- Books Name
- ABCD CLASSES Mathematics Book
- Publication
- ABCD CLASSES
- Course
- CBSE Class 9
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Surface Areas and Volume
Surface area and volume are calculated for any three-dimensional geometrical shape. The surface area of any given object is the area or region occupied by the surface of the object. Whereas volume is the amount of space available in an object.
In geometry, there are different shapes and sizes such as spheres, cubes, cuboids, cones, cylinders, etc. Each shape has its surface area as well as volume. But in the case of two-dimensional figures like squares, circles, rectangles, triangles, etc., we can measure only the area covered by these figures and there is no volume available. Now, let us see the formulas of surface areas and volumes for different 3d-shapes.
What is Surface Area?
The space occupied by a two-dimensional flat surface is called the area. It is measured in square units. The area occupied by a three-dimensional object by its outer surface is called a surface area. It is also measured in square units.
Generally, Area can be of two types:
(i) Total Surface Area
(ii) Curved Surface Area/Lateral Surface Area
Total surface area
Total surface area refers to the area including the base(s) and the curved part. It is the total of the area covered by the surface of the object. If the shape has a curved surface and base, then the total area will be the sum of the two areas.
Curved surface area/Lateral surface area
Curved surface area refers to the area of only the curved part of the shape excluding its base(s). It is also referred to as lateral surface area for shapes such as a cylinder.
What is Volume?
The amount of space, measured in cubic units, that an object or substance occupies is called volume. Two-dimensional doesn’t have volume but has area only. For example, the Volume of the Circle cannot be found, though the Volume of the sphere can be. It is so because a sphere is a three-dimensional shape.
Surface Area and Volume Formulas
Below given is the table for the calculating Surface area and Volume for the basic geometrical figures:
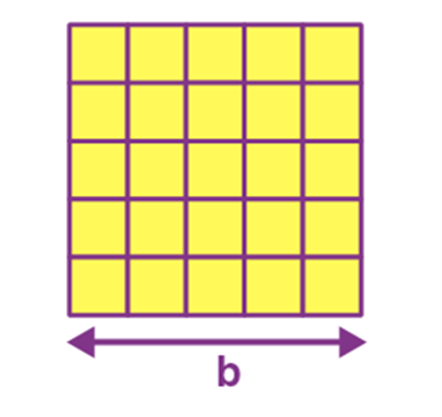
Name: Square
Perimeter: 4a
Total Surface Area: a2
Curved Surface Area/Lateral Surface Area: —
Volume: ---
Figure: -
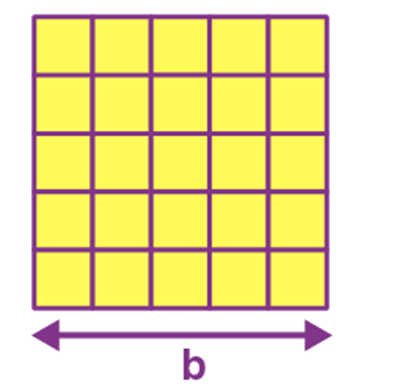
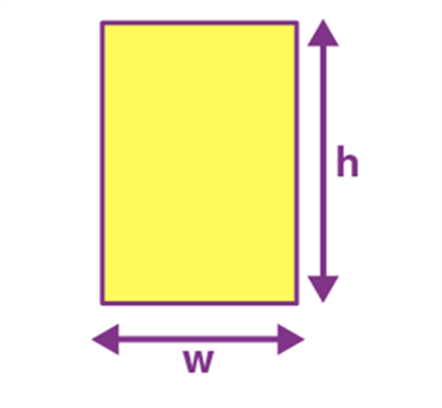
