- Books Name
- Vision classes Accountancy Book
- Publication
- Vision classes
- Course
- CBSE Class 11
- Subject
- Accountancy
Reserves
Some part of profit retained in the business to provide for certain future needs like growth and expansion or to meet future contingencies such as workmen compensation. Reserve is not a charge against profit as it is not meant to cover any known liability or expected loss in future. It is shown under the head Reserves and Surpluses on the liabilities side of the balance sheet after capital.
Examples of reserves are:
- General reserve;
- Workmen compensation fund;
- Investment fluctuation fund;
- Capital reserve;
- Dividend equalization reserve;
- Reserve for redemption of debenture.
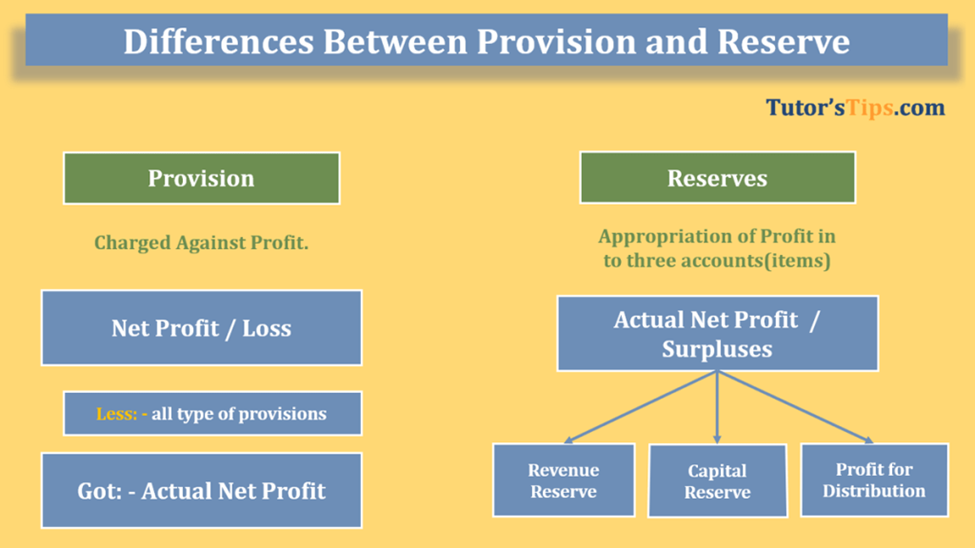
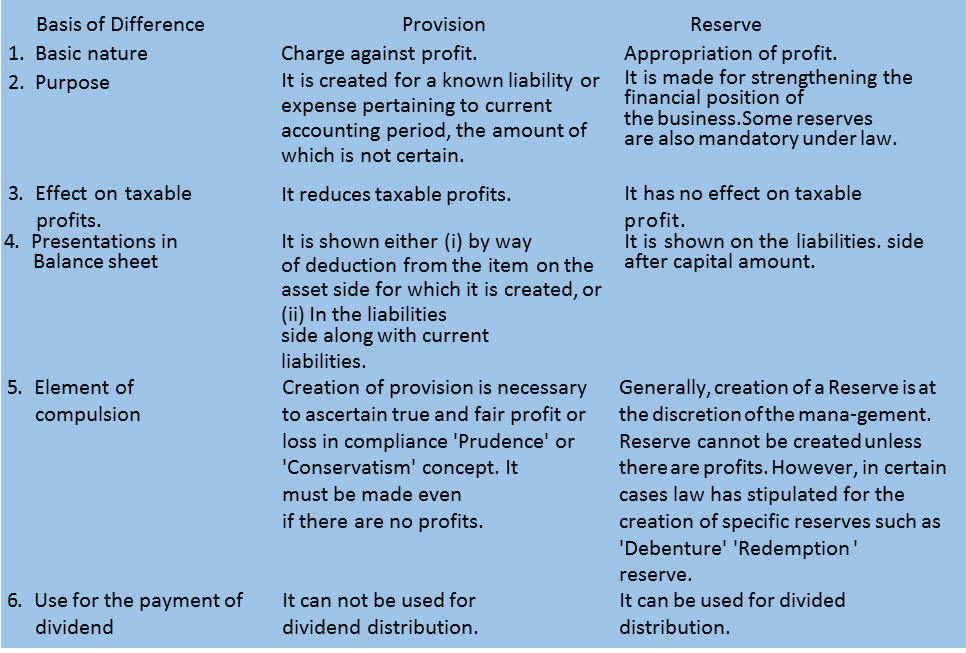
Difference between Reserve and Provision
Types of Reserves
General reserve: General Reserve which is not specified. It is also termed as free reserve because the management can freely utilize it for any purpose. General reserve strengthens the financial position of the business.
