1. Dalton's atomic Theory
Chapter 3
Atoms & Molecules
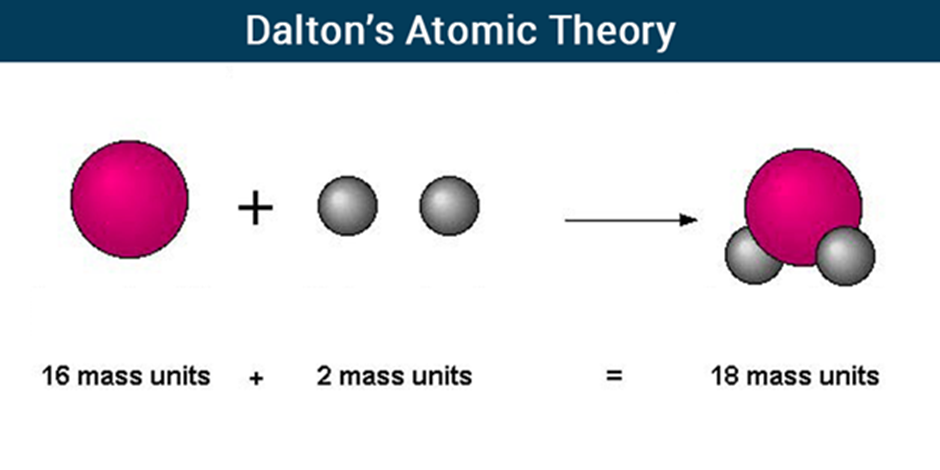
Dalton’s Atomic Theory
The matter is made up of indivisible particles known as atoms.
The properties of all the atoms of a given element are the same, including mass. This can also be stated as all the atoms of an element have identical mass and chemical properties; atoms of different elements have different masses and chemical properties.
Atoms of different elements combine in fixed ratios to form compounds.
Atoms are neither created nor destroyed. The formation of new products (compounds) results from the rearrangement of existing atoms (reactants) in a chemical reaction.
The relative number and kinds of atoms are constant in a given compound.
Laws of Chemical Combination
Given by Lavoisier and Joseph L. Proust as follows:
Law of conservation of mass
According to the law of conservation of mass, matter can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. It remains conserved.
Mass of reactants will be equal to the mass of products.
Law of constant proportions
A pure chemical compound contains the same elements combined together in a fixed proportion by mass is given by the law of definite proportions.
For e.g., If we take water from a river or from an ocean, both have oxygen and hydrogen in the same proportion.
Atom
Atoms are the smallest particles of an element which can take part in a chemical reaction.
Size of an atom: atomic radius is measured in nanometres.
The atomic symbol has three parts: -
The symbol X: the usual element symbol
The atomic number A: equal to the number of protons
The mass number Z: equal to the total number of protons and neutrons in an element.
2. IUPAC and atomic Symbols
Atom
Atoms are the smallest particles of an element which can take part in a chemical reaction.
Size of an atom: atomic radius is measured in nanometres.
The atomic symbol has three parts: -
The symbol X: the usual element symbol
The atomic number A: equal to the number of protons
The mass number Z: equal to the total number of protons and neutrons in an element.
Atomic Mass
Atomic mass and atomic mass unit
Atomic mass is the total of the masses of the electrons, neutrons, and protons in an atom, or in a group of atoms, the average mass.
Mass of an atomic particle is called the atomic mass.
This is commonly expressed as per the international agreement in terms of a unified atomic mass unit (AMU).
It can be best defined as 1/12 of the mass of a carbon -12 atom in its ground state.
Molecule
It is the smallest particle of an element or a compound which can exist independently.
• Molecules of an element constitute the same type of atoms.
• Molecules may be monoatomic, diatomic or polyatomic.
• Molecules of compounds join together in definite proportions and constitute a different type of atoms.
3. Compound
Atomicity
The number of atoms constituting a Molecule is known as its atomicity.
Compounds
A pure substance made up of two or more elements chemically combine together in a fixed ratio under fixed condition is called compound. Example: Calcium carbonate, Common salt, Sugar.
Properties of compound
1.Compounds can be separated into the constituent only by chemical methods.
2. Properties of compound differ from the properties of their constituents.
3. During the formation of a compound energy is absorbed or released.
4. The compound are homogeneous.
Valency
The combining capacity of an element is known as its valency. Valency is used to find out how the atom of an element will combine with the atom of another element to form a chemical compound.
(Every atom wants to become stable, to do so it may lose, gain or share electrons.)
• If an atom consists of 1, 2 or 3 electrons in its valence shell then its valency is 1, 2 or 3 respectively,
• If an atom consists of 5, 6 or 7 electrons in the outermost shell, then it will gain 3, 2 or 1 electron respectively and its valency will be 3, 2 or 1 respectively.
• If an atom has 4 electrons in the outermost shell than it will share this electron and hence its valency will be 4.
• If an atom has 8 electrons in the outermost electron and hence its valency will be 0.
Ions
An ion is an electrically charged atom or group of atoms.
An ion is formed by the loss or gain of electrons by an atom, so it contains an unequal number of electrons and protons.
There are two types of ions:
Cation: A positively charged ion is known as cation.
For Ex: Na+, Mg2+
A cation is formed by the loss of one or more electrons by an atom.
Na – e– ——–>Na+
Z=11 Z=10
2,8,1 2,8
K, L, M K, L
Mg – e– ——–> Mg2+
Z=12 Z=10
2,8,2 2,8
K,L,M K,L
Anion: A negatively charged ion is known as anion.
For Ex: Cl–, O2-
An anion is formed by gain of one or more electron by an atom.
Cl + e– ——–> Cl–
Z=17 Z=18
2,8,7 2,8,8
K, L, M K, L, M
O + e– ———> 02-
Z=8 Z=10
2,6 2,8
K, L K, L
Radicals
An atom or group of atoms having a charge, i. e. either negative or positive, on it.
The radicals having positive charge are called cations.eg. Sodium ion.
The radicals having negative charge are called anions. eg. Chloride ion.
4. Chemical Formula
Chemical Formulae
Rules:
(i) The valencies or charges on the ion must balance.
(ii) Metal and non-metal compound should show the name or symbol of the
metal first.
e.g., Na+ Cl– → NaCl
(ii) If a compound consists of polyatomic ions. The ion is enclosed in a bracket before writing the number to indicate the ratio.
e.g., [SO4]2- → polyatomic radical
H1+ SO42- → H2SO4
Molecular Mass
It is the sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms in a molecule of the substance. It is expressed in atomic mass unit (u).
Formula Unit Mass
It is the sum of the atomic masses of all atoms in a formula unit of a compound. The constituent particles are ions.
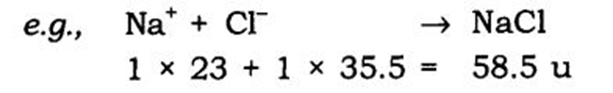
Mole Concept
Definition of mole: It is defined as one mole of any species (atoms, molecules, ions or particles) is that quantity in number having a mass equal to its atomic or molecular mass in grams.
1 mole = 6.022 x 1023 in number
Molar mass = mass of 1 mole → is always expressed in grams and is also known as gram atomic mass.
l u of hydrogen has → 1 atom of hydrogen and 1g of hydrogen has → 1 mole of hydrogen
= 6.022 x 1023 atoms of hydrogen.

 Science Made Easy
Science Made Easy
 ACERISE INDIA
ACERISE INDIA
