The Fundamental Unit of Life
Introduction of cell
The introduction to cell began back in the year 1655 when a revolutionary observation was made by an English scientist Robert Hooke.
In all the living beings, cells are the basic structural units. We can compare the presence of cells in our body to the bricks in a building. All the bricks are assembled to make a building. Similarly, all the cells are assembled to make the body of an organism.
Thus, it is the basic structural and functional unit of life and all the organisms are made up of cells. The subcellular structures of the cell comprise of the plasma membrane, organelles and in some cases a nucleus as well. As for the size of the cell, it is variable and maybe anything from 1 to 100 micrometre.
Robert Hooke was examining a dried section of the cork tree using a crude light microscope. In this analysis, he observed multiple small chambers which he named the cells.
The first theory was proposed by the German botanist Matthias Jacob Schleiden and the German physiologist Theodore Schwann in 1838. This theory was formalized in the year 1858 by the German researcher Rudolf Virchow by suggesting that all cells arise from pre-existing cells.
Cell Theory
• The cell is the basic functional and structural unit of life. All the living organisms are composed of cells.
• All cells are formed by the division of the already existing cells which in terms of biology means reproduction. Every cell of our body comprises of genetic material which is passed down during the process.
• All the basic physiological and chemical functions i.e. the growth, repair, movement, communication, immunity and digestions are performed inside the cells.
• All the activities of the cell depend mainly on the activities of the subcellular structures that lie within the cell. These subcellular structures comprise of the plasma membrane, organelles and if present, the nucleus.
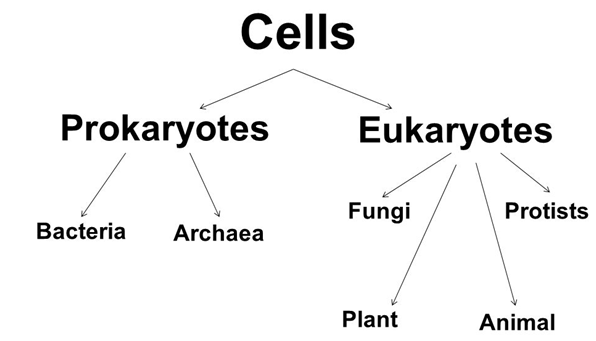
Types of Cells
Broadly, there are two key types of cells i.e., the Prokaryotic Cell and the Eukaryotic Cell. The difference between the two is defined mainly by the presence or the absence of the nuclear membrane.
- Prokaryotic Cell
If a cell has a nuclear material without a nuclear membrane, then it is known as the prokaryotic cell, where ‘pro’ stands for primitive and ‘karyon’ stands for the nucleus. Some of the organisms that have prokaryotic cells include bacteria and the blue-green algae.
- Eukaryotic Cell
If a cell has a nuclear material with a nuclear membrane, then it is known as the Eukaryotic Cell, where ‘EU’ stands for true and ‘karyon’ stands for the nucleus. All the living organisms except bacteria and blue-green algae have Eukaryotic Cells.
