- Books Name
- Class-8 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 8
- Subject
- Science
TYPES OF CHARGES AND THEIR INTERACTION
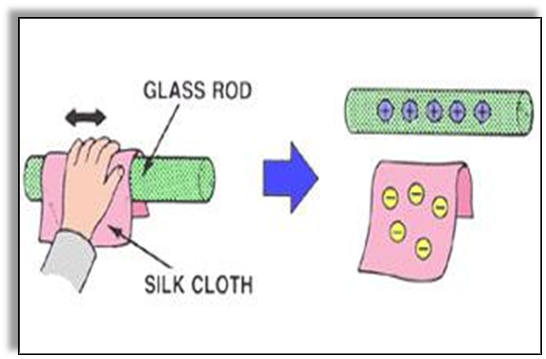
- We know that charged objects may have a shortage or excess of electrons.
- Objects having an excess of electrons are called negatively charged while an object having a shortage of electrons is called positively charged.
- For instance, when a glass rod is rubbed with silk cloth it becomes positively charged while the silk cloth becomes negatively charged.
- These charged objects are now capable of attracting other charged and uncharged objects.
- Objects having the same kind of charges repel each other while objects with different kinds of charges attract each other.
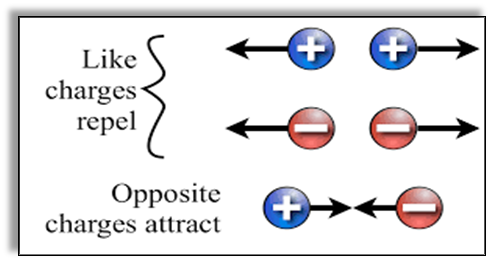
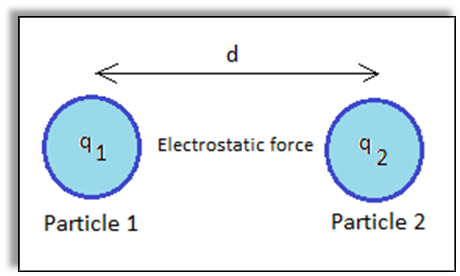
What is an Electrostatic Force?
The force of attraction or repulsion experienced by charged objects is called electrostatic force.
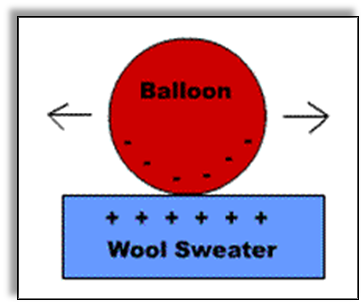
What is a Static Electric Charge?
A static charge or static electricity is an electric charge which does not move. Static charges are a result when two objects are rubbed with each other. When two surfaces come in contact with each other repeatedly it results in the transfer of electrons from one material to another. The strength of an electric charge depends upon different factors such as:
- The temperature and humidity
- Properties of the surface such as its material


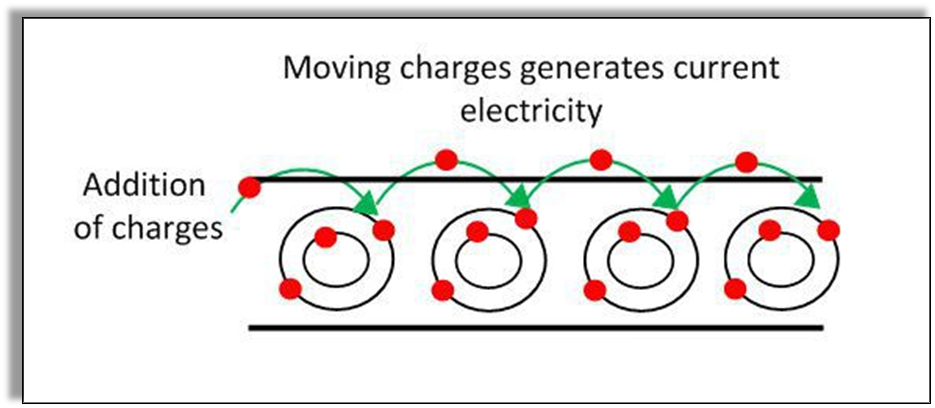
In opposite to static charge, there is an electric current. The electric current results when the charges flow or move from one point to another. This electric current results in the glowing of bulb or working of all the electrical appliances.

 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
