- Books Name
- AMARENDRA PATTANAYAK Mathmatics Book
- Publication
- KRISHNA PUBLICATIONS
- Course
- CBSE Class 11
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Chapter 8
Binomial Theorem
Binomial Theorem for Positive Integral Indices:
The Binomial Theorem is the method of expanding an Binomial expression that has been raised to any finite power.
Binomial Expression: A binomial expression is an algebraic expression that contains two dissimilar terms. Ex: a + b, a3 + b3,a-b, etc.
The binomial theorem states a formula for the expression of the powers of sums.
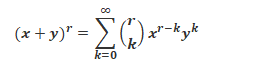
From the above representation, we can expand (a + b)n as given below:
(a + b)n = nC0 an + nC1 an-1 b + nC2 an-2 b2 + … + nCn-1 a bn-1 + nCn bn
This is the binomial theorem formula for any positive integer n.
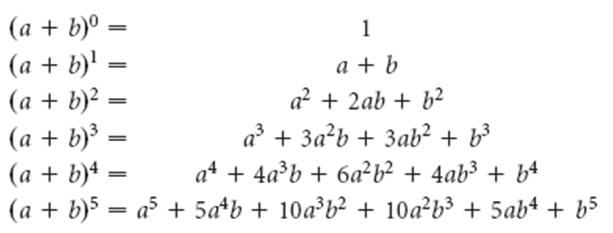
Some special cases from the binomial theorem can be written as:
- (x + y)n = nC0 xn + nC1 xn-1 by+ nC2 xn-2 y2 + … + nCn-1 x yn-1 + nCn xn
- (x – y)n = nC0 xn – nC1 xn-1 by + nC2 xn-2 y2 + … + (-1)n nCn xn
- (1 – x)n = nC0 – nC1 x + nC2 x2 – …. (-1)n nCn xn
Also, nC0 = nCn = 1
However, there will be (n + 1) terms in the expansion of (a + b)n.
Example: (√2 + 1)5 + (√2 − 1)5
Sol:
We have
(x + y)5 + (x – y)5 = 2[5C0 x5 + 5C2 x3 y2 + 5C4 xy4]
= 2(x5 + 10 x3 y2 + 5xy4)
Now (√2 + 1)5 + (√2 − 1)5 = 2[(√2)5 + 10(√2)3(1)2 + 5(√2)(1)4]
=58√2
Properties:
- The total number of terms in the expansion of (x+y)n are (n+1)
- The sum of exponents of x and y is always n.
- nC0, nC1, nC2, … .., nCn are called binomial coefficients and also represented by C0, C1, C2, ….., Cn
- The binomial coefficients which are equidistant from the beginning and from the ending are equal i.e. nC0 = nCn, nC1 = nCn-1 , nC2 = nCn-2 ,….. etc.
Some other expansions:
- (x + y)n + (x−y)n = 2[C0 xn + C2 xn-1 y2 + C4 xn-4 y4 + …]
- (x + y)n – (x−y)n = 2[C1 xn-1 y + C3 xn-3 y3 + C5 xn-5 y5 + …]
- (1 + x)n = nΣr-0 nCr . xr = [C0 + C1 x + C2 x2 + … Cn xn]
- (1+x)n + (1 − x)n = 2[C0 + C2 x2+C4 x4 + …]
- (1+x)n − (1−x)n = 2[C1 x + C3 x3 + C5 x5 + …]
- The number of terms in the expansion of (x + a)n + (x−a)n are (n+2)/2 if “n” is even or (n+1)/2 if “n” is odd.
- The number of terms in the expansion of (x + a)n − (x−a)n are (n/2) if “n” is even or (n+1)/2 if “n” is odd.
Question: Find the 4th term in the expansion of (x – 2y)12.
Solution:
The general term Tr+1 in the binomial expansion is given by Tr+1 = n C r an-r br
Here a= x, n =12, r= 3 and b = -2y
By substituting the values we get
T4 = 12C3 x9 (-2y)3
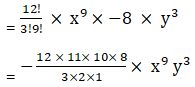
= -1760 x9 y3

 KRISHNA PUBLICATIONS
KRISHNA PUBLICATIONS