- Books Name
- Yash Tyagi Coaching Science Book
- Publication
- ACERISE INDIA
- Course
- CBSE Class 9
- Subject
- Science
Chapter-1
The Fundamental Unit of Life
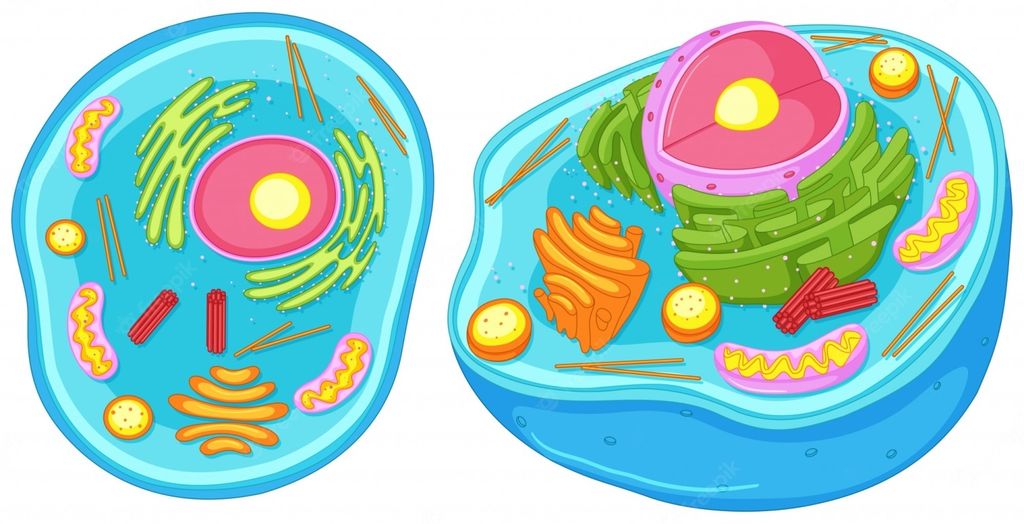
About Cell and Cell Theory
Introduction of cell
As you all know the body of an individual is of complex type. If we study about the detailed structure of the human body or of any lower organism, we will come across many things that makeup the body. But at the smallest level, our body is made up of tiny units called cells. Let us learn about cell in detail.
Cell is often referred as “structural and functional unit of living organisms”. The reason is that the cell is the smallest unit of body and directly or indirectly, it is responsible for functions also. If we study about the hierarchy then we will notice that the level of organization is :
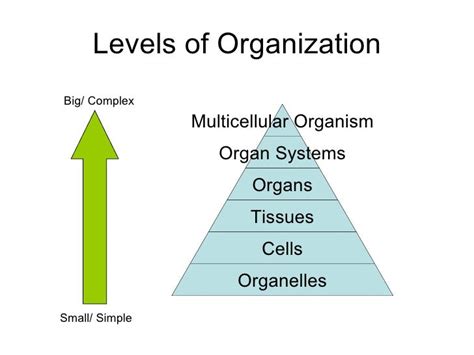
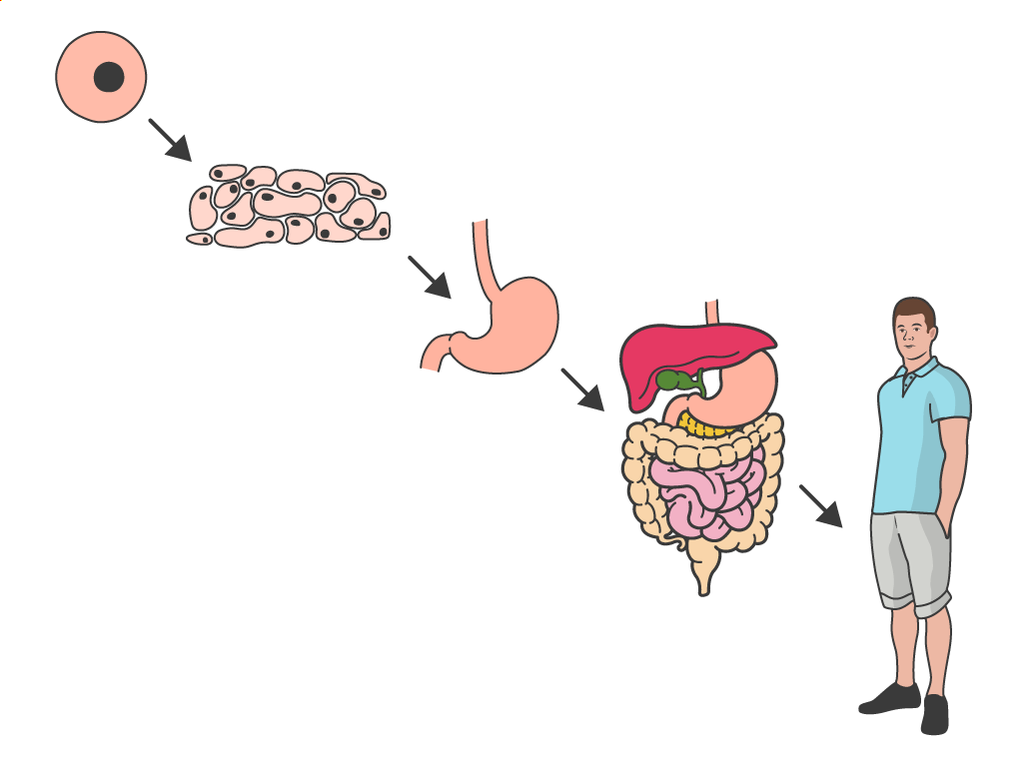
That means that the smallest unit of body is cell.