Name: Rectangle
Perimeter: 2(w+h)
Total Surface Area: w.h
Curved Surface Area/Lateral Surface Area: —
Volume: ---
Figure: -
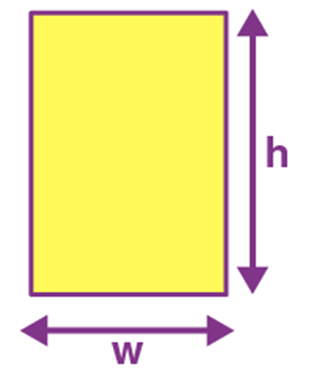
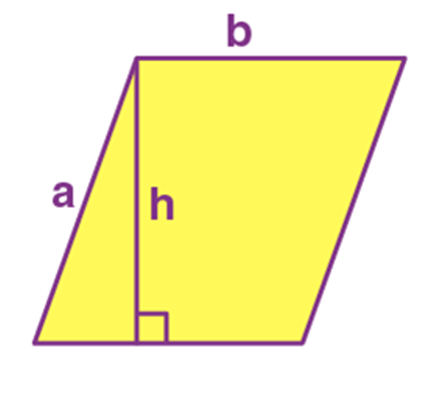
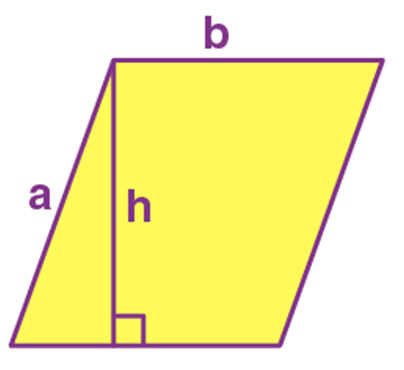
Name: Parallelogram
Perimeter: 2(a+b)
Total Surface Area: b.h
Curved Surface Area/Lateral Surface Area: —
Volume: ---
Figure: -
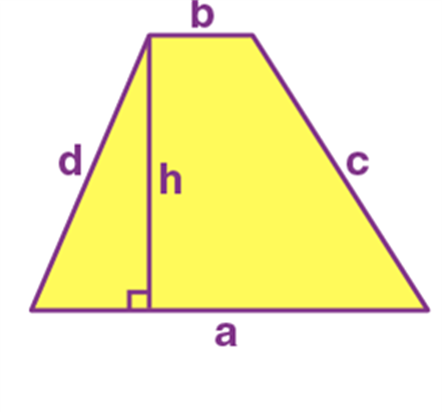
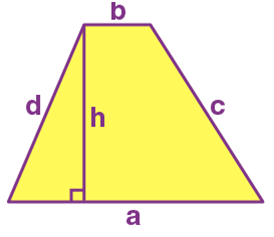
Name: Trapezoid
Perimeter: a+b+c+d
Total Surface Area: 1/2(a+b).h
Curved Surface Area/Lateral Surface Area: —
Volume: ---
Figure: -
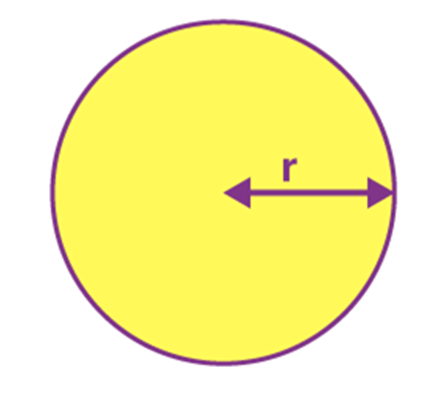
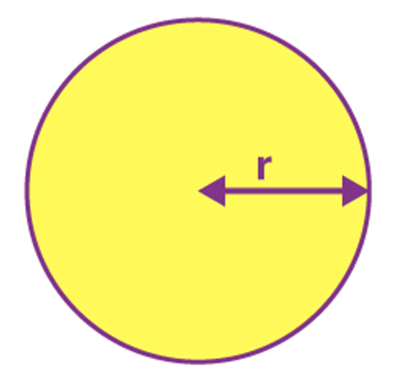
Name: Circle
Perimeter: 2 π r
Total Surface Area: π r2
Curved Surface Area/Lateral Surface Area: —
Volume: ---
Figure: -
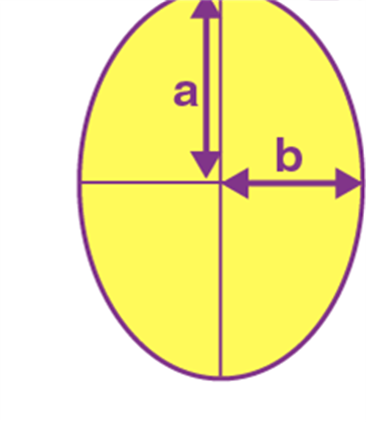
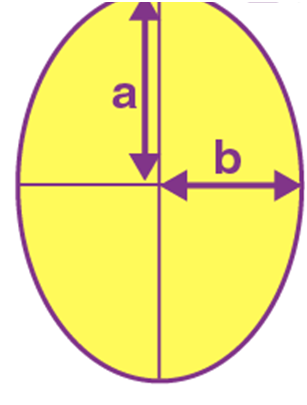
Name: Ellipse
Perimeter: 2π√(a2 + b2)/2
Total Surface Area: π a.b
Curved Surface Area/Lateral Surface Area: —
Volume: ---
Figure: -
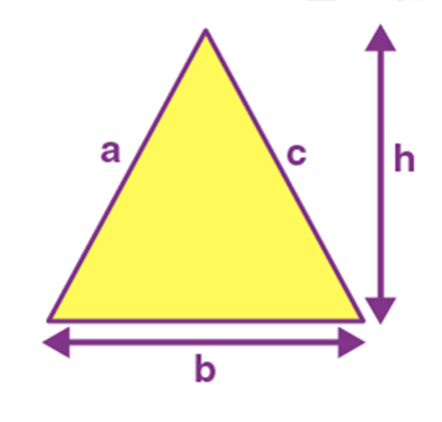
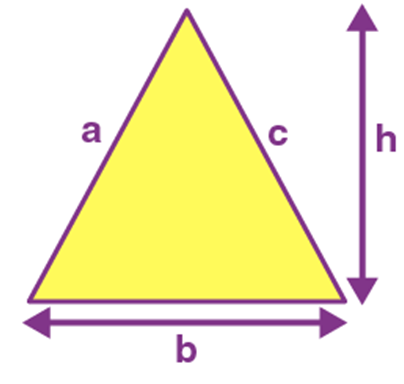
Name: Triangle
Perimeter: a+b+c
Total Surface Area: 1/2 * b * h
Curved Surface Area/Lateral Surface Area: —
Volume: ---
Figure: -
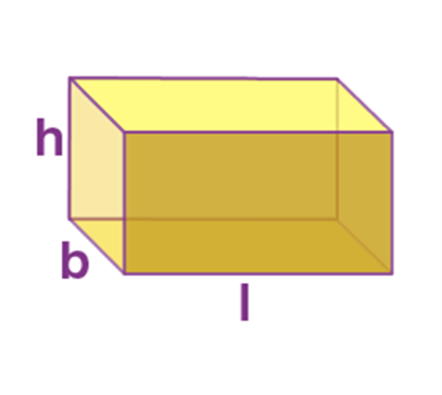
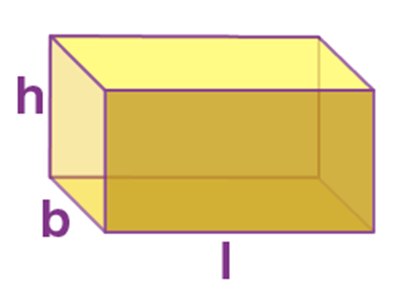
Name: Cuboid
Perimeter: 4(l+b+h)
Total Surface Area: 2(lb+bh+hl)
Curved Surface Area/Lateral Surface Area: 2h(l+b)
Volume: l * b * h
Figure: -
Name: Cube
Perimeter: 6a
Total Surface Area: 6a2
Curved Surface Area/Lateral Surface Area: 4a2
Volume: a3
Figure: -
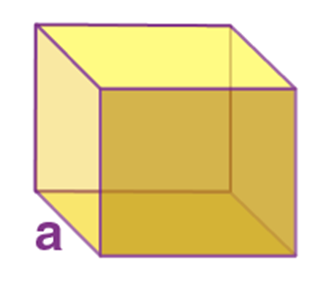
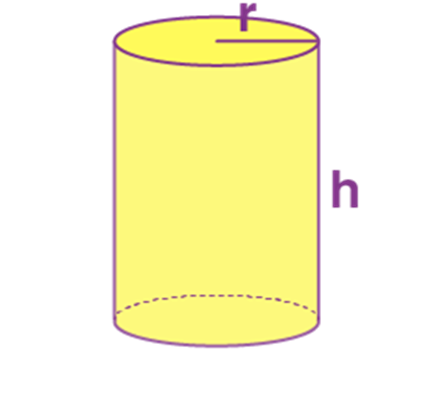
Name: Cylinder
Perimeter: ------
Total Surface Area: 2 π r(r+h)
Curved Surface Area/Lateral Surface Area: 2πrh
Volume: π r2 h
Figure: -
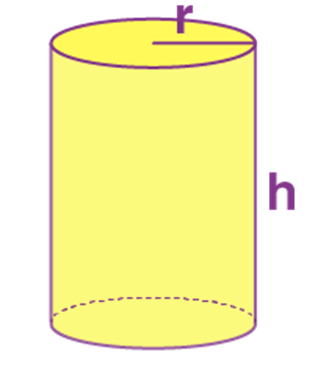
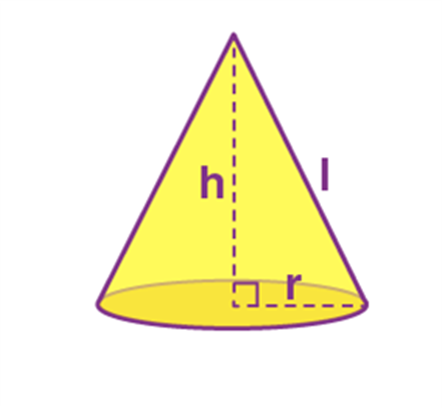
Name: Cone
Perimeter: -----
Total Surface Area: π r(r+l)
Curved Surface Area/Lateral Surface Area: π r l
Volume: 1/3π r2 h
Figure: -
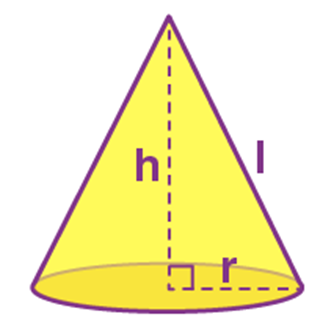
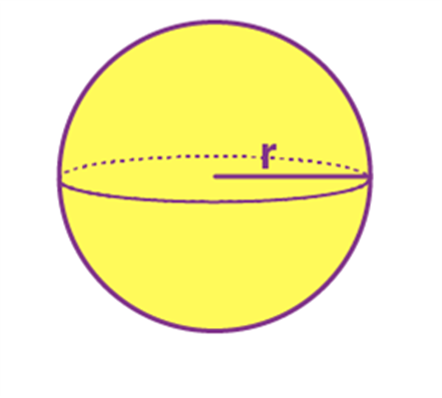
Name: Sphere
Perimeter: ------
Total Surface Area: 4 π r2
Curved Surface Area/Lateral Surface Area: 4π r2
Volume: 4/3π r3
Figure: -
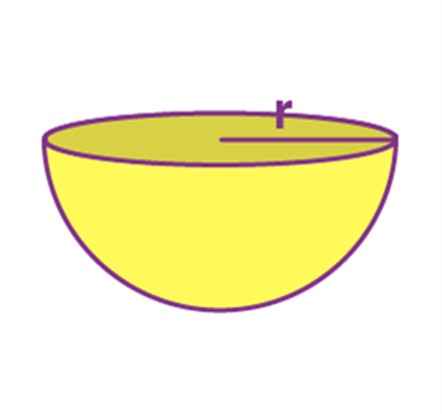
Name: Hemisphere
Perimeter: ------
Total Surface Area: 3 π r2
Curved Surface Area/Lateral Surface Area: 2 π r2
