- Books Name
- ABCD CLASSES Mathematics Book
- Publication
- ABCD CLASSES
- Course
- CBSE Class 9
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Surface Area of a Right Circular Cone
A right circular cone is a cone where the axis of the cone is the line meeting the vertex to the midpoint of the circular base. That is, the center point of the circular base is joined with the apex of the cone and it forms a right angle. A cone is a three-dimensional shape having a circular base and narrowing smoothly to a point above the base. This point is known as apex.
We come across many geometrical shapes while dealing with geometry. We usually study two-dimensional and three-dimensional figures in school. Two-dimensional shapes have length and breadth. They can be drawn on paper, for example – circles, rectangles, squares, triangles, polygons, parallelograms etc. The three-dimensional figures cannot be drawn on paper since they have an additional third dimension as height or depth. Examples of 3D shapes are a sphere, hemisphere, cylinder, cone, pyramid, prism etc.
Right Circular Cone Definition
A right circular cone is one whose axis is perpendicular to the plane of the base. We can generate a right cone by revolving a right triangle about one of its legs.
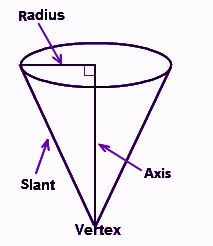
In the figure, you can see a right circular cone, which has a circular base of radius r and whose axis is perpendicular to the base. The line which connects the vertex of the cone to the center of the base is the height of the cone. The length at the outer edge of the cone, which connects a vertex to the end of the circular base is the slant height.
Right Circular Cone Formula
For a right circular cone of radius ‘r’, height ‘h’ and slant height ‘l’, we have;
- Curved surface area of right circular cone = π r l
- Total surface area of a right circular cone = π(r + l) r
- Volume of a right circular cone = 1/3π r2 h
Surface Area of a Right Circular Cone
The surface area of any right circular cone is the sum of the area of the base and lateral surface area of a cone. The surface area is measured in terms of square units.
Surface area of a cone = Base Area + Curved Surface Area of a cone
= π r2 + π r l
= πr(r + l)
Here, l = √(r2+h2)
Where ‘r’ is the radius, ‘l’ is the slant height and ‘h’ is the height of the cone.
Volume of a Right Circular Cone
The volume of a cone is one-third of the product of the area of the base and the height of the cone. The volume is measured in terms of cubic units.
Volume of a right circular cone can be calculated by the following formula,
Volume of a right circular cone = ⅓ (Base area × Height)
Where Base Area = π r2
Hence, Volume = ⅓ π r2h
Properties of Right Circular Cone
- It has a circular base whose center joins its vertex, showing the axis of the respective cone.
- The slant height of this cone is the length of the sides of the cone taken from the vertex to the outer line of the circular base. It is denoted by ‘l’.
- The altitude of a right cone is the perpendicular line from the vertex to the center of the base. It coincides with the axis of the cone and is represented by ‘h’.
- If a right triangle is rotated about its perpendicular, considering the perpendicular as the axis of rotation, the solid constructed here is the required cone. The surface area generated by the hypotenuse of the triangle is the lateral surface area.
- Any section of the right circular cone parallel to the base forms a circle that lies on the axis of the cone.
- A section that contains the vertex and two points of the base of a right circular cone is an isosceles triangle.
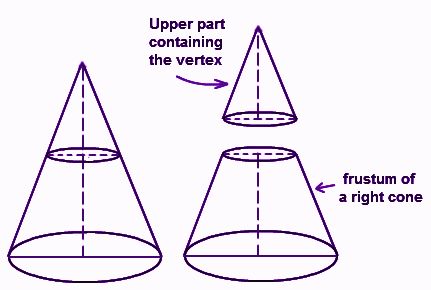
Frustum of a Right Circular Cone
A frustum is a portion of the cone between the base and the parallel plane when a right circular cone is cut off by a plane parallel to its base.
Equation of Right Circular Cone
The equation of the right circular cone with vertex origin is:
(x2+y2+z2)cos2θ=(lx+my+nz)2
Where θ is the semi-vertical angle and (l, m, n) are the direction cosines of the axis.
Let us find the equation of the right circular cone whose vertex is the origin, the axis is the line x = y/3 =z/2 and which makes a semi-vertical angle of 60 degrees.
The direction cosines of the axis are:
[(1/√(12+32+22) , (3/√(12+32+22), (2/√(12+32+22)] = (1/√14, 3/√14, 2/√14)
The semi-vertical angle is, θ = 60°
Therefore, the equation of the right circular cone with vertex (0, 0, 0) is:
(x2+y2+z2) ¼ = 1/14 (x + 3y + 2z)2
7(x2+y2+z2) = 2(x2+9y2+4z2+6xy+12yz+4xz)
5x2-11y2-z2-12xy-24yz-8xz = 0; which is the required equation.
Examples
Q. 1: Find the surface area of the right cone if the given radius is 6 cm and slant height is 10 cm.
Solution: Given,
Radius (r) = 6 cm
Slant height (l) = 10 cm
Surface area of a cone = π r(r + l)
Solving surface area,
SA = 3.14 × 6(6 + 10)
SA = 3.14 × 6 × 16
SA = 301.44
Therefore, Surface area of the right cone is 301.4 sq. cm.
Question 2: Calculate the Volume of the right cone for the given radius 6 cm and height 10 cm.
Solution: Given,
Radius (r) = 6 cm
Height (h) = 10 cm
Volume of right cone = 1/3π r2 h
Volume, V = ⅓ × π × (6)2 × 10
V = 3.14 × 12 × 10
V = 376.8
Therefore, Volume of a right cone is 376.8 cubic cm.

 Vision classes
Vision classes
