CHAPTER -4
Linear equation in two variables
Linear Equations
Linear equations are equations of the first order. The linear equations are defined for lines in the coordinate system. When the equation has a homogeneous variable of degree 1 (i.e. only one variable), then it is known as a linear equation in one variable. A linear equation can have more than one variable. If the linear equation has two variables, then it is called linear equations in two variables and so on. Some of the examples of linear equations are 2x – 3 = 0, 2y = 8, m + 1 = 0, x/2 = 3, x + y = 2, 3x – y + z = 3. In this article, we are going to discuss the definition of linear equations, standard form for linear equation in one variable, two variables, three variables and their examples with complete explanation.
Linear Equation Definition
An equation is a mathematical statement, which has an equal sign (=) between the algebraic expression. Linear equations are the equations of degree 1. It is the equation for the straight line. The solutions of linear equations will generate values, which when substituted for the unknown values, make the equation true. In the case of one variable, there is only one solution. For example, the equation x + 2 = 0 has only one solution as x = -2. But in the case of the two-variable linear equation, the solutions are calculated as the Cartesian coordinates of a point of the Euclidean plane.
Below are some examples of linear equations in one variable, two variables and three variables:
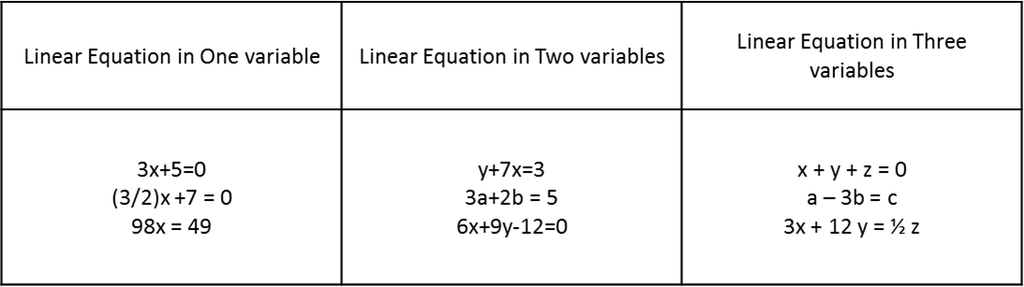
Forms of Linear Equation
The three forms of linear equations are
- Standard Form
- Slope Intercept Form
- Point Slope Form
Now, let us discuss these three major forms of linear equations in detail.
Standard Form of Linear Equation
Linear equations are a combination of constants and variables. The standard form of a linear equation in one variable is represented as
ax + b = 0, where, a ≠ 0 and x is the variable.
The standard form of a linear equation in two variables is represented as
ax + by + c = 0, where, a ≠ 0, b ≠ 0 , x and y are the variables.

 ABCD CLASSES
ABCD CLASSES
