- Books Name
- Yash Tyagi Coaching Science Book
- Publication
- ACERISE INDIA
- Course
- CBSE Class 9
- Subject
- Science
Interconversion of States of Matter
You must have noticed that if we keep ice out in kitchen, with time it gets converted into water or when water is heating and you forget to turn the gas knob off, then it keeps boiling and a stage is reached when the vessel gets empty and no water is seen inside. This is due to interconversion of states of matter.
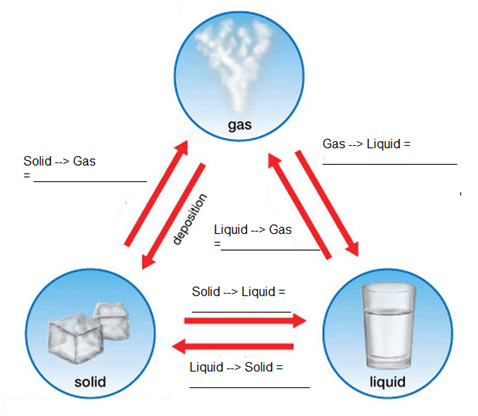
The phenomenon due to which matter changes from one state to another and then back to its original state on altering the conditions of temperature and pressure is called interconversion of states of matter.
The state of the substance can also be changed by heating or by applying pressure.
As you all have LPG cylinders at home or must have seen CNG cylinders installed in cars, these cylinders contain Liquefied Petroleum Gas or Compressed Natural Gas which means that in these cylinders the gases are liquefied by applying pressure. So, keep in mind that on applying pressure the gas can change into liquid. Similarly, on applying pressure, liquid changes into solid.
For example, when pressure is applied on Carbon Dioxide gas, it forms dry ice (Solid state). So, interconversion tells us about the change of one state of matter in to another state.
Solid ↔ liquid ↔ gas
1. The conversion of solid to liquid is called melting and it occurs at fixed temperature called melting point
2. The conversion of liquid to gas is called evaporation and it occurs at fixed temperature called as boiling point
3. The conversion of gas to liquid is called condensation or liquefaction and it occurs at liquefaction point
4. The conversion of liquid to solid is called freezing and it occurs at temperature called freezing point.
5. The conversion of solid liquid gas involves absorption of heat energy
6. And the conversion of gas liquid solid involves release of heat energy
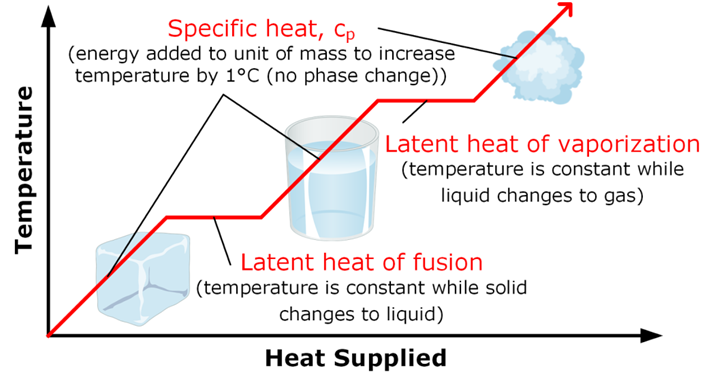
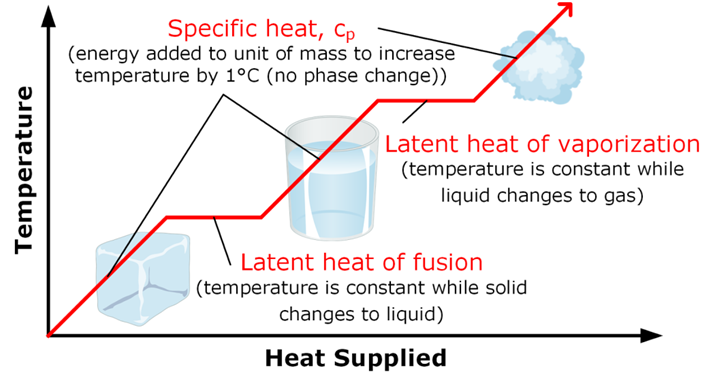
The energy which is required to change the state whether released or absorbed is called latent heat
Latent heat
It is the amount of heat released or absorbed during change of state of a substance.
Solid liquid
Like when we convert Solid to Liquid, heat is supplied and that heat is called latent heat of fusion that is –
Latent Heat of Fusion:
it is the amount of heat required to convert one unit mass of substance from solid to liquid state at its melting point. Example: for ice it is equal to 3.34 x 105 3/Kg
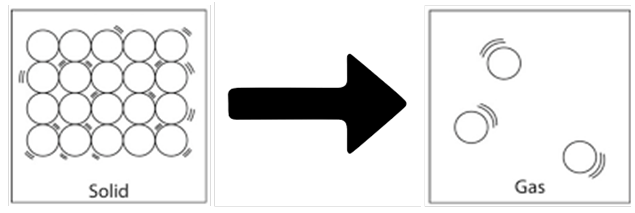
Change of state of solid to liquid on the basis of molecular structure
When we heat any solid substance, the particles gain energy and start vibrating with greater amplitude. Their kinetic energy increases due to which their intermolecular space increases and intermolecular force decreases and it gets converted into liquid state.