Volume: 2/3π r3
Figure: -
Surface Area of Cube and Cuboid
Cube and cuboid are three-dimensional shapes that consist of six faces, eight vertices and twelve edges. The primary difference between them is a cube has all its sides equal whereas the length, width and height of a cuboid are different. Both shapes look almost the same but have different properties. The area and volume of a cube, cuboid and also cylinder differ from each other.
In everyday life, we have seen many objects like wooden boxes, a matchbox, a tea packets, a chalk box, a dice, a book, etc. All these objects have a similar shape. All these objects are made of six rectangular planes or square planes. In mathematics, the shape of these objects is either a cuboid or a cube. Here, in this article, we will learn the difference between cube and cuboid shapes with the help of their properties and formulas of surface area and volume.
Definition of Cube and Cuboid Shape
The cube and cuboid shapes in Maths are three-dimensional shapes. The cube and cuboid are obtained from the rotation of the two-dimensional shapes called square and rectangle respectively.
Cube: A cube is a three-dimensional shape that is defined XYZ plane. It has six faces, eight vertices and twelve edges. All the faces of the cube are in square shape and have equal dimensions.
Cuboid: A cuboid is also a polyhedron having six faces, eight vertices and twelve edges. The faces of the cuboid are parallel. But not all the faces of a cuboid are equal in dimensions.
Hence, cube and cuboid shapes have six faces, eight vertices and twelve edges.
Difference Between Cube and Cuboid
The difference between the cube and cuboid shapes are as follows:
- The sides of the cube are equal but for cuboids they are different.
- The sides of the cube are square in shape but for cuboid, they are in a rectangular shape.
- All the diagonals of the cube are equal but a cuboid has equal diagonals for only parallel sides.
Cube and Cuboid Shape
As we already know, both cube and cuboid are in 3D shape, whose axes go along the x-axis, y-axis and z-axis. Now, let us learn in detail.
A cuboid is a closed 3-dimensional geometrical figure bounded by six rectangular plane regions.
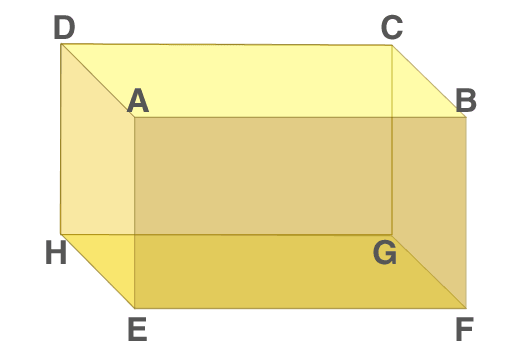
Properties of a Cuboid
Below are the properties of the cuboid, its faces, base and lateral faces, edges and vertices.
