- Books Name
- Ritan Sheth Chemistry Book
- Publication
- Ritan Sheth
- Course
- CBSE Class 11
- Subject
- Chemistry
SOME IMPORTANT COMPOUNDS OF CARBON AND SILICON
Carbon Monoxide
Preparation: It is prepared by direct oxidation of C in limited supply of oxygen.
2C + O2 → 2CO
Properties:
(i) Carbon monoxide is a colourless and odourless gas.
(ii) It is almost insoluble in water.
(iii) It is powerful reducing agent and reduces almost all metal oxides except alkali and alkaline earth metal oxides.
(iv) In CO molecule there are one σ (sigma) and two π bonds between carbon and oxygen.
: C = O :
(v) It is highly porous in nature. It forms a complex with haemoglobin which is about 300 times more stable than the oxygen-haemoglobin complex. This prevents haemoglobin in the red blood corpuscles from carrying oxygen round the body, thereby causing suffocation ultimately leading to death.
Carbon Dioxide
Preparation: It is prepared by complete combustion of carbon and carbon containing fuels in
- CaCO3 + 2HCl → CaCl2 + H2O + CO2
- CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
Structure:
Carbon dioxide, or CO2, has three resonance structures, out of which one is a major contributor.
The CO2 molecule has a total of 16 valence electrons - 4 from carbon and 6 from each oxygen atom.
Here are the three resonance structures for CO2, all accounting for the 16 valence electrons
The atoms in all three resonance structures have full octets; however, structure 1 will be more stable, and thus contribute more, because it has no separation of charge.
Structures 2 and 3 show charge separation caused by the presence of formal charges on both oxygen atoms. Moreover, the presence of a positive charge on oxygen further reduces the stability of these two structures.
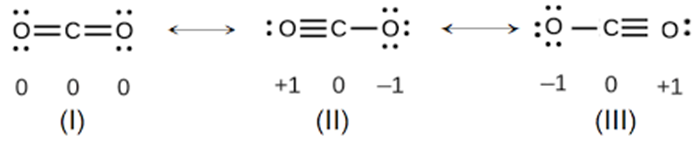
Properties:
(i) It is a colourless and odourless gas.
(ii) It is slightly soluble in water. When C02 dissolves in water only some of the molecules react with water to form carbonic acid.
(iii) It is not poisonous like CO.
But increase in combustion of fossil fuels and decomposition of limestone for cement manufacture increase of C02 in the atmosphere is one of the main reasons of green house effect.
Silicon dioxide (Si02)
Silicon dioxide, commonly known as silica, occurs in various crystallographic forms.
For example, Quartz, Cristobalite and thermite are some of the crystalline forms of silica.
Structure:
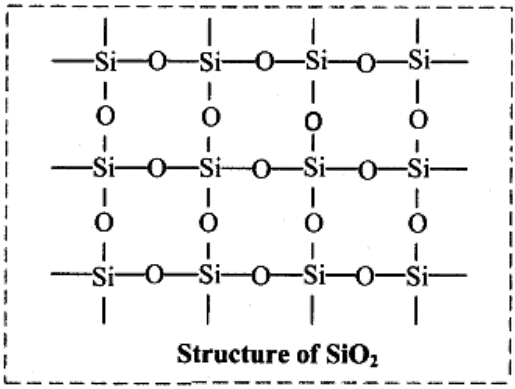
Silicon dioxide is a covalent three dimensional network solid.
Each silicon atom is covalently bonded in a tetrahedral manner to four oxygen atoms.
Each oxygen atom in turn covalently bonded to another silicon atoms as shown below
Properties:
(i) In normal form silica is very less reactive.
(ii) At elevated temperature it does not reacts with halogens, dihydrogen and most of the acids and metals. But it reacts with HF and NaOH.
Si02 + 2NaOH —–> Na2Si03 + H2O
Si02+ 4HF ——–> SiF4+ 2H20
Uses:
(i) Quartz is extensively used as a piezoelectric material.
(ii) Silica gel is used as adsorbent in chromatography.
(iii) An amorphous form of silica, kieselguhr is used in filtration plants.
Zeolites
1. Zeolites are three dimensional crystalline solids containing aluminium, silicon and oxygen in their regular three-dimensional framework.
2. They are hydrated sodium alumino silicates with general formula, Na2O. (Al2O3). x(SiO2)y(H2O) (x = 2 to 10; y = 2 to 6)
3. Zeolites have porous structure in which the monovalent sodium ions and water molecules are loosely held.
4. The Si and Al atoms are tetrahedrally coordinated with each other through shared oxygen atoms.
5. Zeolites structure looks like a honeycomb consisting of a network of interconnected tunnels and cages.
6. Zeolite crystal to act as a molecular sieve. They helps to remove permanent hardness of water.
• P-Block elements: Contains, metals, non-metals and metalloids.
• General configuration: ns2np1-6
– Boron is a typical non-metal and the other members are metals.
– Boron halides are considered to behave like Lewis acids.
– Boric acid is a Lewis acid.
– Borax is a white crystalline solid formula is Na2 [B4O5(OH)4] . 8H20
– Aluminium exhibits +3 oxidation state.
– Allotropy: The important allotropes of carbon are diamond, graphite, and fullerenes.
– The members of carbon family exhibit +4 and +2 oxidation state. The tendency to show +2 oxidation state increases among heavier elements.
– Lead in +2 state is stable whereas in +4 oxidation state it is a strong oxidising agent.
– Carbon monoxide is neutral whereas C02 is acidic in nature.
– Carbon monoxide having lone pair of electrons on C forms metal carbonyls.
– Carbon monoxide forms a haemoglobin complex which is deadly poisonous due to its higher stability.
– Zeolites are complex aluminium silicates.

 Ritan Sheth
Ritan Sheth
