- Books Name
- Kaysons Academy Chemistry Foundation Book
- Publication
- Kaysons Publication
- Course
- JEE
- Subject
- Chemistry
Writing Chemical Formulae
The shortest way to represent a compound with the help of symbols and valency of elements is known as chemical formula. Chemical formula of a compounds shows of each combining element.
In ionic compounds, the charge on each ion is used to determine the chemical formula of a compound.
There are some rules for writing the chemical formula
(i):- The valencies or charges on the ion must be balanced.
(ii):- When a compound consists of a metal and a non-metal, the symbol of the metal is written first and on the left whereas of non-metal on its right.
(iii):- When compound is formed with polyatomic ions, the ion is enclosed in a bracket before writing the number to indicate the ratio. e.g. Ca(OH)2.
Formulae of Simple Compounds
To write the chemical formula for simple compounds.
(i):- Write the symbols of constituent elements and their valencies as shown below.
(ii):- Write the symbol of cation first followed by the symbol of anion.
(iii):- Then criss-cross their charges or valencies to get the formula.
Note:- The simplest compounds made up of two different elements are also called binary compounds.
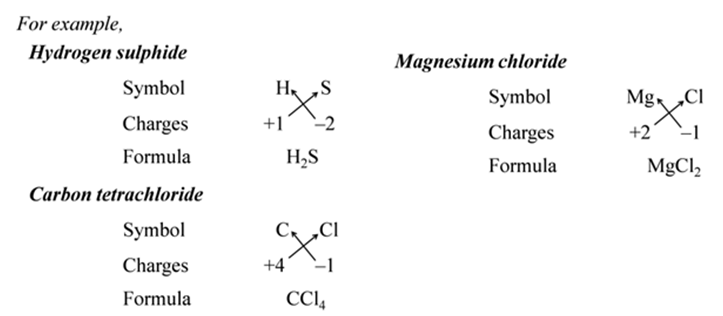
In other words, the positive and negative charges must balance each other and the overall structure must be neutral.

Note:- When the valency of both elements are numerically equal, the subscripts are also not written.
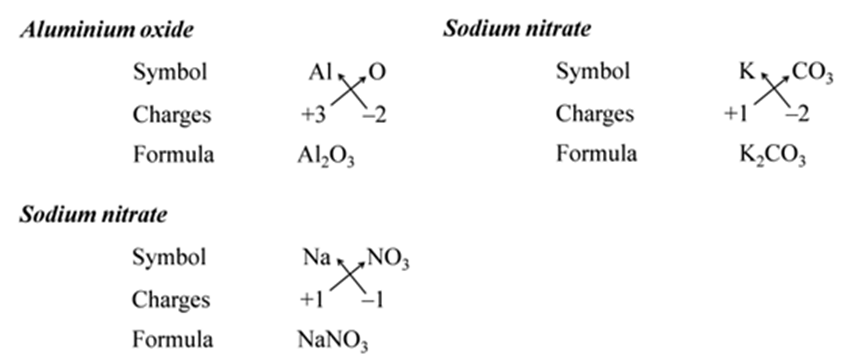
We use brackets when we have two or more of the same ions in the formulae. For Example:-
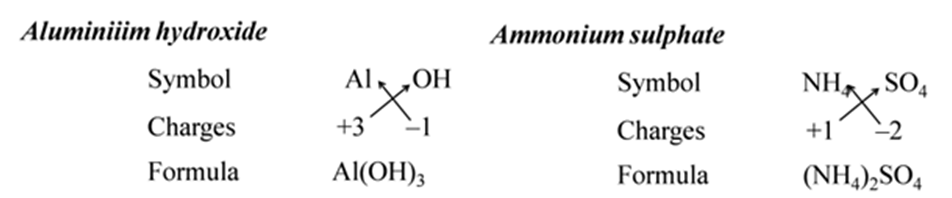
All subscripts must be reduced to lowest term (except for molecule or covalent compound). For Example:-

Molecular Mass
The molecular mass of a substance is the sum of the atomic Masses of all the atoms in a molecule of the substance. Therefore, the relative molecular mass of a molecule is its relative mass expresses in atomic mass units (u).
For example,
The relative molecular mass of water (H2O) is 18 u, which can be calculated as
Atomic mass of hydrogen =1 u
Atomic mass of oxygen = 16 u
H2O contains two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. Therefore, molecular mass of water is
= 2x1 + 1 x 16 = 18 u
Formula Unit Mass
It is the sum of the atomic masses of all atoms present in a formula unit of a compound.
Formula unit mass is calculated in the same manner as we calculate the molecular mass.
e.g. formula unit mass for sodium chloride (NaCI)
= 1 x 23 + 1 x 35.5 = 58.5 u
Mole Concept
One mole of any species (atoms, molecules, ions or particles) is that quantity in number having a mass equal to its atomic or molecular mass in grams.
e.g. 1 mole of carbon (atomic mass =12) is equal to 12 g.
1 mole of oxygen (O2, molecular mass = 2 x 16) is equal to 32 g.
1 mole of water (H2O, molecular mass = 2 x 1 + 1 x 16) is equal to 18 g.
Avogadro Constant
The number of particles present in 1 mole of any substance is same and fixed, which is equal to 6.022 x 1023. This is a constant, known as Avogadro constant or Avogadro number (NA).
Thus, mole is also defined as number of particles equal to the Avogadro constant, NA(6.022 x 1023).
1 mole = 6.022 x 1023 particles, in number.
Molar Mass and Moles
The mass of 1 mole of a substance is equal to its relative atomic or molecular mass in gram. Since the atomic mass or molecular mass of an element gives us the mass of one atom of that element in atomic mass units (u). Thus, to get the mass of 1 mole of an atom of that element we have to take the same numerical value but change the units from `if to 'g‘.
Percentage Composition
The percentage composition of an element in a compound is the percentage of the mass contributed by the element to the total mass of the compound. It is obtained by dividing mass of that element in the compound by the total mass of the compound and multiplying by 100, i.e.,.
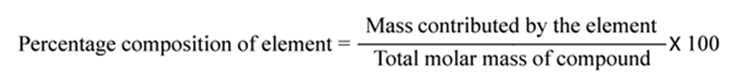

 Kaysons Publication
Kaysons Publication
