- Books Name
- Ritan Sheth Chemistry Book
- Publication
- Ritan Sheth
- Course
- CBSE Class 11
- Subject
- Chemistry
HYDROGEN PEROXIDE (H202)
Preparation: Merck's method
Sodium peroxide is gradually added to an ice-cold solution of 20% H2SO4.
Na2O2+H2SO4→Na2SO4+H2O2
Upon cooling, crystals of Na2SO4.10H2O separates out and the resulting solution contains 30% H2O2.
Preparation of hydrogen peroxide from barium peroxide
By the action of dilute sulphuric acid:
BaO2.8H2O(s)+H2SO4(aq)→BaSO4(s)+H2O2(aq)+8H2O(l)
By the action of carbon dioxide:
BaO2+H2O+CO2→BaCO3+H2O2
By the action of sulphuric acid:
3BaO2+2H3PO4→Ba3(PO4)2+3H2O2
Limitation of preparation of hydrogen peroxide
H2O2 prepared from barium peroxide ( laboratory method of preparation ) contains appreciable amount of Ba2+ ions which catalyse the decomposition of H2O2. Therefore, hydrogen peroxide cannot be stored for a long time. It is unstable and also explosive, so it is usually preserved in water solution.
Manufacture of hydrogen peroxide
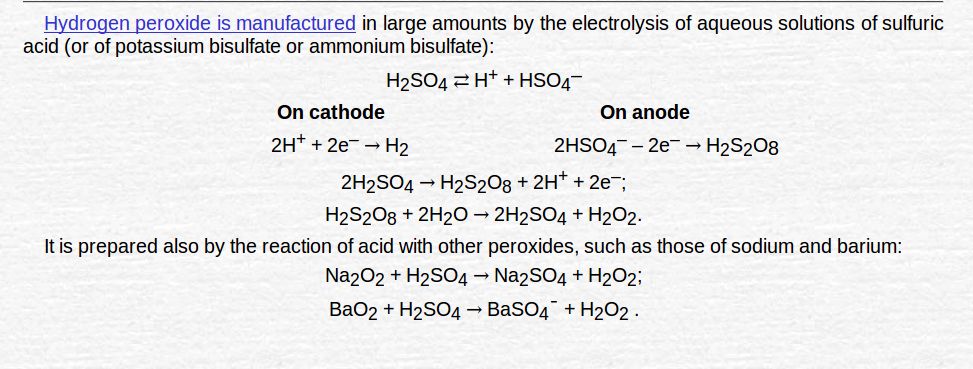
- By electrolysis of 50% H2O2
- By auto oxidation of 2-ethylanthraquinol
Methods of concentration of Hydrogen peroxide
- Evaporation on a water bath
- Dehydration in a vacuum dessicator
- Distillation under reduced pressure
- Removal of last traces of water
Strength of hydrogen peroxide solution
Strength is expressed in two ways:
- Percentage strength: It expresses the amount of H2O2 by weight present in 100 ml of the solution.
- Volume strength: The volume of oxygen liberated at N.T.P by the decomposition of 1 ml of that sample of hydrogen peroxide.
Physical properties of Hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is colorless and odorless liquid.
2) It is bitter in taste.
3) Pure H2O2 is thick syrupy liquid with pale blue colour.
4) It is completely miscible with water, alcohol and ether in all proportion.
Chemical properties of hydrogen peroxide
1. Decomposition: Pure H2O2 is unstable in nature, hence it decomposes into water and oxygen.
2H2O2(aq)→2H2O(l)+O2(g)
2. Acidic nature: It turns blue litmus red but it dil. solution is neutral to litmus. The acidic nature of H2O2 is shown by its neutralization reactions with hydroxides.
NaOH+H2O2→NaHO2+H2O
Ba(OH)2+H2O→BaO2+2H2O
3. Oxidising and reducing nature:
It oxidises lead sulphide to lead sulphate (in neutral solution)
It oxidizes acidified ferrous sulphate to ferric sulphate (in acidic medium)
H2O2→H2O+O
2FeSO4+H2SO4+H2O2→Fe2(SO4)3+H2O
4. In the presence of other oxidizing agents, hydrogen peroxide acts as a reducing agent. This is because it can take up an atom of oxygen to give water and oxygen gas.
Ag2O+H2O2→2Ag+H2O+O2
Tests of hydrogen peroxide
- It liberates iodine from KI solution.
- It decolourizes KMnO4 solution.
- It turns filter paper containing black stains of PbS white.
Structure of hydrogen peroxide
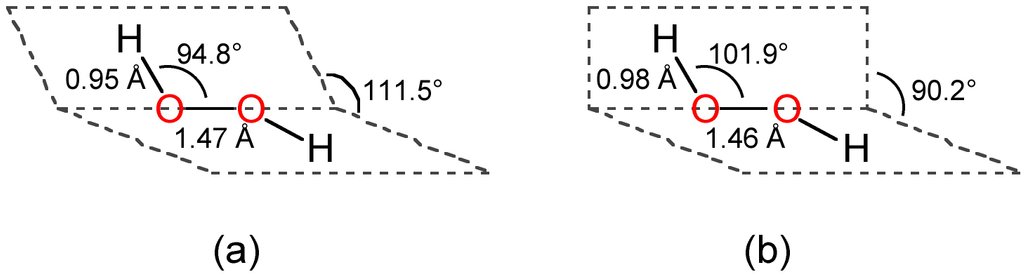
It has a open book structure. It is shown in the image.
Uses of hydrogen peroxide
- It acts as a bleaching agent for delicate material.
- It is used in the production of epoxides, inorganic chemicals like sodium perborate.
- It is used as an antiseptic for washing wounds.
- It is used in the laboratory for detecting the presence of chromium, titanium, etc.
Uses of H202:
(i) It is used as a mild disinfectant. It is marketed as perhydrol (an Antiseptic).
(ii) It is used in the manufacture of high quality detergents.
(iii) It is used in the synthesis of hydroquinone tartaric acid and certain food products and pharmaceuticals.
(iv) It is used as bleaching agent for textilies, paper pulp etc.
(v) It is used for pollution control treatment of domestic and industrial effluents.
(vi) 93% H202 is used as an oxidant for rocket fuel.

 Ritan Sheth
Ritan Sheth
