- Books Name
- Iti Shree Science Book
- Publication
- Vaishnav Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Science
Chapter 13
Magnetic Effects of Electric current
Magnetic field: The region surrounding a magnet, in which the force of the magnet can be detected, is named as magnetic field.
Magnetic field lines: The magnetic field lines can be explained as imaginary lines that graphically represent the magnetic field acting around a magnet.
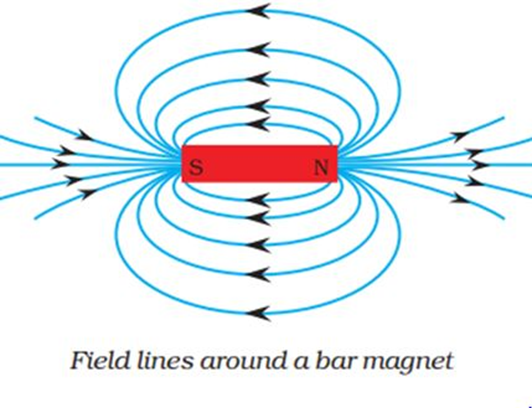
Characteristics of magnetic field lines:
→ The field lines emerge from north pole and merge at the south pole
→ Inside the magnet, the direction of field lines is from its south pole to its north pole.
→ Thus the magnetic field lines are closed curves.
→ Magnetic field lines never intersect with each other.
Properties of magnetic field lines:
→ The tangent drawn to the magnetic field lines gives the direction of the magnetic field.
→ The closeness or density of the field lines is directly proportional to the strength of the field.
→ The field lines emerge from north pole and merge at the south pole.
→ Inside the magnet, the direction of field lines is from its south pole to its north pole.
→ Magnetic field lines form closed curves.
→ Magnetic field lines never intersect with each other.
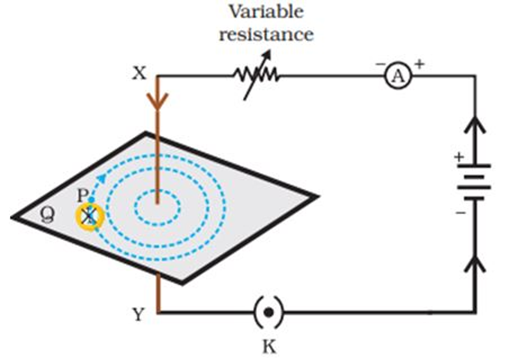
Field due to a current carrying conductor:
When current is passed through a straight current-carrying conductor, a magnetic field is produced around it.
The magnetic field lines are represented in the form of concentric circles around the conductor.
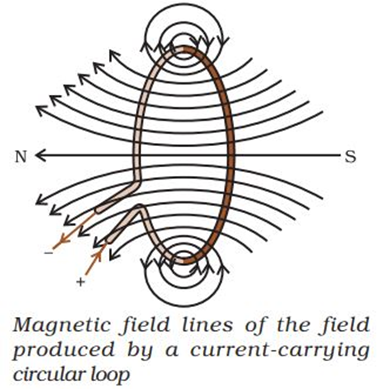
Magnetic field due to current through a circular loop:
→ Every point on the circular loop will act as a straight conductor.
→ Magnetic field lines are closer near the conductor which means the magnetic field is stronger near the periphery of the loop.
→ Magnetic field lines move away from each other as we move towards the centre of the current carrying loop.
→ At the centre, the magnetic field lines appear as straight lines.
Field due to a current carrying coil or solenoid
A coil of many circular turns of insulated copper wire wrapped closely in the shape of a cylinder is called a solenoid. When current is passed through it, it behaves similar to a bar magnet. One end of solenoid behaves as the north pole and another end behaves as the south pole.
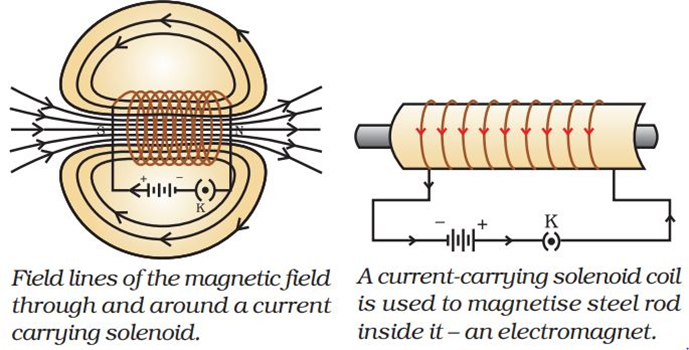
The field lines inside the solenoid are in the form of parallel straight lines. This indicates that the field is uniform inside the solenoid.
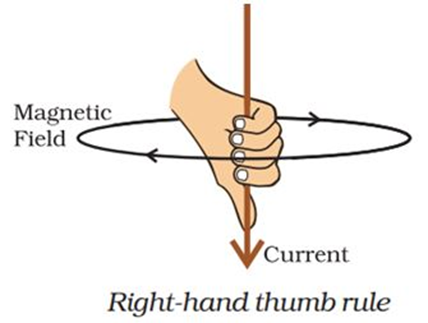
Right-Hand Thumb Rule:
If a straight conductor is held in the right hand in such a way that the thumb points along the direction of the current then the fingers curl in the direction of magnetic field around it.

 Vaishnav Publication
Vaishnav Publication