Faces of Cuboid
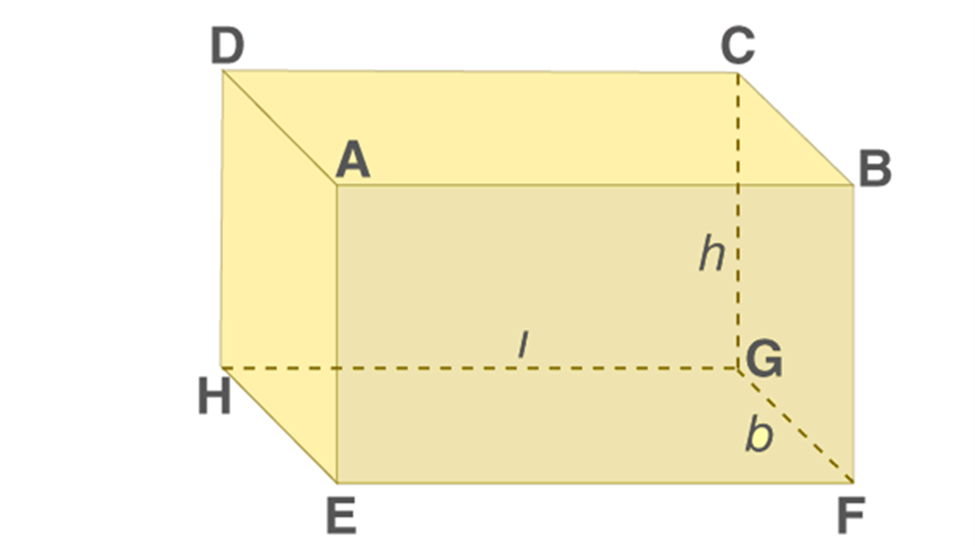
A Cuboid is made up of six rectangles, each of the rectangles is called the face. In the figure above, ABFE, DAEH, DCGH, CBFG, ABCD and EFGH are the 6 faces of the cuboid.
The top face ABCD and bottom face EFGH form a pair of opposite faces. Similarly, ABFE, DCGH, and DAEH, CBFG are pairs of opposite faces. Any two faces other than the opposite faces are called adjacent faces.
Consider a face ABCD, the adjacent face to this are ABFE, BCGF, CDHG, and ADHE.
Base and lateral faces
Any face of a cuboid may be called the base of the cuboid. The four faces which are adjacent to the base are called the lateral faces of the cuboid. Usually, the surface on which a solid rests is known to be the base of the solid.
In Figure (1) above, EFGH represents the base of a cuboid.
Edges
The edge of the cuboid is a line segment between any two adjacent vertices.
There are 12 edges, they are AB, AD, AE, HD, HE, HG, GF, GC, FE, FB, EF and CD and the opposite sides of a rectangle are equal.
Hence, AB = CD = GH = EF, AE = DH = BF = CG and EH = FG = AD = BC.
Vertices of Cuboid
The point of intersection of the 3 edges of a cuboid is called the vertex of a cuboid.
A cuboid has 8 vertices. A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H represent vertices of the cuboid in fig 1.
By observation, the twelve edges of a cuboid can be grouped into three groups, such that all edges in one group are equal in length, so there are three distinct groups and the groups are named as length, breadth and height.
A solid having its length, breadth, and height all to be equal in measurement is called a cube. A cube is a solid bounded by six square plane regions, where the side of the cube is called the edge.
Properties of Cube
- A cube has six faces and twelve edges of equal length.
- It has square-shaped faces.
- The angles of the cube in the plane are at a right angle.
- Each face of the cube meets four other faces.
- Each vertex of the cube meets three faces and three edges.
- The opposite edges of the cube are parallel to each other.
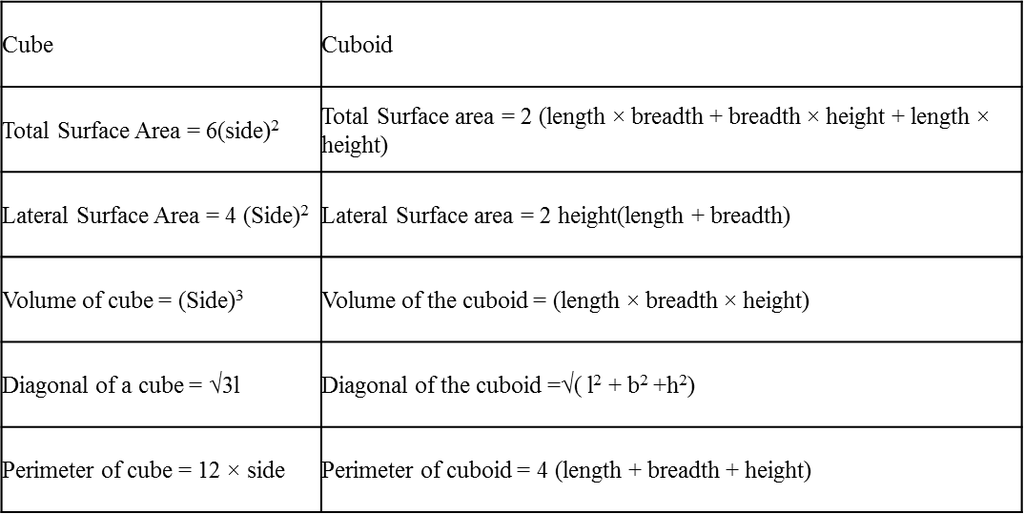
Cube and Cuboid Formulas
The formulas for cube and cuboid shapes are defined based on their surface areas, lateral surface areas and volume.
|
Cube |
Cuboid |
|
Total Surface Area = 6(side)2 |
Total Surface area = 2 (length × breadth + breadth × height + length × height) |
|
Lateral Surface Area = 4 (Side)2 |
Lateral Surface area = 2 height(length + breadth) |
|
Volume of cube = (Side)3 |
Volume of the cuboid = (length × breadth × height) |
|
Diagonal of a cube = √3l |
Diagonal of the cuboid =√( l2 + b2 +h2) |
|
Perimeter of cube = 12 × side |
Perimeter of cuboid = 4 (length + breadth + height) |
Surface Area of Cube and Cuboid
The surface area of a cuboid is equal to the sum of the areas of its six rectangular faces.
