Permanent Tissue
The cells that are formed by the meristematic tissues often have to take a certain role in the plant and thus, they lose their ability to divide and form more cells. They then become the permanent tissues of the plants.
- Differentiation - The process by which cells of the meristematic tissues convert themselves into a permanent tissue by taking a fixed shape, size and function is called differentiation.
- Types of Permanent Tissues:
- Simple Permanent Tissues
- Complex Permanent Tissues
- Parenchyma
- Chlorenchyma
- Aerenchyma
- Collenchyma
- Sclerenchyma
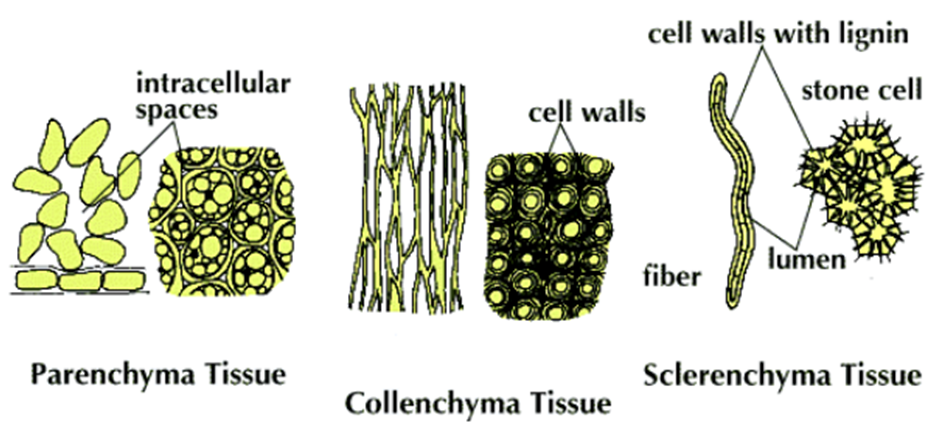
|
Parenchyma |
Collenchyma |
Sclerenchyma |
|
These tissues are responsible for photosynthesis, storage of food, gaseous exchange and floating of plants. |
These tissues are responsible for providing flexibility to the plants so that they can bend easily. |
These tissues are responsible for making plants hard and rigid. |
|
They are a group of living cells with cell wall made of cellulose. |
They are a group of living cells with cell wall made of cellulose and pectin. |
They are made up of dead cells having cell wall made of lignin. |
|
The parenchyma cells have large intercellular spaces between them. |
They have a little intercellular space in between them. |
The cells do not have any intercellular spaces. |
|
There are thin walls that surround each cell. |
The cells present in these tissues are broad and irregularly thick at corners. |
The cells have a long structure with thick walls. |
|
They are found in leaves and newly formed branches. |
They are present in leaves and stems of a plant. |
They are found in stems, veins of the leaves and coverings of nuts and seeds. |
Chlorenchyma
- These tissues are similar to that of parenchyma but they also contain chlorophyll in them.
- Due to the presence of chlorophyll, they are capable of performing the process of photosynthesis in plants.
Aerenchyma
- They are found in aquatic plants.
- They are also similar in structure to that of the parenchyma but they have large air cavities in them.
- These cavities allow the aquatic plants to float in water.
What is Lignin?
The cell walls of dead cells have a substance called lignin in them which provides rigidity to the cells. Lignin acts as the cement for the cells.
Epidermis
- The outermost layer of the cell is known as the Epidermis.
- It covers the entire plant.
- It is a thin layer of single cells but in places with less water, the epidermis of the plants can become thick in order to avoid frequent water loss.
- The cells are flat and they have no intercellular spaces between them.
- The outer walls of the epidermal cells are thick and the inner walls are thin.
- The epidermal cells often have long hair-like structures in roots which facilitate the absorption of water.
- The main function of the epidermis is to protect the plants from fungi, water loss and any injuries by secrets a wax-like water-resistant substance called as Cuticle on the surface of the plants which protects the plants.
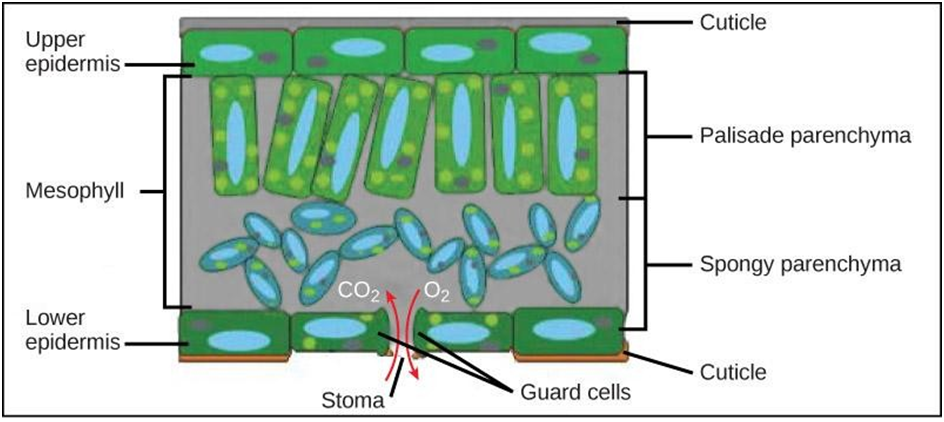
Stomata
- Stomata are pore-like structures that are present in the epidermis of the leaves.