Specific reserve: Specific reserve is created and utilized only for some specific purpose.
Examples of specific reserves are given below:
- Dividend equalization reserve: This reserve is created to stabilize or maintain dividend rate. In the year of high profit, amount is transferred to Dividend Equalization reserve. In the year of low profit, this reserve amount is used to maintain the rate of dividend.
- Workmen compensation fund: It is created to provide for claims of the workers due to accident, etc.
- Investment fluctuation fund: It is created to make for decline in the value of investment due to market fluctuations.
- Debenture redemption reserve: It is created to provide funds for redemption of debentures.
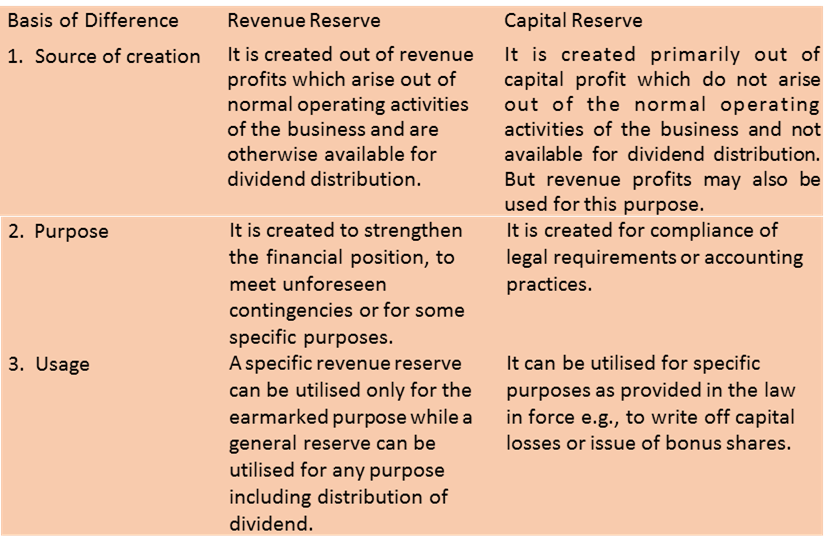
Reserves are also classified as revenue and capital reserves according to the nature of the profit out of which they are created.
(a) Revenue reserves: It is created from revenue profits which arise out of the normal operating activities of the business and are otherwise freely available for distribution as dividend.
Examples of revenue reserves are:
- General reserve;
- Workmen compensation fund;
- Investment fluctuation fund;
- Dividend equalization reserve;
- Debenture redemption reserve;
(b) Capital reserves: It is created out of capital profits which do not arise from the normal operating activities. Such reserves are not available for distribution as dividend. These reserves can be used for writing off capital losses or issue of bonus shares in case of a company.
Examples of capital profits are -
- Premium on issue of shares or debenture.
- Profit on sale of fixed assets.
- Profit on redemption of debentures.
- Profit on revaluation of fixed asset & liabilities.
- Profits prior to incorporation.
- Profit on reissue of forfeited shares
Difference between Revenue and Capital Reserve
Importance of Reserves
A business protect itself from the consequences of unknown expenses and losses, it may be required to bear in future. It may also regard it as more appropriate in certain cases to reduce the amount that can be drawn by the proprietors as profit in order to conserve business resource to meet certain significant demands in future. An example of such a demand is the much needed expansion in the scale of business operations.
The amount so set aside may be meant for the purpose of:
- Meeting a future contingency
- Strengthening the general financial position of the business;
- Redeeming a long-term liability like debentures, etc.
Secret Reserves
It does not appear in the balance sheet. It may also help to reduce the disclosed profits and also the tax liability. The secret reserve can be merged with the profits during the lean periods to show improved profits. It is termed as 'Secret Reserve', as it is not known to outside stakeholders.
Secret reserve can also be created by way of:
Undervaluation of inventories/stock.
Charging capital expenditure to profit and loss account.
Making excessive provision for doubtful debts.
Showing contingent liabilities as actual liabilities.

 Vision classes
Vision classes