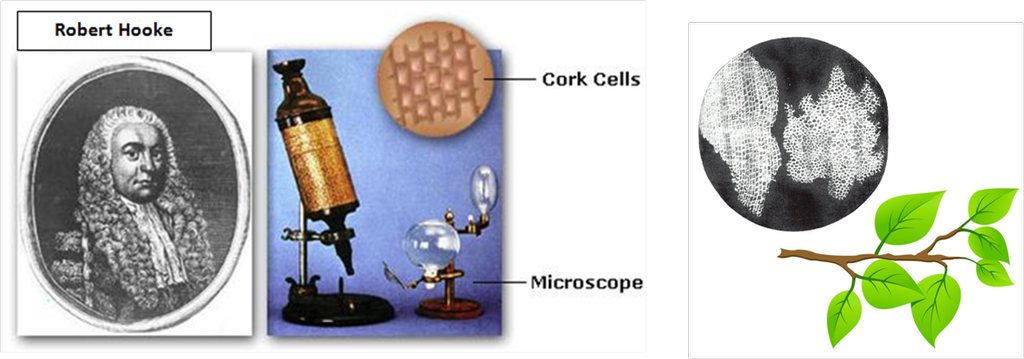
Discovery of cell
The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in a thin slice of cork in 1665. Cork is actually a dead part of tree that is bark of tree .He discovered it with the help of instrument called microscope. This microscope is an instrument that enables us to see those things that can’t be otherwise seen with the help of naked eye. It has the property to magnify the objects. He discovered with the help of instrument that is microscope which was discovered by Anton von Leeuwenhoek.
When he saw the internal structure of cork with the help of microscope it looked like compartments .So, earlier these cells were named as compartments but later on it was replaced by term cell. It was concluded that all the cells have three basic characteristics. –
- They contain plasma membrane: – made up of lipid & proteins
- They contain genes: – Genetic material in form of DNA or RNA containing genes is present.
- They contain metabolic machinery: – Cytoplasm is present which contain organelles like mitochondria etc.
These all arts like plasma membrane, cytoplasm, RNA, DNA etc will be taken in to consideration step wise step. Let us first learn more about cell.
Cell theory
To know more about cell, few scientists sum up their views about cell as cell theory. It was given by volunteers: Sheldon & Schwann. According to this theory: –
- Cell is the structural unit of life.
- Cell is functional unit of life.
- All cells arise from pre-existing cells. Every organism starts life as a single cell. (It was given by R. Virchow)
Types of cells – Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells
There are two main types of divisions of cells depending upon their basic and important difference in their structures. The types are:
- Prokaryotic (primitive cell)
- Eukaryotic (advanced type)
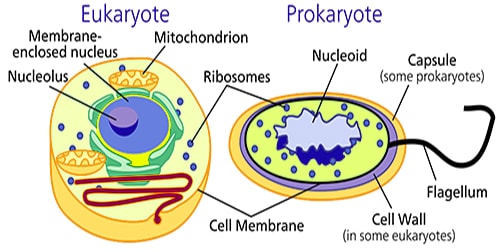
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell: The basic difference between the two is: In prokaryotic, the nuclear material lies naked in cytoplasm that is no special membrane is present that separates it from the cytoplasm. It is present as such in cytoplasm.