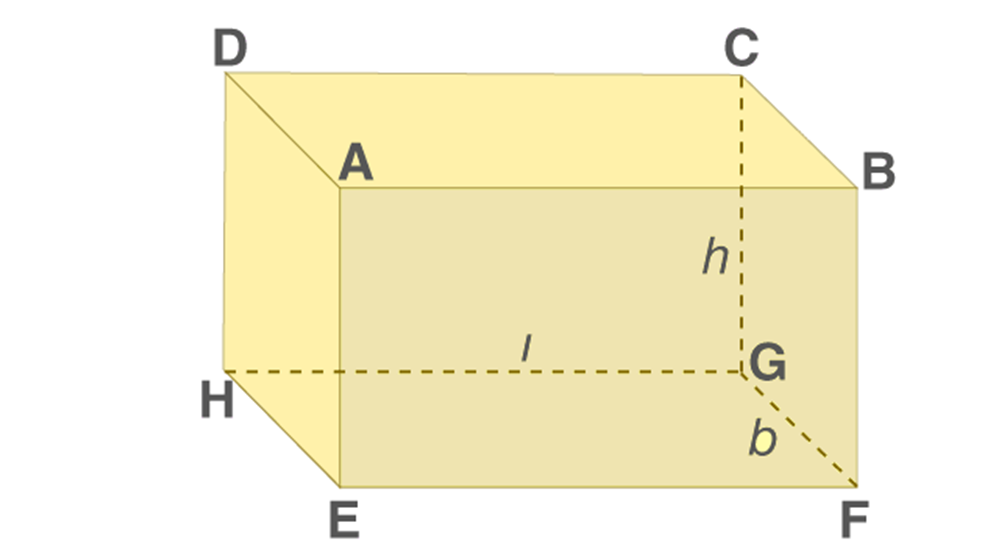
Consider a cuboid having the length to be ‘l’ cm, breadth be ‘b’ cm and height be ‘h’ cm.
- Area of face EFGH = Area of Face ABCD = (l × b) cm2
- Area of face BFGC = Area of face AEHD = (b × h) cm2
- Area of face DHGC = Area of face ABFE = (l × h) cm2
Total surface area of a cuboid = Sum of the areas of all its 6 rectangular faces
Total Surface Area of Cuboid= 2(lb + bh +lh)
Example: If the length, breadth and height of a cuboid are 5 cm, 3 cm and 4 cm, then find its total surface area.
Given, Length, l = 5 cm, Breadth, b = 3 cm and Height, h = 4 cm.
Total surface area (TSA) = 2(lb + bh + lh)
= 2(5 × 3 + 3 × 4 + 5 × 4)
= 2(15 + 12 + 20)
= 2(47)
= 94 sq.cm.
Lateral surface area of a Cuboid
The sum of surface areas of all faces except the top and bottom face of a solid is defined as the lateral surface area of a solid.
Consider a Cuboid of length, breadth and height to be l, b and h respectively.
Lateral surface area of the cuboid= Area of face ADHE + Area of face BCGF + Area of face ABFE + Area of face DCGH
=2(b × h) + 2(l × h)
=2h(l + b)
LSA of Cuboid = 2h(l +b)
Example: If the length, breadth and height of a cuboid are 5 cm, 3 cm and 4 cm, then find its lateral surface area.
Given, Length = 5 cm, Breadth = 3 cm and Height = 4 cm
LSA = 2h(l + b)
LSA = 2 × 4(5 + 3)
LSA = 2 × 4(8)
LSA = 2 × 32 = 64 cm2
Surface Area of a Cube
For cube, length = breadth = height
Suppose the length of an edge = l
Hence, surface area of the cube = 2(l × l +l × l + l × l) = 2 x 3l2 = 6l2
Total Surface Area of Cube= 6l2
Example: If the length of the side of the cube is 6 cm, then find its total surface area.
Given, side length = 6 cm
TSA of cube = 6l2
TSA = 6 (6)2
TSA = 6 × 36
TSA = 216 sq.cm
Lateral surface area of a Cube
Formula to find the Lateral surface area of the cube is:
2(l × l + l × l) = 4l2
LSA of Cube = 4l2
Example: If the length of the side of the cube is 6 cm, then find its lateral surface area.
Given,
Side length, l = 6 cm
LSA of cube = 4l2
LSA = 4 (6)2
LSA = 4 x 36 = 144 sq.cm
Volume of the Cube and Cuboid
Volume of Cuboid:
The volume of the cuboid is equal to the product of the area of one surface and height.
Volume of the cuboid = (length × breadth × height) cubic units
Volume of the cuboid = ( l × b × h) cubic units
Example: If the length, breadth and height of a cuboid are 5 cm, 3 cm and 4 cm, then find its volume.
Given, Length (l) = 5 cm, Breadth (b) = 3 cm and Height (h) = 4 cm
Volume of cuboid = l × b × h
V = 5 × 3 × 4
V = 60 cubic cm
Volume of the Cube:
The volume of the cube is equal to the product of the area of the base of a cube and its height. As we know already, all the edges of the cube are of the same length. Hence,
Volume of the cube = l2 × h
Since, l = h
Therefore,
Volume of the cube = l2 × l
Volume of the cube = l3 cubic units
Example: If the length of the side of the cube is 6 cm, then find its volume.
Given, side length = 6 cm
Volume of cube = side3
V = 63
V = 216 cubic cm
Diagonal of Cube and Cuboid
The length of the diagonal of the cuboid is given by:
Diagonal of the cuboid =√( l2 + b2 +h2)
The length of the diagonal of a cube is given by:
Diagonal of a cube = √3l
The perimeter of Cube and Cuboid
The perimeter of the cuboid is based on its length, width and height. Since the cuboid has 12 edges and the value of its edges are different from each other, therefore, the perimeter is given by:
Perimeter of a cuboid = 4 (l + b + h)
where l is the length
b is the breadth
h is the height
Example: If the length, width and height of a cuboid are 5 cm, 3 cm and 4 cm, find its Perimeter.
