- Books Name
- CBSE Class 6 Mathematics Book
- Publication
- Param Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 6
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Polygons
A figure is a polygon if it is a simple closed figure made up entirely of line segments.
For example, triangle, quadrilateral, pentagon, etc., are all examples of polygon.
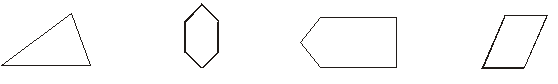
If all sides of a polygon are equal and all angles are also equal , then it is called a regular polygon.
Sides, Vertices and Diagonals
The line segments forming a polygon are called its sides.
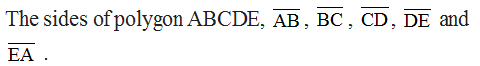 The meeting point of a pair of sides is called its vertex.
The meeting point of a pair of sides is called its vertex.
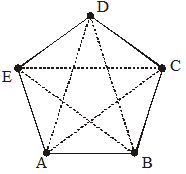
Sides ![]() and
and ![]() meet at E, so E is a vertex of the polygon ABCDE. Points B and C are its other vertices.
meet at E, so E is a vertex of the polygon ABCDE. Points B and C are its other vertices.
Any two sides with a common end point are called the adjacent sides of the polygon. Sides
![]()
The end points of the same side of a polygon are called the adjacent vertices. Vertices E and D are adjacent, whereas vertices A and D are not adjacent vertices.
The line joining two non-adjacent vertices of a polygon is called a diagonal. Since A and C are non-adjacent vertices, so ![]() is a diagonal.
is a diagonal.

 Param Publication
Param Publication
