- Books Name
- Kaysons Academy Chemistry Book
- Publication
- Kaysons Publication
- Course
- JEE
- Subject
- Chemistry
PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
1. Solids have definite mass.
2. Solids have definite Volume
3. Solids have definite shape
PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
- Intermolecular distances are short.
- Intermolecular forces are strong.
- Their constituent particles (atoms, molecules or ions) have fixed positions and can only oscillate about their mean positions.
- In general they are incompressible and rigid
Solids are classified as crystalline and amorphous

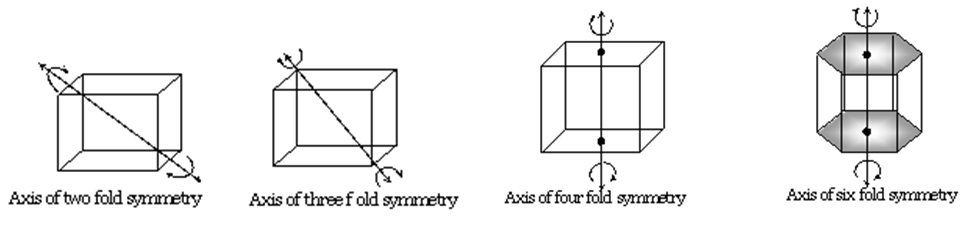
AXIS OF SYMMETRY
- An imaginary axis through which if we rotate the solid then same figure is seen more than once before completing 360o
- For a cube we have
- Two fold symmetry
- Three fold symmetry
- four fold symmetry
Axis of symmetry
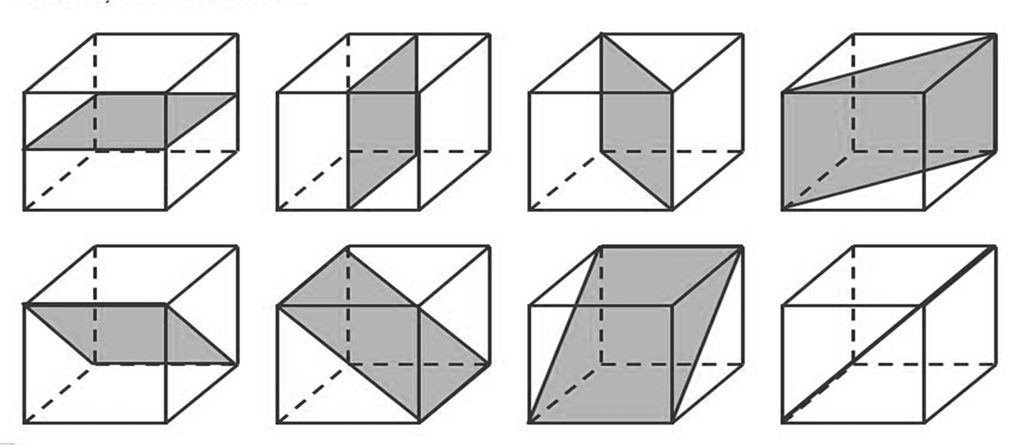
PLANE OF SYMMETRY
An imaginary plane through if we cut the solid the two parts will be mirror image of each other
Centre of symmetry
- An imaginary point through if we pass an imaginary line it will touch the opposite plane, edge or vertices at equal distance
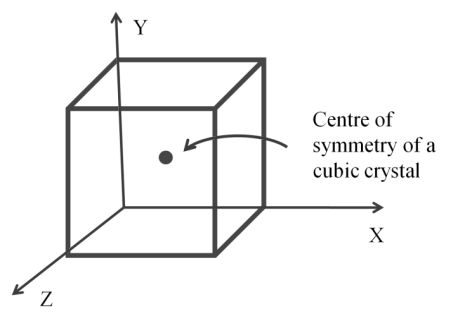
PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
- Cleavage plains: Cleavage is the tendency of a mineral to break along smooth planes parallel to zones of weak bonding. Crystals have cleavage plains where as amorphous solids do not have these plains
- Crystals are called true solids whereas amorphous solids are called pseudo solids or super cooled liquid.
Polymorphic forms or polymorphs: The different crystalline forms of a same substance are known as polymorphic forms or polymorphs. For example: graphite and diamond are polymorph’s of carbon
Crystals classification based on the nature of intermolecular forces
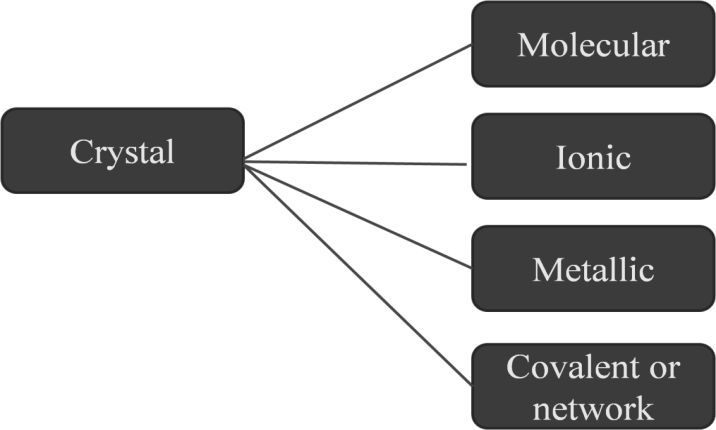
Molecular crystals
They have constituent particles as molecules and are divided into three parts
- Non polar: here the intermolecular forces are weak Vanderwaal's forces (Dispersion or London forces) . They are soft, do not conduct electricity and have very low melting point. Ex: Argon, CCl4
- Polar: here the intermolecular forces are Dipole-dipole interactions. They are soft, do not conduct electricity and have low melting point. Ex: HCl, SO2
- Hydrogen bonding: here the intermolecular forces are Hydrogen bonds. They are hard, do not conduct electricity and have low melting point. Ex: Ice(H2O)
- Ionic crystals: The constituent particles are ions. These have strong columbic intermolecular forces. They are hard but brittle. They do not conduct electricity in solid state but are good conductors on molten and aqueous state. They have very high melting point. Ex: Rock salt (NaCl), MgCl2
- Metallic solid: The constituent particles are positive ions floating in sea delocalized electrons. These have strong metallic intermolecular forces. They are hard but ductile and malleable. They are good conductor of electricity. They have high melting point. Ex: Iron, Copper etc
- Covalent or network solids: The constituent particles are atoms. These have strong covalent bonding. They are hard .They do not conduct electricity. They have very high melting point. Ex: Silica, Diamond etc. Graphite is an exception because it is soft and conducts electricity.


 Kaysons Publication
Kaysons Publication
