- Books Name
- Kaysons Academy Chemistry Book
- Publication
- Kaysons Publication
- Course
- JEE
- Subject
- Chemistry
INTRODUCTION
The attractive force which holds together the constituent particles (atoms, ions or molecules) in chemical species is known as chemical bond.
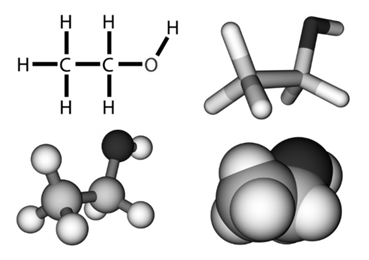
- Kössel-Lewis Approach to Chemical Bonding
They assumed that atom have positive kernel surrounded by electrons occupying the corners of a cube. If they have all the eight electrons in their outer shell they will be stable (octet rule). Otherwise they achieve stability (octet) through chemical bonding.
LEWIS STRUCTURE
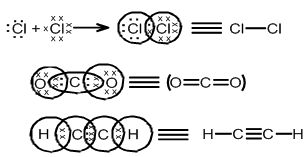
Why chemical bonds are formed.
If the resultant molecule has lower Gibb's energy then the reacting species, then chemical bonds are formed.
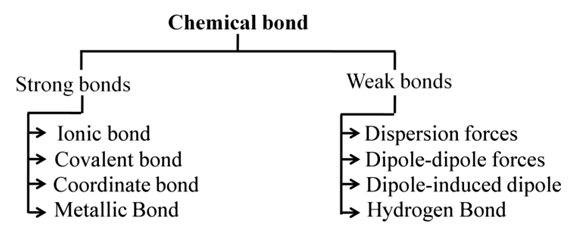
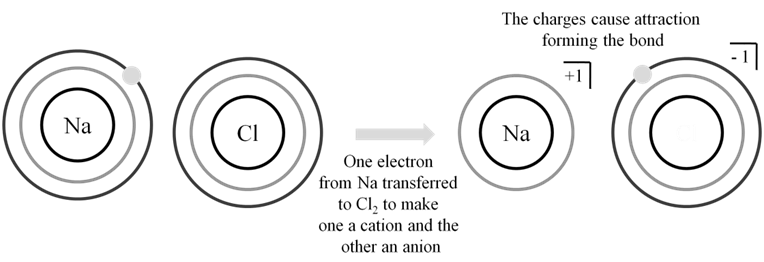
IONIC BOND
Ionic bonds are strong electrostatic forces between cation & anion which are formed when an atom looses an electron or gains an electron.
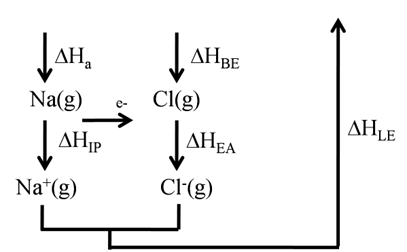
BORN HABER CYCLE FOR SODIUM CHLORIDE
![]()
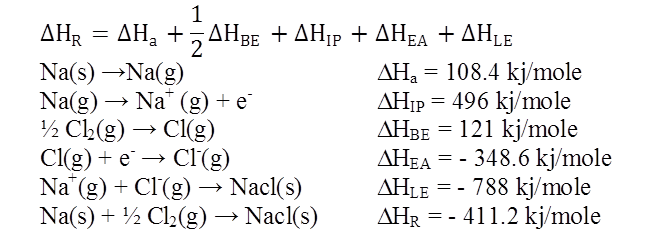
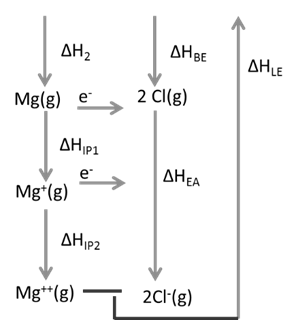
Ex.1: Draw Born Haber cycle for formation of Magnesium chloride
![]()
![]()
PROPERTIES OF IONIC COMPOUNDS
- They are crystalline in nature
- They have high Melting and Boiling point
- Hard and Brittle
- Soluble in polar solvents
- Conduct electricity in molten state and aqueous state but not in solid state.