In eukaryotic, the nuclear material is well protected and enclosed by special membrane that is nuclear membrane .We can say in it the nucleus is present. Let us some up more difference in them.

Cell shape and Cell size
Now, let’s talk about the cell shape and size. It is seen that cells can be of different shapes and sizes and even their number that make up a body can be different in different living forms as it depends upon the function the cell is going to perform. Accordingly the structures, sizes, shapes are assigned to cells . The shape of a cell may change or fixed.
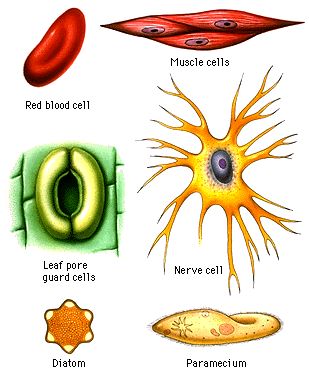
Shape of cells
- The shape can be fixed or can be variable.
- The cells with Variable shape are WBC (white blood cell) and Amoeba.
Please do remember that “the shape of the cell depends upon the function it performs”.
Different Shapes that the cell can have: –
- Spherical => eggs of many animals
- Spindle shaped => smooth muscle fiber
- Elongated => nerve cell
- Branched => cells of skin
- Discoid => RBC.
Size of cell
Sizes also show a lot of variations. We have cell that is too tiny like PPLO to largest cell in the form of an ostrich egg
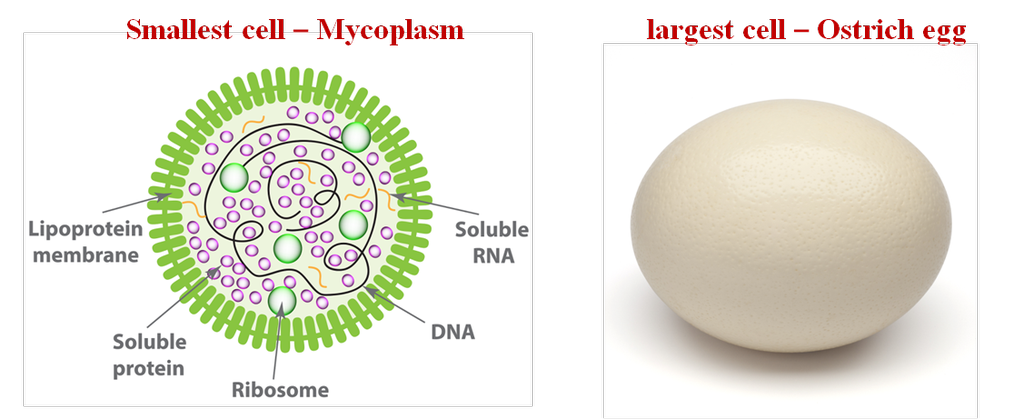
In Human body the smallest cell is: – RBC and longest /largest is Nerve cell .Nerve cell is designed accordingly to function it performs. As we cleared above also shapes are in accordance to function. Like, nerve cell help in transmission of impulse. So, it has to be long and branched.
