Chapter 2 - Polynomials
Polynomials
Polynomials are algebraic expressions that consist of variables and coefficients. Variables are also sometimes called indeterminates. We can perform arithmetic operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication and also positive integer exponents for polynomial expressions but not division by variable. An example of a polynomial with one variable is x2+x-12. In this example, there are three terms: x2, x and -12.
Also, Check: What is Mathematics
The word polynomial is derived from the Greek words ‘poly’ means ‘many‘ and ‘nominal’ means ‘terms‘, so altogether it said “many terms”. A polynomial can have any number of terms but not infinite. Learn about degree, terms, types, properties, polynomial functions in this article.
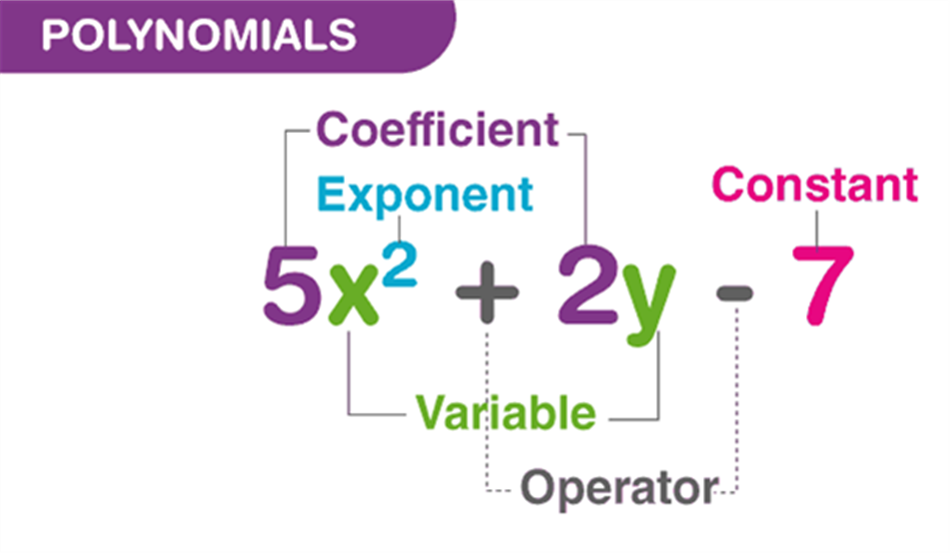
What is a Polynomial?
Polynomial is made up of two terms, namely Poly (meaning “many”) and Nominal (meaning “terms.”). A polynomial is defined as an expression which is composed of variables, constants and exponents, that are combined using the mathematical operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication and division (No division operation by a variable). Based on the numbers of terms present in the expression, it is classified as monomial, binomial, and trinomial. Examples of constants, variables and exponents are as follows:
- Constants. Example: 1, 2, 3, etc.
- Variables. Example: g, h, x, y, etc.
- Exponents: Example: 5 in x5 etc.
Notation
The polynomial function is denoted by P(x) where x represents the variable. For example,
P(x) = x2-5x+11
If the variable is denoted by a, then the function will be P(a)

 ABCD CLASSES
ABCD CLASSES
