Buoyancy
• Whenever an object is immersed in a liquid, the liquid exerts a buoyant force or upthrust in the opposite direction of the gravitational force. This is also called the Force of Buoyancy.
• It depends upon the density of the fluid.
• Therefore, an object is able to float in water when the gravitational force is less than the buoyant force.
• Similarly, an object sinks into the water when the gravitational force is larger than the buoyant force.
Archimedes principle
• According to the Archimedes principle, whenever an object is immersed in a liquid (fully or partially), the liquid exerts an upward force upon the object. The amount of that force is equivalent to the weight of the liquid displaced by the object.
Why does an object sink or float on water?
• An object can sink or float on water based on its density with respect to water. The density is defined as mass per unit volume.
• Objects having a density less than water float in it. For Example, Cork flows in water because its density is lower than that of water.
• Objects that have a density higher than water sink in it. For Example, Iron nail sinks in water because the density of iron is more than water's density.
Thus, we can conclude that buoyancy depends upon:
The density of the liquid
The volume of the object (as the volume of object increases, its density decreases and vice-versa
Application of Archimedes Principle:
• In evaluating relative density
• In designing ships and submarines
• In making lactometers and hydrometers
Relative Density
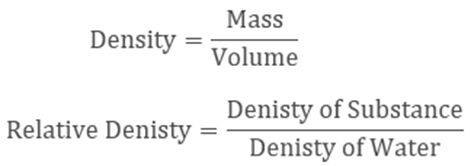

 Science Made Easy
Science Made Easy