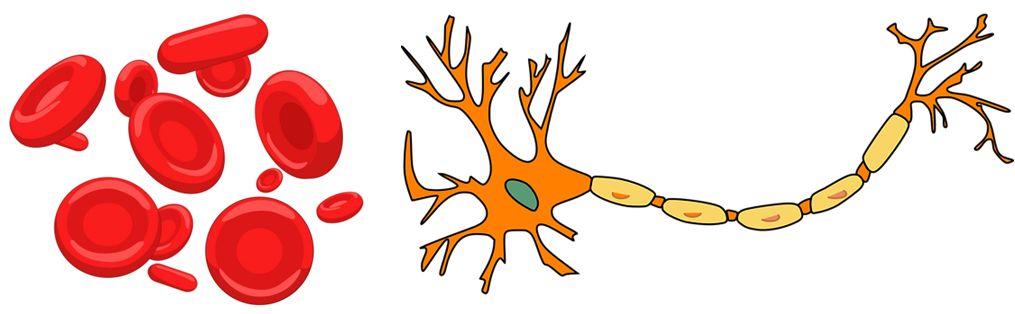
Cell number
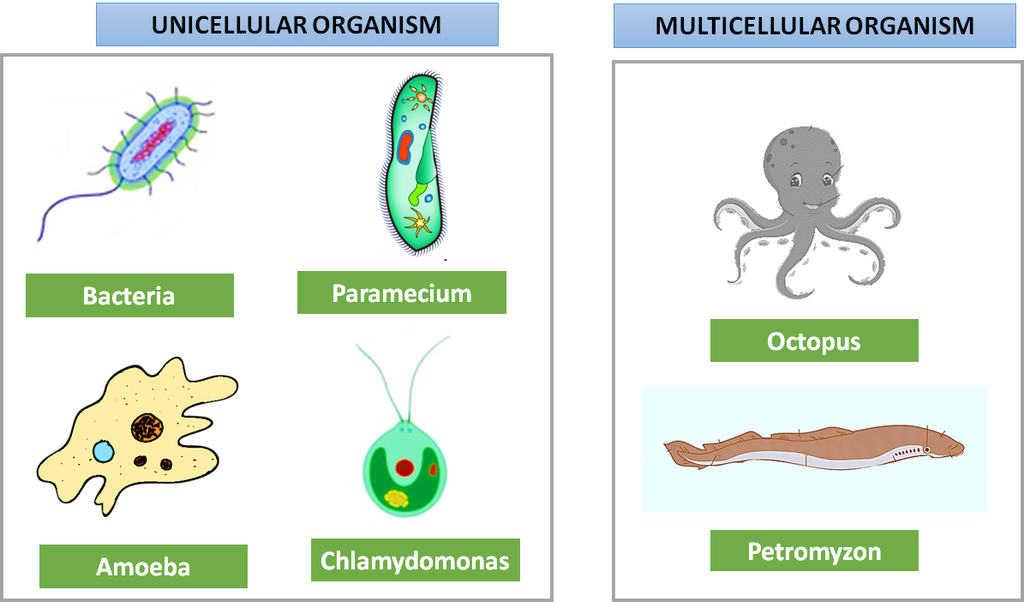
The number of cells also varies from species to species. There can be organism made up of one cell and there can also be organism like us whose body is made up of many cells. Depending upon the number of cells present, cells are of two types:
- Unicellular
- Multicellular
Unicellular organisms – are single celled body (example Amoeba).
Multicellular organisms – are multi-celled body that is many cells (example Man)
Structure of cell
If we look at the structure of cell we have already seen that all cells have three things in common:
- Cell membrane
- Nuclear material
- Metabolic machinery.
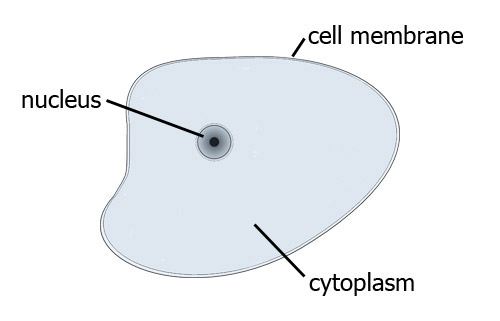
Let us study about cell membrane first:

 Vaishnav Publication
Vaishnav Publication
 ACERISE INDIA
ACERISE INDIA