- These pores are enclosed by two cells that have a similar shape as a kidney. These are called Guard Cells of Stomata. Guard cells are modified epidermal cells.
- Guard cells are responsible for the exchange of gases and transpiration.
Why do plants in desert areas have a waxy coating of cutin over them?
The epidermis cells of plants that are found in deserts have a waxy coating of cutin over them because it prevents water loss from the plants surface since water is already scarce in such areas.
Why do branches of old trees are different than the stems of a new plant?
- As a plant grows older the meristematic cells start covering the upper layer of the plants instead of the epidermis.
- These are the dead cells that have no special function in the plants but to provide them rigidity. They make the branches of the plants thick.
- This is often called the Bark or the thick cork of the tree.
- The bark of the trees contains a substance called Suberin which makes it waterproof and does not allow gaseous exchanges.
Complex Permanent Tissues
Complex Permanent Tissues comprise of different kinds of cells. These different types of cells coordinate with each other and perform a common function in these tissues. Two Complex Permanent Tissues are
Xylem and Phloem.
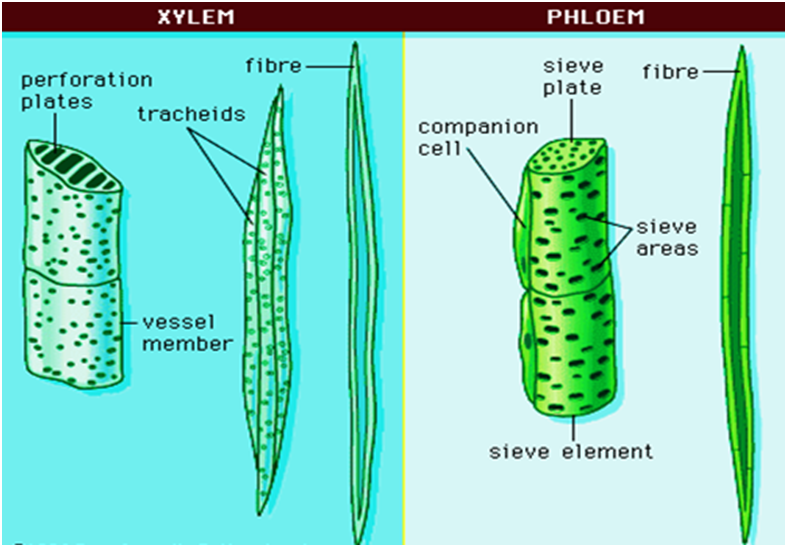
Xylem and Phloem
Similarities between Xylem & Phloem
- Their main function is to carry food and water in the plant.
- Both have a vascular bundle which is a conductive tissue in plants that helps them survive in different environmental conditions.
Xylem
Xylem is made up of dead cells having a thick cell lining. It consists of following elements-
- Tracheids and Vessels – They have broad tubular structure so that we can allow transportation of food and water in the plants vertically.
- Xylem Parenchyma – It stores food and helps in transportation of water horizontally in the plants.
- Xylem Fibers – They support transportation
Phloem
Phloem is made up of living cells and it allows the movement of food from leaves to other parts of the plant. It has the following elements –
Sieve Tubes – Broad shaped cells with porous walls
- Companion Cells – They facilitate the functions of the sieve tubes
- Phloem Fibers – Provide flexibility to the phloem
- Phloem Parenchyma – Stores starch and proteins
|
|
Xylem |
Phloem |
|
Made of |
Dead Cells |
Living Cells |
|
Cell wall thickness |
Thick |
Thin |
|
Cell wall material |
Lignin (rigid) |
Celluloses |
|
Permeability |
Impermeable |
Permeable |
|
Cytoplasm |
None |
Cytoplasm lining |
|
Transports… |
Water & minerals |
Food |
|
Carried to…. |
Leaves |
Growing parts & storage organs |
|
Direction of flow |
Upwards |
Up & down |
|
Tissue alos has … |
Fibres |
Companion cells |

 ACERISE INDIA
ACERISE INDIA
 Vaishnav Publication
Vaishnav Publication
