Energy
Energy of a body is defined as the capacity or ability of a body to do work.
The SI unit of energy is joule (J)
Forms of energy
There are various forms of energy in the nature, few of them are mechanical energy (potential energy + kinetic energy) heat energy, chemical energy and light energy.
1. Mechanical energy
Mechanical energy includes kinetic energy and potential energy.
a) Kinetic energy
The energy possessed by a body by the virtue of its motion is called kinetic energy.
Kinetic energy possessed by a body can be calculated by
EK=1/2 mv2
m = mass of body
V = velocity of body
Derivation of kinetic energy
Let us consider an object lying on a frictionless surface having mass ‘m’
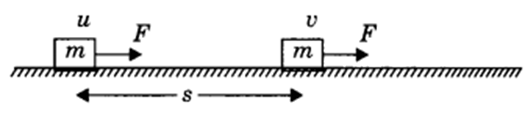
A force of constant magnitude F is acting on the body. Here initial velocity of the body is u and final velocity is v. As there is no dissipative forces, work done on the body will be stored in the form of change in kinetic energy.
W=Fs
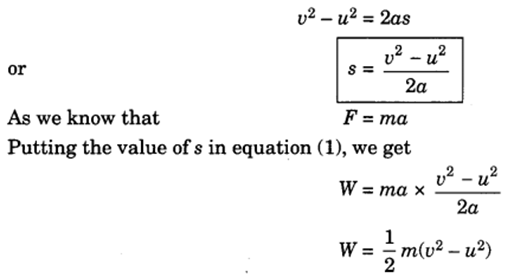
If the object is starting from a stationary position u = 0, then
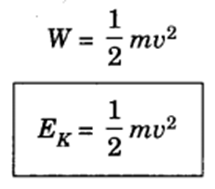
Factors affecting Kinetic energy
• Mass
• Velocity
• Momentum
b) Potential energy
The energy possessed by a body due to its position or configuration is called potential energy.
(i) Gravitational potential energy
Potential energy at any height (h) from a reference can be calculated by formula
Ep = mgh
where, m = mass of object
v = height from reference
The gravitational potential energy of an object at a point above the ground is defined as the work done in raising it from the ground to that point against gravity.
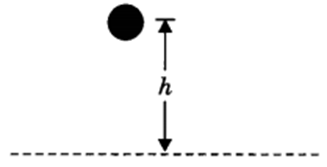
Derivation of potential energy
When work is done on the body, the work is stored in the form of energy. Consider an object of mass, m. Let it be raised through a height, h from the ground. A force is required to do this. The minimum force required to raise the object is equal to the weight of the object, mg. The object gains energy equal to the work done on it. Let the work done on the object against gravity be W.
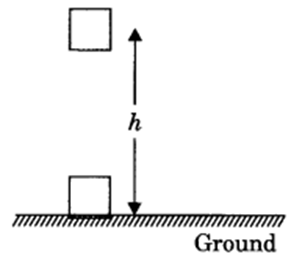
W = force x displacement
= mgh.
Since work done on the object is equal to mgh, an energy equal to mgh units is gained by the object. This is the potential energy (Ep) of the object.
Ep = mgh

 Science Made Easy
Science Made Easy