- Do not show Isomerism.
VARIABLE ELECTROVALENCY
Fe (26) → 3s2 3p6 3d6 4s2
Fe+2 (24) → 3s2 3p6 3d6 (less stable)
Fe+3 (23) → 3s2 3p6 3d5 (more stable)
Solubility of ionic compounds in water. There are two things happen on dissolving ionic compounds in water.
1. Breaking of ionic lattice
2. Mixing of ions in water
For the first process, lattice energy to be provided to the solution and for second process hydration energy will be released by the system
If ΔHhyd >ΔHL.E. Compound is soluble in water
(a) Lattice Energy
1. If depends on size of cation and anion.
Smaller the size greater is the Lattice Energy.
Ex. → LiCl > NaCl > KCl
→ NaCl > NaBr > NaI
2. If depends on Charge of cation and anion.
Bigger the charge, lesser is it Lattice energy.
Ex. MgCl2 > NaCl
3. In case anions are extremely large, then the rule one charges smaller the cation lesser is Lattice Energy.
Ex. MgSO4 < CaSO4 < SrSO3 < BaSO4
(b) Hydrogen energy
Smaller the cation, greater is the hydration enthalpy.
Ex. Compare Solubility BaSO4 and CaSO4
L.E. Þ BaSO4 > CaSO4
Hyd. Energy Þ CaSO4 > BaSO4
So CaSO4 is more soluble.
Ex. Compare solubility of NaCl and BaCl2
L.E. Þ BaCl2 > NaCl
Hyd. Energy Þ NaCl > BaCl2
So NaCl is more soluble.
COVALENT BOND
Combining of unpaired electrons of atoms to achieve a stable configuration and formation of molecules is called covalent bond.
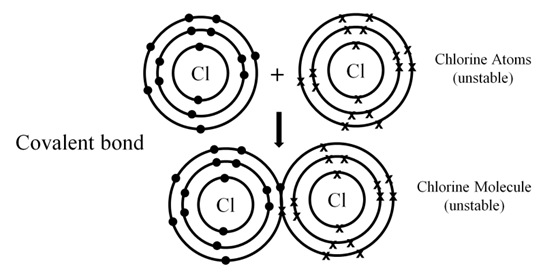
SIGMA (s) BOND: THIS TYPE OF COVALENT BOND is formed by the end to end (head-on) overlap of bonding orbitals along the inter-nuclear axis. This is called as head on overlap or axial overlap
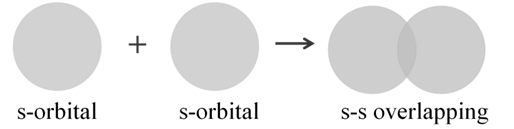
s - s overlapping: In this case, there is overlap of two half killed s-orbitals along the inter-nuclear axis as shown below:
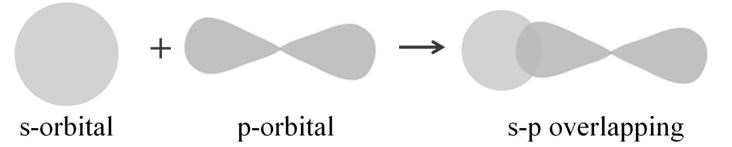
s-p overlapping: This type of overlap occurs between half filled s-orbitals of one atom and half filled p-orbitals of another atom:
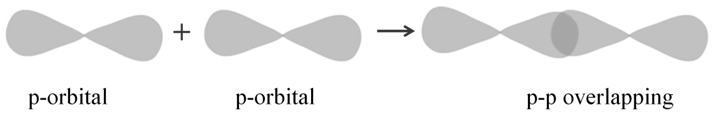
p-p overlapping: This type of overlap takes place between half filled p-orbitals of the two approaching atoms:
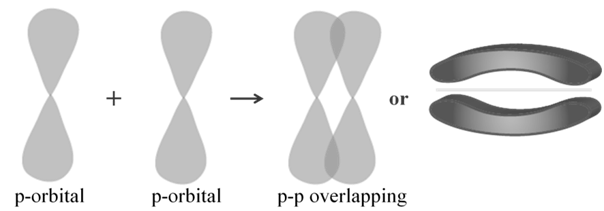
Pi (π) BOND: IN THE FORMATION OF π BOND
The atomic orbitals overlap in such a way that their axes remain parallel to each other and perpendicular to the inter-nuclear axis.
