- Books Name
- Yash Tyagi Coaching Science Book
- Publication
- ACERISE INDIA
- Course
- CBSE Class 9
- Subject
- Science
Chapter-3
Atoms and Molecules
Atoms and Molecules Introduction
We come across different things around us like chair, table, etc. and all the things that surround us have mass and weight. They all constitute matter. Matter is anything that occupies space and has mass. Matter is made up of small particles called atoms.
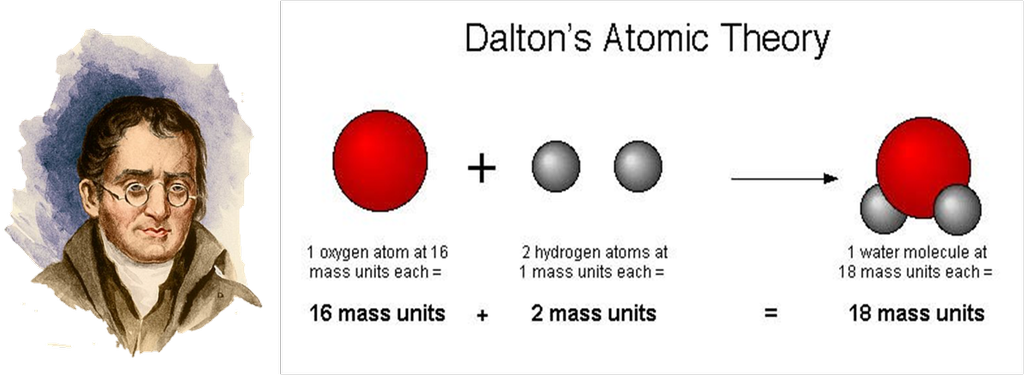
Dalton's atomic Theory
Dalton’s atomic theory
According to Dalton’s Atomic Theory,
- All matter is made up of small particles called atoms.
- Atom is invisible.
- Atom is indivisible.
- Atoms of an element are alike in all aspects.
- Atoms of different elements combine in fixed whole number ratios to form compounds.
Atoms can neither be created nor destroyed.
Drawbacks of Dalton’s Atomic Theory were as follows
1. According to Dalton, an atom is indivisible but later on it was proved that atom can be subdivided into electrons, protons and neutrons.
2. Atoms of an element can somehow differ from each other.
So, these drawbacks led to the failure of Dalton’s theory of an atom. We also know that a lot of chemical reactions take place in our day to day life like making of tea, changing milk to curd, making cheese from milk and lots more. All the chemical reactions taking place obey certain set of laws. Let us study these chemical reactions and the rules that they obey.
Chemical reaction
The process by which some substances react to form a new substance. The substances which react are called reactants and the new ones formed are called products.
For example: A+B C+D
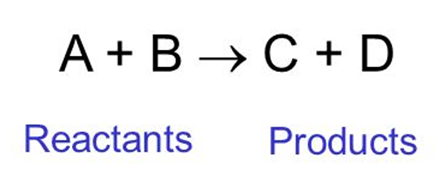
In this, A and B are reactants and C and D are called products.
For example: when we make tea, we add sugar, tea, milk and water. We mix them and heat the mixture. The result is that we get a new substance that is tea.
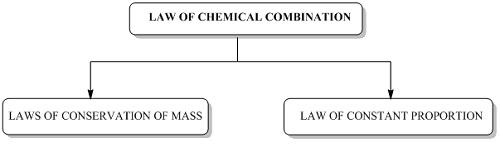
Laws of chemical combination
There are certain sets of laws that are obeyed by all chemical reactions. These laws are given by Lavoisier & Joseph. Let us study them in detail.
Law of conservation of mass
According to this law, ?matter can not be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.? That is, it always remains constant.
Like, in all chemical reactions the total mass of products is equal to the total mass of reactants.
