- Books Name
- Iti Shree Science Book
- Publication
- Vaishnav Publication
- Course
- CBSE Class 10
- Subject
- Science
What is Galvanometer?
- A galvanometer is a device (instrument) used in a circuit to detect weak electrical voltages and currents.
- It has a coil of a solid laminated horse shoe magnet pivoted (or suspended) between concave pole faces.
- It deflects as an electrical current travels through the coil.
Faraday’s Experiment
In First experiment,
- Faraday connected a coil to a galvanometer.
- A bar magnet was pushed towards the coil, such that the North Pole is pointing towards the coil.
- As the bar magnet is shifted, the pointer in the galvanometer gets deflected, thus indicating the presence of current in the coil under consideration.
Observation:
- When the bar magnet is stationary, the pointer shows no deflection and the motion lasts only till the magnet is in motion.
- Here, the direction of the deflection of the pointer depends upon the direction of motion of the bar magnet.
- Also, when the south pole of the bar magnet is moved towards or away from the coil, the deflections in the galvanometer are opposite to that observed with the north-pole for similar movements.
- Apart from this, the deflection of the pointer is larger or smaller depending upon the speed with which it is pulled towards or away from the coil.
- The same effect is observed when instead of the bar magnet, the coil is moved and the magnet is held stationary.
Observation:
- As we move the second coil towards the primary coil, the pointer in the galvanometer undergoes deflection, which indicates the presence of the electric current in the first coil.
Conclusion:
- The direction of the deflection of the pointer depends upon the direction of motion of the secondary coil towards or away from the primary coil.
- Also, the magnitude of deflection depends upon the speed with which the coil is moved.
- All these results show that the system in the second case is analogous to the system in the first experiment.
In Third experiment,
- From the above two experiments, it was concluded by Faraday that the relative motion between the magnet and the coil resulted in the generation of current in the primary coil.
- But another experiment conducted by Faraday proved that the relative motion between the coils was not really necessary for the current in the primary to be generated.
- In third experiment, he placed two stationary coils and connected one of them to the galvanometer and the other to a battery, through a push-button.
Observation:
As the button was pressed, the galvanometer in the other coil showed a deflection, indicating the presence of current in that coil.
Conclusion:
The deflection in the pointer was temporary and if pressed continuously, the pointer showed no deflection and when the key was released, the deflection occurred in the opposite direction.
Flemming Right Hand Rule
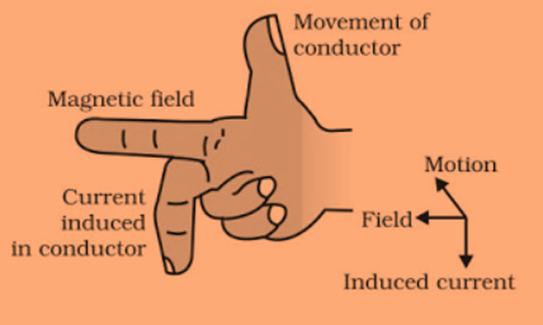
Fleming right hand rule
Hold the forefinger, middle finger and thumb of right hand at right angles to each other. Forefinger points towards the direction of magnetic field, thumb points in the direction of motion of conductor and middle finger shows direction of induced current.
Electric Generator
Electric Energy is a device used to convert mechanical energy into alternating form of electrical energy. It consists of insulated copper wire, magnetic poles, split rings, axle, brushes and galvanometer.
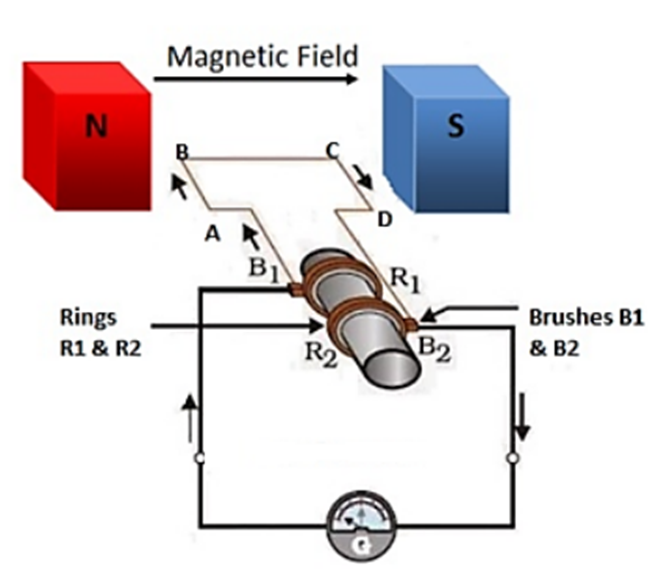
Electric generator
The axle is rotated so that it moves clockwise direction that is AB moves up and CD moves down. After half rotation, CD starts to move up and AB moves down. After every half rotation current changes its direction, this is called AC current.
Domestic Electric Circuits
Three kinds of wires are used in domestic electric circuits.
- Live wire red in colour.
- Neutral wire with black insulation cover
- Earth wire with green insulation cover.
The potential difference between live and neutral wire in India is 220V.
Electric Fuse
- It is a safety device to limit the current in an electric circuit.
- It prevents the electric appliances from damage.
- It is made up of material which has high resistivity and low melting point.

 Vaishnav Publication
Vaishnav Publication
