- Books Name
- Kaysons Academy Maths Foundation Book
- Publication
- Kaysons Publication
- Course
- JEE
- Subject
- Maths
Chapter-7
Quadratic equations
Introduction
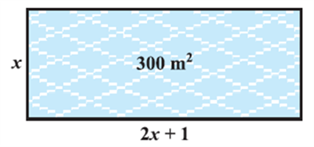
In Chapter 2, you have studied different types of polynomials. One type was the quadratic polynomial of the form ax2 + bx + c, a ≠ 0. When we equate this polynomial to zero, we get a quadratic equation. Quadratic equations come up when we deal with many real-life situations. For instance, suppose a charity trust decides to build a prayer hall having a carpet area of 300 square metres with its length one metre more than twice its breadth. What should be the length and breadth of the hall? Suppose the breadth of the hall is x metres. Then, its length should be (2x + 1) metres. We can depict this information pictorially as shown in Fig.
Now, area of the hall = (2x + 1). xm2 = (2x2 + x) m2
So, 2x2 + x = 300 (Given)
Therefore, 2x2 + x – 300 = 0
So, the breadth of the hall should satisfy the equation 2x2 + x – 300 = 0 which is a quadratic equation.
Quadratic Equations
A quadratic equation in the variable x is an equation of the form ax2 + bx + c = 0, where a, b, c are real numbers, a ≠ 0. For example, 2x2 + x – 300 = 0 is a quadratic equation.
Similarly, 2x2 – 3x + 1 = 0, 4x – 3x2 + 2 = 0 and 1 – x2 + 300 = 0 are also quadratic equations.
In fact, any equation of the form p(x) = 0, where p(x) is a polynomial of degree 2, is a quadratic equation. But when we write the terms of p(x) in descending order of their degrees, then we get the standard form of the equation. That is, ax2 + bx + c = 0, a ≠ 0 is called the standard form of a quadratic equation.
Quadratic equations arise in several situations in the world around us and in different fields of mathematics.
Relationship between Zeroes and Coefficients of a Polynomial
In general, a real number α is called a root of the quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0, a ≠ 0 if a α2 + bα + c = 0. We also say that x = α is a solution of the quadratic equation, or that α satisfies the quadratic equation. Note that the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial ax2 + bx + c and the roots of the quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 are the same.
Note:- That we have found the roots of 2x2 – 5x + 3 = 0 by factorizing 2x2 – 5x + 3 into two linear factors and equating each factor to zero.

 Kaysons Publication
Kaysons Publication