Given, Length = 5 cm, Width = 3 cm and Height = 4 cm
Perimeter = 4 (l + b + h) = 4 (5 + 3 + 4)
P = 4 (12)
P = 48 cm
The perimeter of the cube also depends upon the number of edges it has and the length of the edges. Since the cube has 12 edges and all the edges have equal length, the perimeter of the cube is given by:
The perimeter of a cube = 12l
where l is the length of the edge of the cube
Example: If the side length of the cube is 6 cm, then find its perimeter.
Given , l = 6 cm
The perimeter of the cube = 12l
P = 12 × 6
P = 72 cm
Example Problems on Cube and Cuboid Shape
Example 1:
Find the total surface area of the cuboid with dimensions 2 inches × 3 inches × 7 inches.
Solution:
Given,
Length (l) = 2 inches
Breadth (b) = 3 inches
Height (h) = 7 inches
Total Surface Area(TSA) = 2 (lb + bh + hl )
TSA = 2 ( 2 × 3 + 3 × 7 + 7 × 2)
= 2 ( 6 + 21 + 14 )
= 2 × 41
= 82
So, the total surface area of this cuboid is 82 inches2
Example 2:
The length, width and height of a cuboid are 12 cm, 13 cm and 15 cm, respectively. Find the lateral surface area of a cuboid.
Solution:
Given,
Length (l) = 12 cm
Width (w) = 13 cm
Height (h) = 15 cm
Lateral surface area of a cuboid is given by:
LSA = 2h ( l + w )
LSA = 2 × 15 ( 12 + 13 )
= 30 × 25
= 750 cm2
Example 3:
Find the surface area of a cube having its sides equal to 8 cm.
Solution: Given,
Length of the side ‘a’= 8 cm
Surface area = 6a2
= 6 × 82
= 6 × 64
= 384 cm2
Example 4:
If the side length of the cube shape object is 3 cm and the dimensions of the cuboid-shaped object are 2 cm × 4 cm × 6 cm. Find the volume of cube and cuboid-shaped objects.
Solution:
Given: Side length of cube, l = 3 cm.
We know that the volume of cube = l3 cubic units.
The volume of cube-shaped object = 33 = 27 cm3.
Given: Dimension of the cuboid-shaped object = 2 cm × 4 cm × 6 cm.
We know that the volume of cuboid = lbh cubic units
The volume of cuboid-shaped object = 2 cm × 4 cm × 6 cm = 48 cm3.
Therefore, the volume of the cube and cuboid-shaped object are 27 cm3 and 48 cm3 respectively.
Chapter 13 - Surface areas and Volumes
Surface Areas and Volume
Surface area and volume are calculated for any three-dimensional geometrical shape. The surface area of any given object is the area or region occupied by the surface of the object. Whereas volume is the amount of space available in an object.
In geometry, there are different shapes and sizes such as sphere, cube, cuboid, cone, cylinder, etc. Each shape has its surface area as well as volume. But in the case of two-dimensional figures like square, circle, rectangle, triangle, etc., we can measure only the area covered by these figures and there is no volume available. Now, let us see the formulas of surface areas and volumes for different 3d-shapes.
What is Surface Area?
The space occupied by a two-dimensional flat surface is called the area. It is measured in square units. The area occupied by a three-dimensional object by its outer surface is called surface area. It is also measured in square units.
Generally, Area can be of two types:
(i) Total Surface Area
(ii) Curved Surface Area/Lateral Surface Area
Total surface area
Total surface area refers to the area including the base(s) and the curved part. It is total of the area covered by the surface of the object. If the shape has curved surface and base, then total area will be the sum of the two areas.
Curved surface area/Lateral surface area
Curved surface area refers to the area of only the curved part of the shape excluding its base(s). It is also referred to as lateral surface area for shapes such as a cylinder.
What is Volume?
The amount of space, measured in cubic units, that an object or substance occupies is called volume. Two-dimensional doesn’t have volume but has area only. For example, Volume of Circle cannot be found, though Volume of the sphere can be. It is so because a sphere is a three-dimensional shape.
Surface Area and Volume Formulas
Below given is the table for calculating Surface area and Volume for the basic geometrical figures:
|
Name |
Perimeter |
Total Surface Area |
Curved Surface Area/Lateral Surface Area |
Volume |
Figure |
|
Square |
4a |
a2 |
—- |
—- |
|
|
Rectangle |
2(w+h) |
w.h |
—- |
—- |
|
|
Parallelogram |
2(a+b) |
b.h |
—- |
—- |
|
|
Trapezoid |
a+b+c+d |
1/2(a+b).h |
—- |
—- |
|
|
Circle |
2 π r |
π r2 |
—- |
—- |
|
|
Ellipse |
2π√(a2 + b2)/2 |
π a.b |
—- |
—- |
|
|
Triangle |
a+b+c |
1/2 * b * h |
—- |
—- |
|
|
Cuboid |
4(l+b+h) |
2(lb+bh+hl) |
2h(l+b) |
l * b * h |
|
|
Cube |
6a |
6a2 |
4a2 |
a3 |
|
|
Cylinder |
—- |
2 π r(r+h) |
2πrh |
π r2 h |
|
|
Cone |
—- |
π r(r+l) |
π r l |
1/3π r2 h |
|
|
Sphere |
—- |
4 π r2 |
4π r2 |
4/3π r3 |
|
|
Hemisphere |
—- |
3 π r2 |
2 π r2 |
2/3π r3 |
|
Surface Area of Cube and Cuboid
Cube and cuboid are three-dimensional shapes that consist of six faces, eight vertices and twelve edges. The primary difference between them is a cube has all its sides equal whereas the length, width and height of a cuboid are different. Both shapes look almost the same but have different properties. The area and volume of cube, cuboid and also cylinder differ from each other.
