- Books Name
- Psychology Book Class-12
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 12
- Subject
- Psychology
Counselling Skills (Empathy, Positive Regard and Authenticity)
- Counselling is a domain where a person entering the field is required to engage in self-introspection in order to assess her/his inclination and basic skill set for being effective in her/his vocation.
- Counselling provides a system for:
- planning the interview
- analysing the counsellor’s and client’s behaviour
- determining the developmental impact on the client
- A counsellor is most often interested in building an understanding of the clients problem by focusing on what understanding the client has of her/his problem and how s/he feels about it.
- Counselling involves helping relationship, that includes someone seeking help, and someone willing to give help, who is capable of or trained to help in a setting that permits help to be given and received.
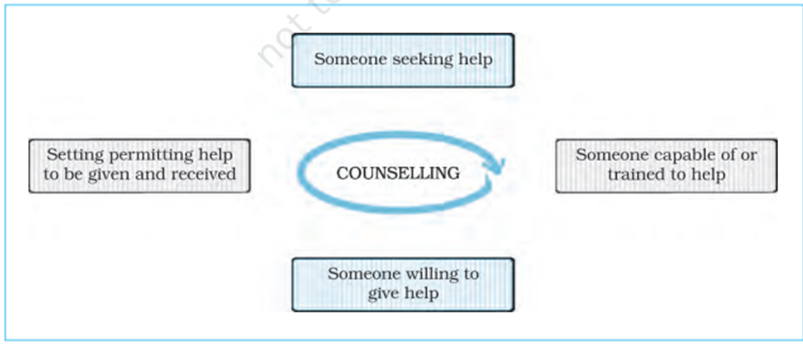
Pre-requisites of Counselling Process - The following elements about counselling are common to the major theoretical approaches to counselling:
- Counselling involves responding to the feelings, thoughts, and actions of the clients.
- Counselling involves a basic acceptance of the client’s perceptions and feelings, without using any evaluative standards.
- Confidentiality and privacy constitute essential ingredients in the counselling setting. Physical facilities that preserve this quality are important.
- Counselling is voluntary. It takes place when a client approaches a counsellor. A counsellor never uses any kind of coercion for obtaining information.
- Counsellors and clients both transmit and receive verbal and non-verbal messages during the process.
Therefore, awareness and sensitivity to the nature of the message is an important prerequisite for a counsellor’s effectiveness.
Breaking the Myths of Counselling

Developing Effective Relationships
- Counselling usually has an all inclusive outcome for the clients.
- Effective behavioural change that takes place in the client is multifaceted.
- It may show up in the form of a client:
- taking greater responsibility
- developing new insight
- learning to engage in different behaviours
- making an effort to develop more effective relationships
Characteristics of Effective Helper
- Being a trained helper, the counsellor has the responsibility for ensuring that her/his client is benefited from counselling and its therapeutic effects are achieved.
- The success of a counselling process depends on the skill, knowledge, attitude, personal qualities and behaviour of a counsellor, any or all of which can enhance or diminish the helping process.
- Four qualities that are associated with effective counsellors are:

- Authenticity
- One’s image or perception of onerself makes up his/her “I”. The self-perceived “I” is revealed through ideas, words, actions, clothing, and your life-style, which communicate one’s “I” to others.
- Those who come into close contact with that person also build their own image of him/her for themselves, and they also sometimes communicate this image to him/her, which develops into a ‘me’. This other perceived ‘me’ is the person that others perceive that person to be. This perception may be the same as or different his/her own self-perception of ‘I’.
- The degree to which he/she is aware of these perceptions of others as well as of his/her own perception of your self indicates that she/he is self-aware.
- Authenticity means that one’s behavioural expressions are consistent with what he/she values and the way he/she feels and relates to his/her inner self-image.
- Positive Regard for Others
- In a client-counsellor relationship, a good relationship allows freedom of expression, which reflects acceptance of the idea that the feelings of both are important.
- Such feelings of uncertainity and anxiety, experienced upon forming a new relationship, get minimised when a counsellor extends a positive regard to the client by accepting that it is all right to feel the way the client is feeling.
- In order to show positive regard to others, the following guidelines may be kept in mind:

- Empathy
- It is the ability of a counsellor to understand the feelings of another person from her/his perspective.
- It is like stepping into someone else’s shoes and trying to understand the pain and troubled feelings of the other person.
- This is one of the most critical competencies that a counsellor needs to have.
- Paraphrasing
- This involves the ability of a counsellor to reflect on what the client says and feels using different words.
- Paraphrasing allows one to understand how much the other person understood of what was communicated.
Ethics of Counselling
- Counsellors have taken important steps to develop their professional identity — the development and implementation of appropriate ethical standards.
- Awareness of the ethical standards and codes is extremely important, because counselling is a part of the service sector.
- Not following the ethical standards may have legal implications.
- The client-counsellor relationship is built on ethical practice.
- The American Psychological Association (APA) has developed a code of ethical conduct for behaviour and decision-making in actual clinical settings.
- The practical knowledge of these ethical domains can guide the practice of counselling in achieving its desired purpose.
- Some of the APA practice guidelines are:
-


 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
