- Books Name
- Kaysons Academy Chemistry Foundation Book
- Publication
- Kaysons Publication
- Course
- JEE
- Subject
- Chemistry
Latent Heat
The heat energy which has to be supplied to change the state of a substance is called its latent heat. Latent heat does not raise (or increase) the temperature.
Latent Heat is of Two Types
- Fusion
- Vaporization
Latent Heat of fusion (Solid to Liquid Change)
The latent heat of fusion (or melting) of a solid is the quantity of heat in joules required to convent 1 kilogram of the solid (at its melting point) to liquid, without any change in temperature.
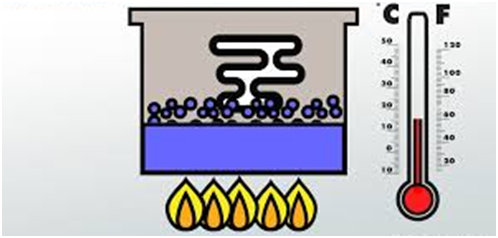
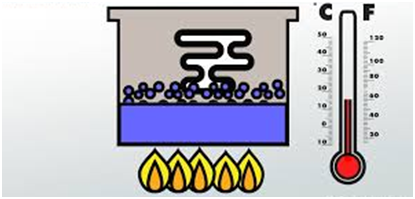
Latent Heat of Vaporization
It is defined as heat required converting 1 mole of liquid into vapors completely at its boiling point.
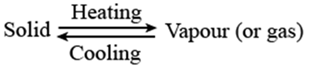
Sublimation
The changing of a solid directly in to vapors on heating. And vapors’ into solid on cooling is known as sublimation. Sublimation can be represented as:
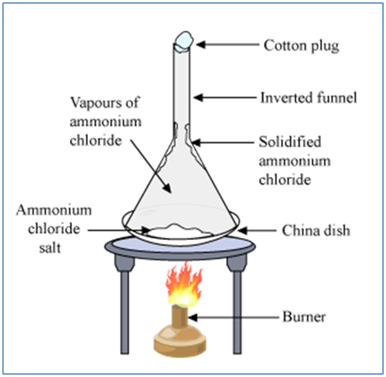
Ex:- Solids carbon dioxide
is a white solid called dry ice.
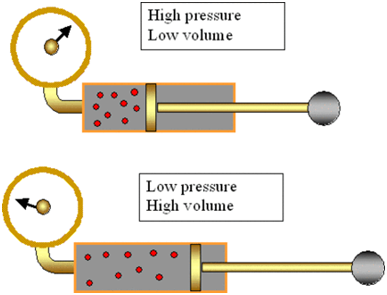
Gases Can be Liquefied by Applying Pressure and Lowering Temperature
Gases can be liquefied by applying pressure and lowering temperature.
Evaporation
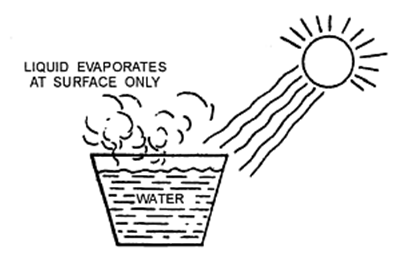
The process of a liquid changing into vapour (or gas) even below its boiling point is called evaporation.
Factors Affecting Evaporation
The evaporation of a liquid depends mainly on the following factors:
- Temperature
- Surface area
- Humidity
- Wind speed
Cooling Caused by Evaporation
The cooling caused by evaporation is based on the fact that when a liquid evaporates, it draws the latent heat of vaporization from ‘anything’ which it touches and makes it cool.

 Kaysons Publication
Kaysons Publication