In everyday life, we have seen many objects like a wooden box, a matchbox, a tea packet, a chalk box, a dice, a book, etc. All these objects have a similar shape. All these objects are made of six rectangular planes or square planes. In mathematics, the shape of these objects is either a cuboid or a cube. Here, in this article, we will learn the difference between cube and cuboid shapes with the help of their properties and formulas of surface area and volume.
Definition of Cube and Cuboid Shape
The cube and cuboid shapes in Maths are three-dimensional shapes. The cube and cuboid are obtained from the rotation of the two-dimensional shapes called square and rectangle respectively.
Cube: A cube is a three-dimensional shape that is defined XYZ plane. It has six faces, eight vertices and twelve edges. All the faces of the cube are in square shape and have equal dimensions.
Cuboid: A cuboid is also a polyhedron having six faces, eight vertices and twelve edges. The faces of the cuboid are parallel. But not all the faces of a cuboid are equal in dimensions.
Hence, cube and cuboid shapes have six faces, eight vertices and twelve edges.
Difference Between Cube and Cuboid
The difference between the cube and cuboid shapes are as follows:
- The sides of the cube are equal but for cuboids they are different.
- The sides of the cube are square in shape but for cuboid, they are in a rectangular shape.
- All the diagonals of the cube are equal but a cuboid has equal diagonals for only parallel sides.
Cube and Cuboid Shape
As we already know, both cube and cuboid are in 3D shape, whose axes go along the x-axis, y-axis and z-axis. Now, let us learn in detail.
A cuboid is a closed 3-dimensional geometrical figure bounded by six rectangular plane regions.
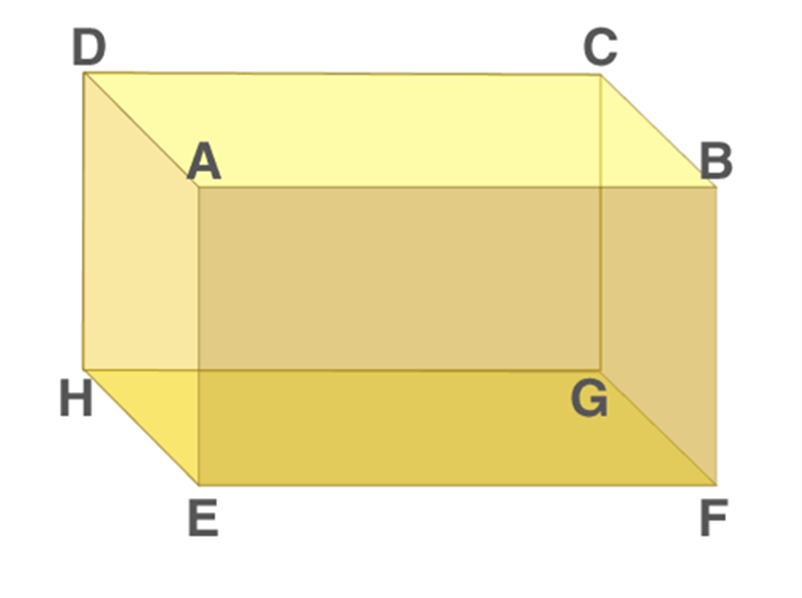
Properties of a Cuboid
Below are the properties of the cuboid, its faces, base and lateral faces, edges and vertices.
Faces of Cuboid
A Cuboid is made up of six rectangles, each of the rectangles is called the face. In the figure above, ABFE, DAEH, DCGH, CBFG, ABCD and EFGH are the 6 faces of the cuboid.
The top face ABCD and bottom face EFGH form a pair of opposite faces. Similarly, ABFE, DCGH, and DAEH, CBFG are pairs of opposite faces. Any two faces other than the opposite faces are called adjacent faces.
Consider a face ABCD, the adjacent face to this are ABFE, BCGF, CDHG, and ADHE.
Base and lateral faces
Any face of a cuboid may be called the base of the cuboid. The four faces which are adjacent to the base are called the lateral faces of the cuboid. Usually, the surface on which a solid rests is known to be the base of the solid.
In Figure (1) above, EFGH represents the base of a cuboid.
Edges
The edge of the cuboid is a line segment between any two adjacent vertices.
There are 12 edges, they are AB, AD, AE, HD, HE, HG, GF, GC, FE, FB, EF and CD and the opposite sides of a rectangle are equal.
Hence, AB = CD = GH = EF, AE = DH = BF = CG and EH = FG = AD = BC.
Vertices of Cuboid
The point of intersection of the 3 edges of a cuboid is called the vertex of a cuboid.
A cuboid has 8 vertices. A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H represent vertices of the cuboid in fig 1.
By observation, the twelve edges of a cuboid can be grouped into three groups, such that all edges in one group are equal in length, so there are three distinct groups and the groups are named as length, breadth and height.
A solid having its length, breadth, and height all to be equal in measurement is called a cube. A cube is a solid bounded by six square plane regions, where the side of the cube is called the edge.
Properties of Cube
- A cube has six faces and twelve edges of equal length.
- It has square-shaped faces.
- The angles of the cube in the plane are at a right angle.
- Each face of the cube meets four other faces.
- Each vertex of the cube meets three faces and three edges.
- The opposite edges of the cube are parallel to each other.
Cube and Cuboid Formulas
The formulas for cube and cuboid shapes are defined based on their surface areas, lateral surface areas and volume.
Surface Area of Cube and Cuboid
The surface area of a cuboid is equal to the sum of the areas of its six rectangular faces.
Consider a cuboid having the length to be ‘l’ cm, breadth be ‘b’ cm and height be ‘h’ cm.
- Area of face EFGH = Area of Face ABCD = (l × b) cm2
- Area of face BFGC = Area of face AEHD = (b × h) cm2
- Area of face DHGC = Area of face ABFE = (l × h) cm2
Total surface area of a cuboid = Sum of the areas of all its 6 rectangular faces
Total Surface Area of Cuboid= 2(lb + bh +lh)
Example: If the length, breadth and height of a cuboid are 5 cm, 3 cm and 4 cm, then find its total surface area.
Given, Length, l = 5 cm, Breadth, b = 3 cm and Height, h = 4 cm.
