- Books Name
- Yash Tyagi Coaching Science Book
- Publication
- ACERISE INDIA
- Course
- CBSE Class 9
- Subject
- Science
Molecular Theory of Matter
Theory of molecular structure of matter
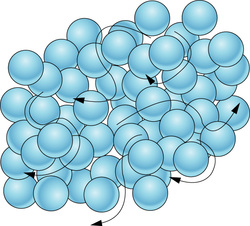
According to this theory,
- Matter is made up of small particles called molecules.
- They are in a state of continuous motion. Due to this, we can say that they possess K.E.
- K.E. Increases with ↑ se in temperature.
- K.E. Is maximum in gases and least in solids.
- The space between molecules is called intermolecular space which is found to be least in solids and maximum in gases.
- There is a force that exists between particles of matter and is called intermolecular force
- Intermolecular force ↓ ses with increase in Intermolecular space
Terminology involved
Before we start with more properties of matter let us know some terms which will be used in this chapter.
- Matter: Anything that occupies space is matter.
- Material: The term is used to describe a particular kind of matter.
Materials are of two Types:
- Homogenous
- Heterogeneous

Homogeneous Materials: Are those that have the same composition and same properties throughout the sample. For example, if you take water in a glass and add salt to it and stir it. It will result in formation of a mixture that has same properties and uniform composition (that is no distinct layers are seen). They mix thoroughly. If you take sample from any part of that mixture, it will show similar properties.
Heterogeneous Materials: are those that have different composition and different properties in different parts of the sample. For example, if we take sand in water, then we will see that inspite of stirring, it does not dissolve in water. It will settle at the bottom of the container and few particles will be seen floating in the water. If you take a sample from any part of it, it will show different properties.
Molecule: Is a term used for particular type of matter that has independent existence in nature like oxygen molecule, carbon dioxide molecule, water molecule, etc.
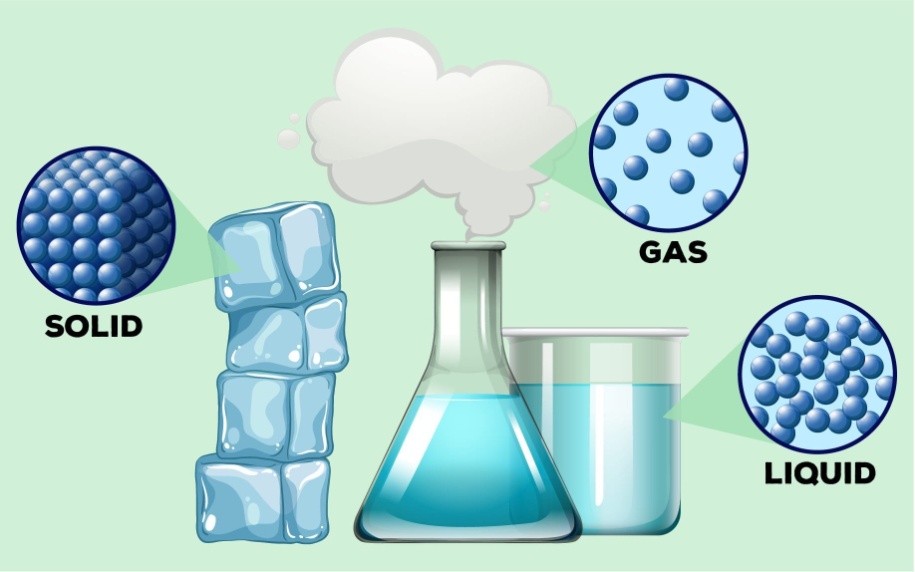
Molecular structures and properties of solids, liquids and gases
Now let us do Physical Classification of Matter: this classification is done on the basis of physical properties of matter, that is the properties that can be seen or felt by touching, looking etc.
