Animal Tissues
Types of Animal Tissues
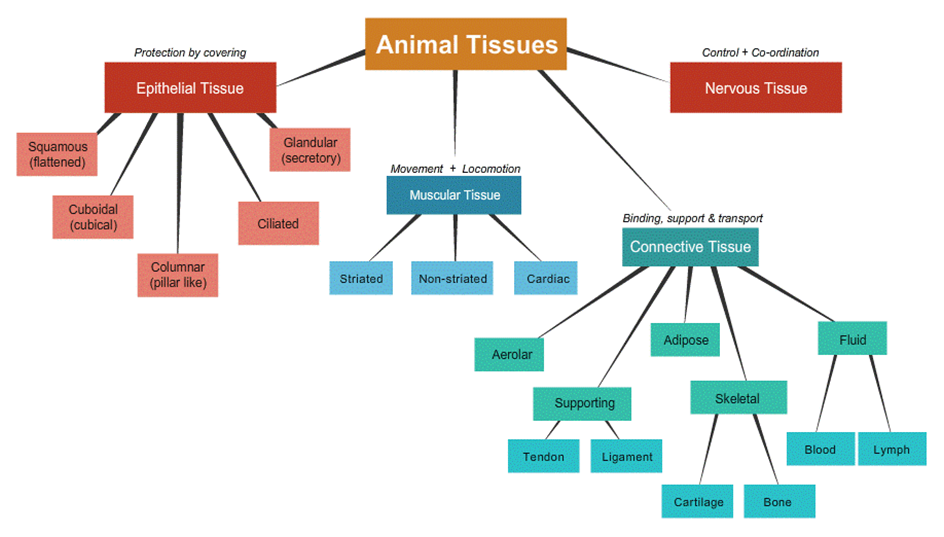
Types of Animal Tissues
-
- Epithelial Tissue
- They are the protective tissues of the human body. They cover many organs and cavities that are present inside the body.
- Where are the epithelial tissues found in the human body?
-
- The lining of the blood vessels
- The lining of the mouth
- Kidney tubules
- Skin
- Lung alveoli
Structure and functions of the epithelial tissues -
-
- The main function of the epithelial tissues is to act as a barrier and separate different organs and systems from each other.
- There is no space between the cells of epithelial tissues
- The cells are permeable. This makes it possible for them to exchange materials between different parts of the body and also between the body and the external environment.
- The epithelial tissues remain separated from the tissues beneath them because of a thin membrane over them.
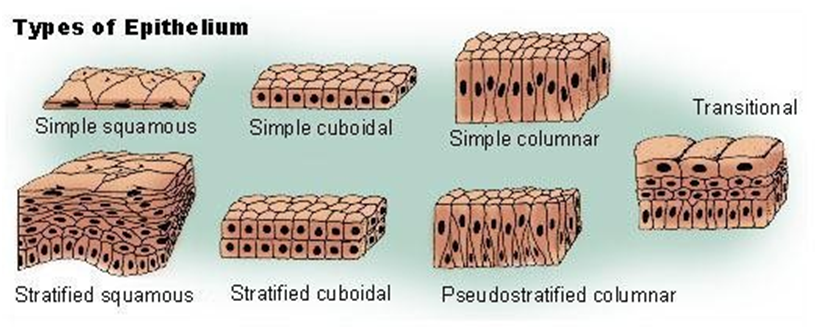
Types of Epithelium
|
Different types of epithelium tissues |
Simple Squamous |
Stratified Squamous |
Columnar |
Ciliated Columnar |
Cuboidal |
Glandular |
|
Structure |
They have delicate cell lining and possess a flat thin structure |
The epithelium Squamous cells are arranged in several layers |
They are the column-like shape tissues |
Columnar epithelial tissues which have Cilia present on them |
They are cube-shaped cells which are involved in absorption and secretion. |
These are special gland cells that can secrete substances |
|
Found in |
Alveoli and bowman’s capsule- nephron in kidney |
Skin |
Intestine |
Respiratory system |
Kidney tubules |
Sweat glands in the skin |
Connective Tissue
Structure and function of connective tissues
-
- They are loosely bound cells present in an intercellular Matrix.
- This matrix can be of different types – Dense, Rigid, Fluid or Jelly-like.
- Depending upon the functionality of the connective tissue, the nature of the matrix varies in them.