Characteristic of Convent compounds
- Physical state ® gases, liquids of law b.p. & soft solids
- Melting Point/Boiling point ® with exception of network solids, they have low M.P. and B.P.
- Electrical conductance ® generally bad conductors
- Solubility ® soluble in non-polar solvents
- Isomerism ® yes Physical state ® gases, liquids of law b.p. & soft solids
- Melting Point/Boiling point ® with exception of network solids, they have low MP/B.
- Electrical conduce ® generally bed conductors
- Solubility ® soluble in non-polar solvents
- Isomerises ® yes
COMPARISON BETWEEN IONIC AND COVALENT BONDS

COMPARISON BETWEEN IONIC AND COVALENT COMPOUNDS

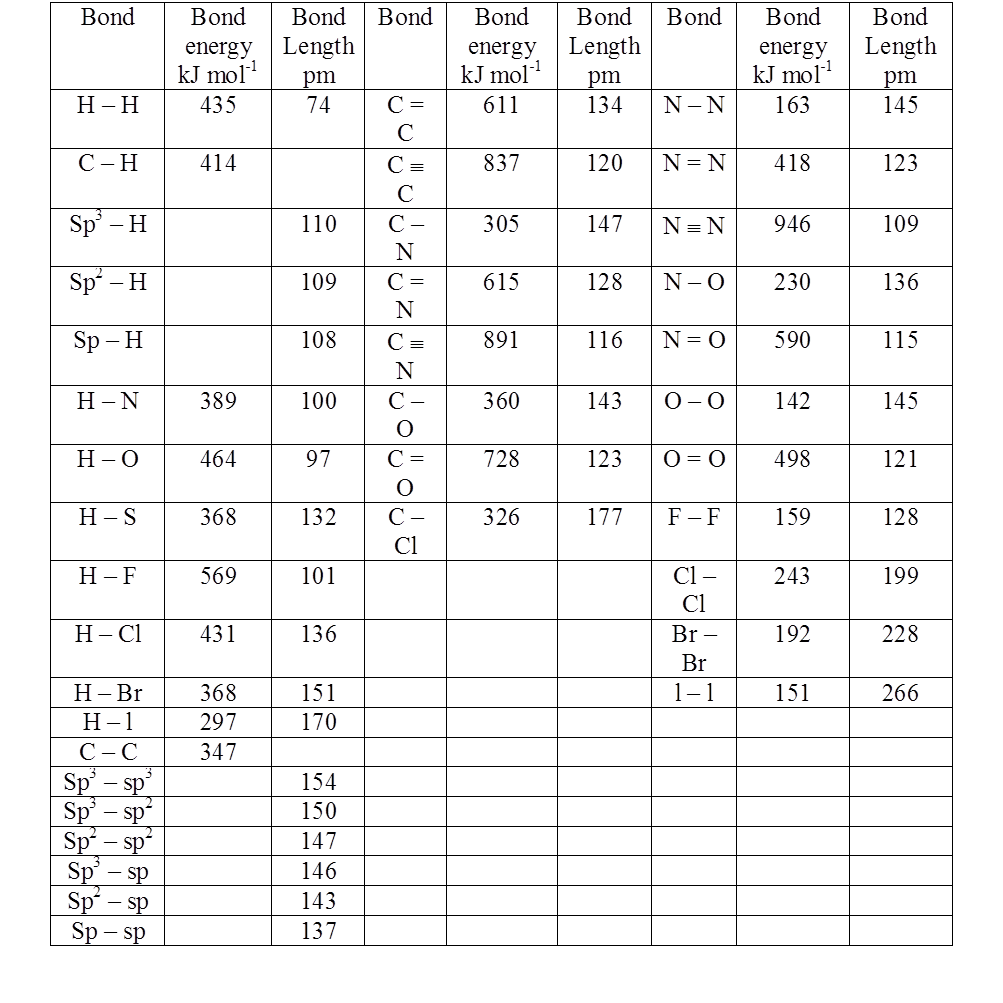
Some representative Bond Energies and Bond Lengths

 Kaysons Publication
Kaysons Publication
