4572 metres. But this is the deepest ocean and the deepest point in this ocean is Mariana Trench, which is 11,033 metres deep from the sea level.
Atlantic Ocean
Atlantic Ocean is almost half the size of the Pacific Ocean. It is S-Shaped and it covers nearly 1/6th of the Earth’s surface. This ocean has a number of islands and marginal seas. It provides busy transport routes between North America and Europe.
Indian Ocean
Indian Ocean is often called as Half An Ocean It is encircled by Africa, Asia and Australia. It is a small ocean and does not open northwards. The average depth of this ocean is 4,000 metres but Sunda Trench, the deepest point of this ocean, is 7,450 metres deep from the sea level.
Arctic Ocean
Arctic ocean is located around the North Pole to the north of Europe, Asia and Canada. Most of this ocean is frozen. This ocean covers an area of 13 million sq.kms.
Southern Ocean
This is a large water body which is around the Antarctic continent. It merges with pacific, Atlantic and Indian Ocean.
* Significance of Oceans
Oceans play a dominant role in order to control all types of life on Earth.
1. They are the main source of humidity in the atmosphere which brings rainfall.
2. They are the storehouse of minerals.
3. They exercise a direct control over the temperature on the oceans and along the coastal landmass.
4. They provide food like fish to us.
5. They are used as highways of trade and commerce.
6. They have the enormous potential to generate energy from tidal waves.
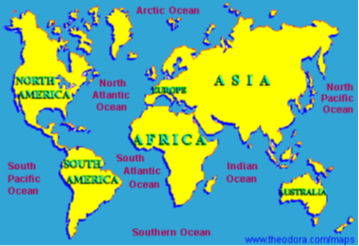
Illustration-1
Explain the Hydrological Cycle (Water Cycle).
Sol. The sun’s heat causes evaporation of water vapour. When the water vapour cools down, it condenses and forms clouds. From there it may fall on the land or sea in the form of rain, snow or sleet.
The process by which water continually changes its form and circulates between oceans, atmosphere and land is known as the Water Cycle Or Hydrological Cycle
* Ocean Circulation
Unlike the calm waters of ponds and lakes, ocean water keeps moving continuously. It is never still. The movements that occur in oceans can be broadly categorised as : waves, tides and currents.
Waves
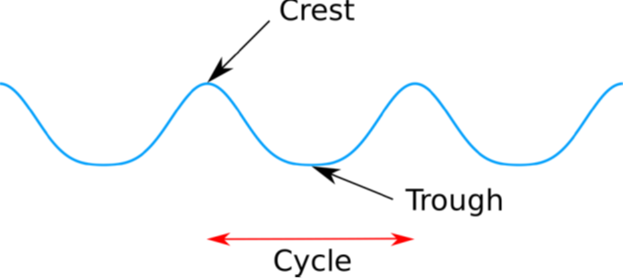
When the wind comes in contact with the sea water, it pushes the water of the sea surface in the direction in which it blows. Thus water particles start moving up and down in the direction of wind forming curls in water. These curls form a Wave. Thus when the water on the surface of the ocean rises and falls alternately, they are called waves.
A wave has two major parts. The upward part is called CREST and the downward part is called TROUGH.
Some waves however are caused by submarine earthquakes or landslides into water bodies. Tsunamis are such big waves.
Tsunami - The earth’s Pandemonium
Tsunami or the harbour wave struck havoc in the Indian Ocean on the 26 December 2004. The wave was the result of the earthquake that had its epicenter close to the western boundary of Sumatra. The magnitude of the earthquake was 9.0 on the Richter scale.
Occurrence: As the Indian plate went under the Burna plate, there was a sudden movement of the sea floor, causing the earthquake. The ocean floor was displaced by about 10 -20m and tilted in a downwardly direction. After thrusting of the Indian plate below the Burma plate, the water mass rushed back towards the coastline. Tsunami travelled at a speed of about 800km. per hour.