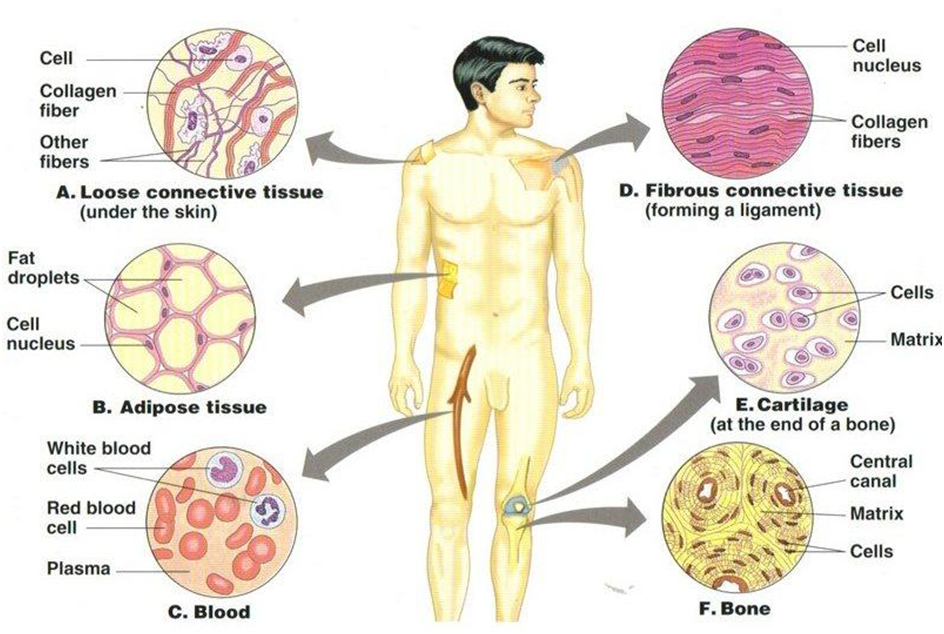
Blood
- The main function of blood is to transport gases, food, waste materials and hormones in the body.
- Therefore, blood has a fluid Matrix present in it which is called Plasma.
- The plasma contains the red blood cells, the white blood cells and blood platelets.
- The RBC have hemoglobin pigment which carries oxygen to tissues.
- White blood cells fight diseases and platelets are involved in clotting of blood when injured.
- The plasma also contains proteins and hormones in it.
Bones
- Bones form a framework of the body over which the muscles are wrapped together.
- The bone tissue is strong and inflexible in nature.
- Therefore, the bone cells are present in a rigid matrix which is formed from calcium and phosphorus.
Cartilage
- Cartilage is present over the joints of the bones and provides them with a smooth structure.
- For Example, in the nose tip and ear pinna, trachea, larynx.
- They contain solid matrix made of protein and sugar. They have homogenous matrix.
- It provides support and flexibility to various parts of our body.
Ligaments
- A ligament connects two bones together.
- It has an elasticity which facilitates the connection.
- The cells of ligaments have a little matrix.
Tendons
- The tendons tissues are responsible for connecting bones and muscles together.
- They have limited flexibility but very great strength.
Areolar
- This tissue acts as a filter in between the spaces present inside the organs of the body.
- It helps in repairing other tissues as well.
- It is found in the skin and bone marrow.
Adipose
- Fats are stored in our body in the adipose tissues.
- They are found below the skin and between the organs of the body.
- Provides cushioning to the organs.
Muscular Tissue
- It is made up of muscle fibers which are long cells.
- It allows movements in our body.
- How muscles can cause movement?
They contain special proteins called Contractile Proteins. These proteins cause contraction and relaxation of the muscles.
- There are two kinds of muscles found in our body - Voluntary Muscles and Involuntary Muscles.
|
Striated/ Skeletal/ Voluntary muscles |
Smooth/ Unstriated/Involuntary muscles |
|
We can move them according to our own will |
We cannot start or stop the movement of involuntary muscles. |
|
They are also called Skeletal Muscles as they are attached to the bones. |
They also called Smooth Muscles. |
|
They are also called Striated Muscles because of the presence of dark and light bands over them |
They are also called Unstriated Muscles because they do not have any light or dark bands on them. |
|
The cells of voluntary muscles have more than one nucleus, they do not have any branches, and have a long cylindrical structure. |
The cells of the involuntary muscles are long and have pointed ends. |
|
For Example, Muscles of our hands and legs. |
For Example, The muscles in the alimentary canal and the Iris of our eyes. |
Cardiac Muscles
- These are special kinds of involuntary muscles.
- The muscles of the heart are called Cardiac Muscles they perform rhythmic contraction and relaxation throughout our life.
- They are cylindrical in shape; they have branches and there is a single nucleus.
- Cardiac muscle consists of individual heart muscle cells connected by intercalated discs to work as a single functional organ

 ACERISE INDIA
ACERISE INDIA
 Vaishnav Publication
Vaishnav Publication