Total surface area (TSA) = 2(lb + bh + lh)
= 2(5 × 3 + 3 × 4 + 5 × 4)
= 2(15 + 12 + 20)
= 2(47)
= 94 sq.cm.
Lateral surface area of a Cuboid
The sum of surface areas of all faces except the top and bottom face of a solid is defined as the lateral surface area of a solid.
Consider a Cuboid of length, breadth and height to be l, b and h respectively.
Lateral surface area of the cuboid= Area of face ADHE + Area of face BCGF + Area of face ABFE + Area of face DCGH
=2(b × h) + 2(l × h)
=2h(l + b)
LSA of Cuboid = 2h(l +b)
Example: If the length, breadth and height of a cuboid are 5 cm, 3 cm and 4 cm, then find its lateral surface area.
Given, Length = 5 cm, Breadth = 3 cm and Height = 4 cm
LSA = 2h(l + b)
LSA = 2 × 4(5 + 3)
LSA = 2 × 4(8)
LSA = 2 × 32 = 64 cm2
Surface Area of a Cube
For cube, length = breadth = height
Suppose the length of an edge = l
Hence, surface area of the cube = 2(l × l +l × l + l × l) = 2 x 3l2 = 6l2
Total Surface Area of Cube= 6l2
Example: If the length of the side of the cube is 6 cm, then find its total surface area.
Given, side length = 6 cm
TSA of cube = 6l2
TSA = 6 (6)2
TSA = 6 × 36
TSA = 216 sq.cm
Lateral surface area of a Cube
Formula to find the Lateral surface area of the cube is:
2(l × l + l × l) = 4l2
LSA of Cube = 4l2
Example: If the length of the side of the cube is 6 cm, then find its lateral surface area.
Given,
Side length, l = 6 cm
LSA of cube = 4l2
LSA = 4 (6)2
LSA = 4 x 36 = 144 sq.cm
Volume of the Cube and Cuboid
Volume of Cuboid:
The volume of the cuboid is equal to the product of the area of one surface and height.
Volume of the cuboid = (length × breadth × height) cubic units
Volume of the cuboid = ( l × b × h) cubic units
Example: If the length, breadth and height of a cuboid are 5 cm, 3 cm and 4 cm, then find its volume.
Given, Length (l) = 5 cm, Breadth (b) = 3 cm and Height (h) = 4 cm
Volume of cuboid = l × b × h
V = 5 × 3 × 4
V = 60 cubic cm
Volume of the Cube:
The volume of the cube is equal to the product of the area of the base of a cube and its height. As we know already, all the edges of the cube are of the same length. Hence,
Volume of the cube = l2 × h
Since, l = h
Therefore,
Volume of the cube = l2 × l
Volume of the cube = l3 cubic units
Example: If the length of the side of the cube is 6 cm, then find its volume.
Given, side length = 6 cm
Volume of cube = side3
V = 63
V = 216 cubic cm
For More Information On Volumes of Cubes and Cuboid, Watch The Below Video:
29,804
Diagonal of Cube and Cuboid
The length of diagonal of the cuboid is given by:
Diagonal of the cuboid =√( l2 + b2 +h2)
The length of diagonal of a cube is given by:
Diagonal of a cube = √3l
Perimeter of Cube and Cuboid
The perimeter of the cuboid is based on its length, width and height. Since the cuboid has 12 edges and the value of its edges are different from each other, therefore, the perimeter is given by:
Perimeter of a cuboid = 4 (l + b + h)
where l is the length
b is the breadth
h is the height
Example: If the length, width and height of a cuboid are 5 cm, 3 cm and 4 cm, find its Perimeter.
Given, Length = 5 cm, Width = 3 cm and Height = 4 cm
Perimeter = 4 (l + b + h) = 4 (5 + 3 + 4)
P = 4 (12)
P = 48 cm
The perimeter of the cube also depends upon the number of edges it has and the length of the edges. Since the cube has 12 edges and all the edges have equal length, the perimeter of the cube is given by:
Perimeter of a cube = 12l
where l is the length of the edge of the cube
Example: If the side length of the cube is 6 cm, then find its perimeter.
Given , l = 6 cm
The perimeter of cube = 12l
P = 12 × 6
P = 72 cm
Example Problems on Cube and Cuboid Shape
Example 1:
Find the total surface area of the cuboid with dimensions 2 inches × 3 inches × 7 inches.
Solution:
Given,
Length (l) = 2 inches
Breadth (b) = 3 inches
Height (h) = 7 inches
Total Surface Area(TSA) = 2 (lb + bh + hl )
TSA = 2 ( 2 × 3 + 3 × 7 + 7 × 2)
= 2 ( 6 + 21 + 14 )
= 2 × 41
= 82
So, the total surface area of this cuboid is 82 inches2
Example 2:
The length, width and height of a cuboid are 12 cm, 13 cm and 15 cm, respectively. Find the lateral surface area of a cuboid.
Solution:
Given,
Length (l) = 12 cm
Width (w) = 13 cm
Height (h) = 15 cm
Lateral surface area of a cuboid is given by:
LSA = 2h ( l + w )
LSA = 2 × 15 ( 12 + 13 )
= 30 × 25
= 750 cm2
Example 3:
Find the surface area of a cube having its sides equal to 8 cm.
Solution: Given,
Length of the side ‘a’= 8 cm
Surface area = 6a2
= 6 × 82
= 6 × 64
= 384 cm2
Example 4:
If the side length of the cube shape object is 3 cm and the dimensions of the cuboid-shaped object are 2 cm × 4 cm × 6 cm. Find the volume of cube and cuboid shaped objects.
Solution:
Given: Side length of cube, l = 3 cm.
We know that the volume of cube = l3 cubic units.
The volume of cube-shaped object = 33 = 27 cm3.
Given: Dimension of the cuboid-shaped object = 2 cm × 4 cm × 6 cm.
We know that the volume of cuboid = lbh cubic units
The volume of cuboid-shaped object = 2 cm × 4 cm × 6 cm = 48 cm3.
Therefore, the volume of the cube and cuboid shaped object are 27 cm3 and 48 cm3 respectively.

 ABCD CLASSES
ABCD CLASSES