Affected Area: Tsunami waves travelled upto a depth of 3 km. from the coast killing more than 10,000 people and affected more than lakh of houses. In India, the worst affected were the coastal areas of Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Pondicherry and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand, Sri Lanka, Myanmar, India, Maldives, Somalia and Tanzania were also affected.
Tides
The rhythmic rise and fall of ocean water twice in a day is called a tide. It is a high tide when water covers much of the shore by rising to its highest level. It is low tide when water falls to its lowest and recedes from the shore.
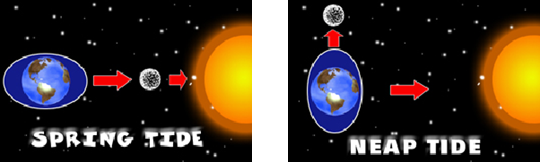
The strong gravitational pull exerted by the sun and the moon on the earth’s surface causes the tides. The water of the earth closer to the moon gets pulled under the influence of the moon’s gravitational force and causes high tide.
Spring Tide: During the full moon and new moon days, the sun, the moon and the earth are in the same line and the tides are highest. These tides are called spring tides.
Neap Tide: When the moon is in its first and last quarter, the ocean waters get drawn in diagonally opposite directions by the gravitational pull of sun and earth resulting in low tides. These tides are called neap tides.
Uses of Tides :
(i) High tides help in navigation. They raise the water level close to the shores. this helps the ships to arrive at the harbour more easily.
(ii) The high tides also help in fishing. Many more fish come closer to the shore during the high tide. This enables fishermen to get a plentiful catch.
(iii) The rise and fall of water due to tides is being used to generate electricity in some places.
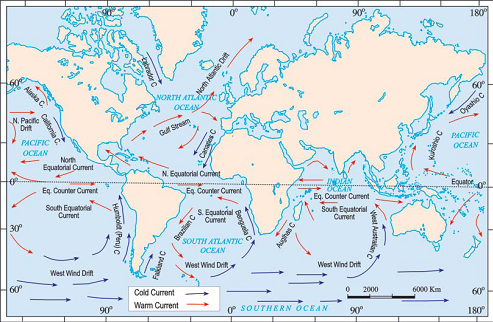
* Ocean currents
Ocean currents are streams of water flowing constantly on the ocean surface in definite directions. The ocean currents may be warm or cold.
The ocean currents originate due to :
(i) Difference in density of sea water.
(ii) The rotation of the earth.
(iii) The planetary winds.

Uses of Ocean Currents :
1. Climate of coastal regions and islands is influenced by the nature of ocean current.
2. Rainfall is often caused by currents.
3. Meeting of warm & cold current leads to ideal condition of fishing.
4. Ocean currents helps in Navigation.
5. The areas where warm and cold current meet also make weather foggy which makes navigation difficult.
* Glossary
Terrarium : It is an artificial enclosure for keeping small house plants.
Hydrosphere : All the water bodies of the Earth’s surface is called hydrosphere.
* Facts to Know
- Salinity is the amount of salt in grams present in 1000 grams of water. The average salinity of the oceans is 35 parts per thousand.
- Dead sea in Israel has salinity of 45 parts per thousand. Swimmers can float in it because the increased salt content make it dense.
- March 22 is celebrated as World Water Day when the need to conserve water is reinforced in different ways.
- Waves are formed when gentle winds scrape across the ocean surface. The stronger the wind blows, the bigger the wave becomes.
- Tsunami is a Japanese word that means “Harbour waves.” as the harbours get destroyed whenever there is tsunami.
Illustration 1
Write any two uses of ocean currents.
Solution
(i) Main source of humidity in the atmosphere which brings rainfall.
(ii) Storehouse of minerals.
Illustration 2
What was the cause of Tsunami that occurred on 26 Dec.2004.
Solution
As the Indian plate went under the Burna plate, there was a sudden movement of the sea floor, causing the earthquake. The ocean floor was displaced by about 10 -20m and tilted in a downwardly direction. After thrusting of the Indian plate below the Burma plate, the water mass rushed back towards the coastline. Tsunami travelled at a speed of about 800km. per hour.

 Param Publication
Param Publication