According to it, matter is divided into 3 types:
- Solids
- Liquids
- Gases
Solids
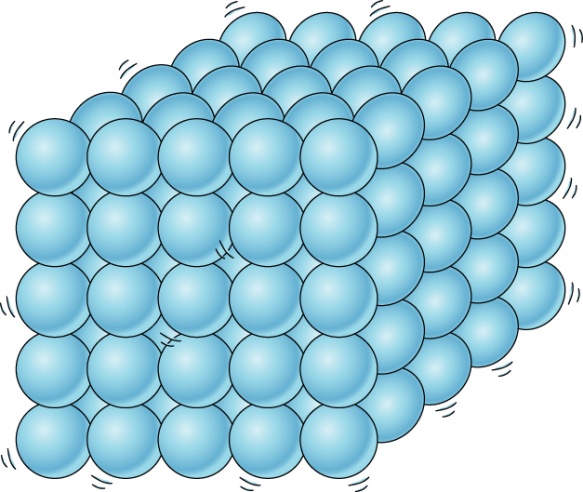
if you take any solid let’s say we consider wood, what properties can you find in it by looking at it.
- First property that we can make out is: That it has fixed shape and volume: we realize this because when wood is kept on the floor or any surface, it occupies definite space.
- Another property that we notice is: It is not compressible: if we it try to squeeze it or change its shape, we cannot do so. This is probably due to the reason that there is no space between solid particles and in order to compress it, there should be space between particles. This is because when we apply force, the particles fill those empty spaces and come closer.
- Another property: They don’t need container to hold them: we don’t have to put an almirah or any other solid in a container. it can be kept as such on the surface.
- They do not flow: This is because when wood is kept at a place, it remains at the same place. It doesn’t flow or move on its own.
- Their diffusion tendency is nil: it is seen that wood doesn’t move from one side of room to another side of room on its own as the particles do not have that much energy that they keep on moving.
Let us try to understand solids on the basis of theory of molecular structure:
Explanation of Solids on the basis of Molecular Structure
If we see any solid we observe that in solids, particles are tightly packed. They are very closely packed due to which there is hardly any space between particles or we can say that intermolecular spaces are very less and when particles are closer, that means the intermolecular forces of attraction are stronger. As a result, solids have fixed shape, volume and can’t be compressed.
Now do you understand that why wood or any other solid doesn’t flow or compress or diffuse and why they possess high density.
Liquids
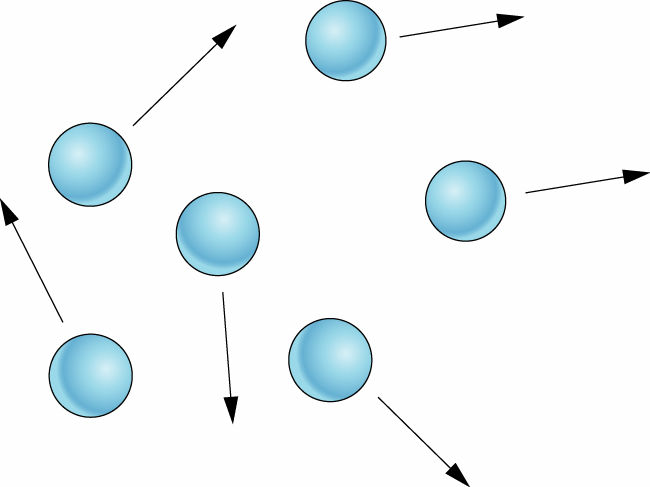
Let’s sum up the properties of gases in comparison to solids and liquids
- They have neither fixed shape nor fixed volume
- They are highly compressible
- They can flow, diffuse to great extent
- They have very very low density
- They can fill the entire space
Explanation of gases on the basis of molecular structure
In gases the particles are very far apart. Due to this, they have high kinetic energy and keep on moving randomly. As a result, the intermolecular spaces are very large and intermolecular forces are almost nil.

 Science Made Easy
Science Made Easy
 ACERISE INDIA
ACERISE INDIA