Liquid state gaseous state
Boiling or Vaporization: it is the change of liquid state of a substance to gaseous state at boiling point. Boiling Pt. => Is the temperature at which liquid changes to gaseous state on heating. Boiling point of water => 100 oC
Latent heat of Vaporization:
it is the amount of heat required to convert one unit mass of substance from liquid to vapour at its boiling point. For example, for H2O it is equal to 22.6 x 105 J/kg.
Change of state of liquid state to gaseous state on the basis of molecular structure
When we heat any liquid substance, the particles gain energy. As a result, their kinetic energy increases and they starts vibrating with greater amplitude due to which their intermolecular space increases and intermolecular force decreases and they get converted into gaseous state.
Gas Liquid
Condensation: It is the change of gaseous state to liquid state on cooling. This occurs at a temperature below the boiling point of substance
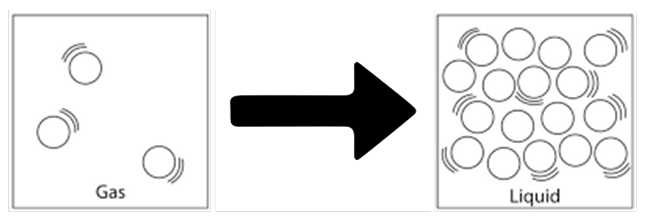
Change of state of gaseous state to liquid state on the basis of molecular structure
It is done by applying pressure and reducing temperature Explanation: When high pressure is applied on gas, distance between particles decreases & particles start attracting each other & gas gets converted in to liquid state.
Solid gas
You must have noticed that the naphthalene balls are used to prevent growth of insects in boxes of beds. With time, these balls disappear. Do you know what is the phenomenon behind this disappearance?
Sublimation: It is the change of solid state directly to gaseous state on heating & vapours back to solid on cooling.
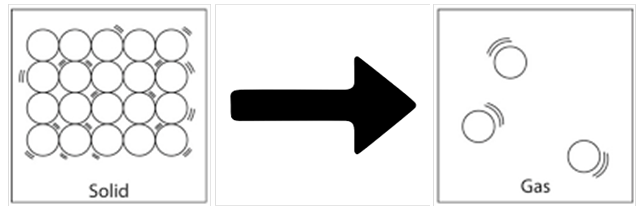
It involves two terms, that is
1. Sublime: A gaseous state that is formed due to sublimation of solid
2. Sublimate: It is the solid that sublimes
Example of Sublimation: Sublimation of Naphthalene Balls
Evaporation
You must have seen that when wet clothes are spread under sun, they dry up or the wheat grains are often dried under the Sun before sending to mill for converting to flour. This is due to the phenomenon of evaporation that is taking place.
Evaporation is the process of change of liquid into vapor at temperature below its boiling point.
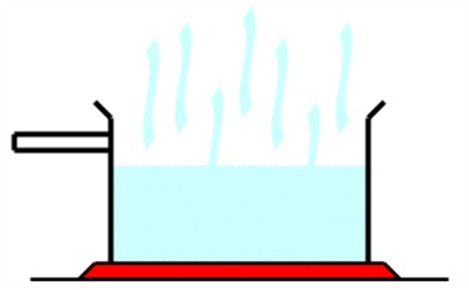
Explanation of Evaporation on the basis of Molecular Structure
During evaporation, the liquid particles are heated or they take the heat energy from the surroundings. When heat is taken by particles, the energy of particles increases due to which they start moving rapidly.
As a result, they collide with one another. In the course of collisions, some particles loose energy and some gain energy. As a result, particles with higher energy overcome their force of attraction and escape into the atmosphere.
Factors on which Evaporation Depends:
- Surface area
- Temperature
- Humidity
- Wind speed

Lets explain the dependence of the phenomenon on these given factors:
1. Surface Area – More is the exposed surface area of any substance more liquid droplets will change to vapor state For xample: Drying of Wet Clothes We have seen that clothes dry faster when they are spread on a line. The reason is that when we spread them, the surface area gets increased, therefore, evaporation gets increased as more and more molecules are exposed.
2. Temperature: Increase in temperature, increases the Kinetic Energy of molecules. They break their force of attraction, hence, escape or evaporate readily. For example: Formation of Water vapor on cup of Hot Tea.It is because as temperature rises, the particles start moving randomly, therefore, evaporation rate is increased. Therefore, when they escape, they also collide with the cup and get condensed.
3. Humidity: More is Humidity less in the Evaporation For example- Clothes dry with difficulty on a humid day: because as humidity is more, that is more vapour in the atmosphere. Due to which the escaping tendency of vapours decreases so as the rate of evaporation decreases.
4. Wind Speed: With increase in speed of wind, evaporation increases. That is the reason why clothes dry faster if there is a windy day. As the speed of wind is high, the liquid particles take up the energy. As a result, their kinetic energy increases and they escape more readily and more easily.
Evaporation Cause Cooling Effect
Evaporation is a surface phenomenon. The particles at the surface having high K.E. break up their force of attraction & form vapours. Since the energy is lost, that means temperature gets lowered and low temperature means cooling effect so, evaporation results in cooling effect
Q. Do you know why we feel more comfortable if we wear cotton clothes in summers?
A. It is because the cotton clothes are very good absorbers of Water. They rapidly absorb sweat and then evaporate taking large amount of heat from our body thereby, giving a cool sensation.

 Science Made Easy
Science Made Easy
 ACERISE INDIA
ACERISE INDIA