For example:- 2H2 + O2 à 2 H2O
(Reactants) (Product)
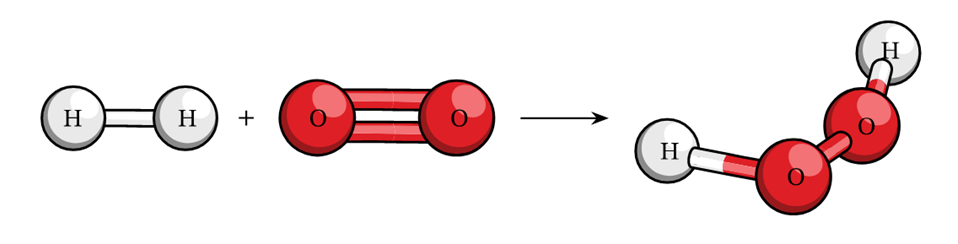
=> 4 + 2 x 16.32 2 x 18 => 36 g = 36 g.
This example shows that the total mass of reactants is equal to the total mass of products formed which is in accordance with the law.
Law of constant proportions: (Law of definite proportion)
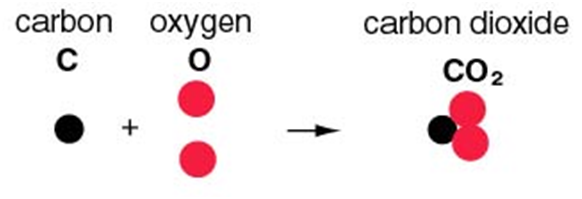
According to it, in a chemical substance, the same elements are always present in a definite proportion by mass and volume irrespective of the method of preparation involved. For example, In Co2 molecule, the elements that form it remain the same that is carbon and oxygen and also, the ratio of C and O remains the same that is 3:8 by mass (i.e. 12.32) and 1 : 2 by volume.
Atom
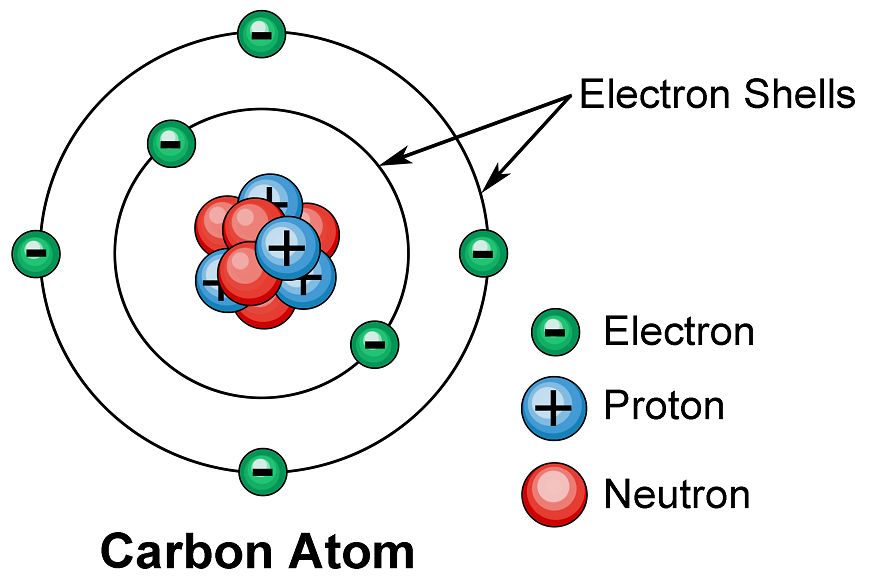
It is the smallest particle of an element which may as may not have an independent existence. An atom is very small in size. The size is measured in unit of nm (nanometer). 1nm = 10^-9 m. Hydrogen atom is the smallest of all. Its size is only 10-10 nm. Atoms are represented by symbols (given by Berzelius).

 Science Made Easy
Science Made Easy
 ACERISE INDIA
ACERISE INDIA
