- Books Name
- Class-8 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 8
- Subject
- Science
Cell Structure and Function
Some of the cells have a simple structure and some are complex, but all cells essentially contain three basic parts. They are:
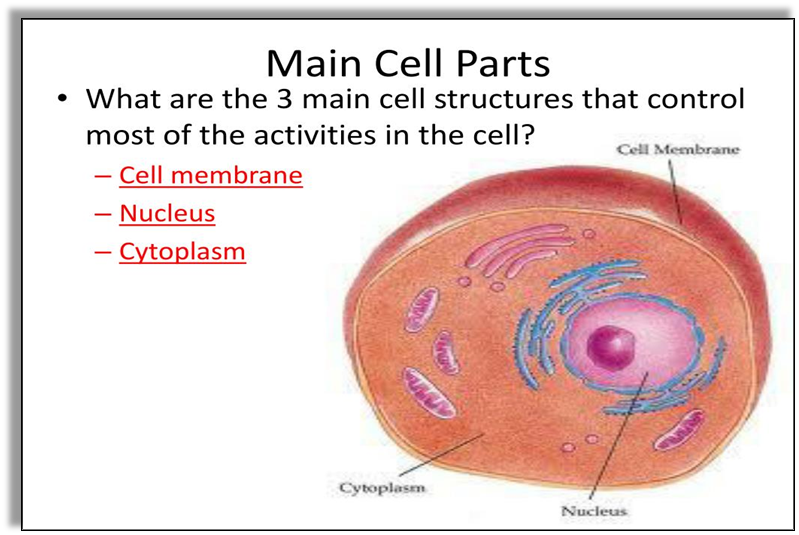
- Cell envelop that contains: Cell membrane: It protects cell content and controls exit and entry of materials from the cell.
- Cell wall: It helps plants to withstand changes in the outside environment without bursting
- Nucleus: It is the control center of a cell.
- It contains chromosomes made up of DNA and protein.
- It contains functional segments of DNA called genes, which are responsible for the transmission of hereditary characters.
- The nucleolus is seen inside the nucleus.
- The nuclear membrane has pores for the exchange of material with the cytoplasm.
- Cytoplasm: It is the fluid content present inside the plasma membrane.
- Protoplasm + Cell organelles = Cytoplasm
- In multicellular organisms, each organ system is made up of several organs.
- Organs are further made up of tissues.
- Tissues are groups of similar cells performing a specific function.
- The number of cells Organisms made up of only a single cell are called unicellular organisms. For example Amoeba and Paramecium
- Single-cell in unicellular organisms performs all the basic functions such as digestion, respiration, and excretion.
- Organisms made up of more than one cell are called multicellular organisms. For example Humans, cows, etc.
- In multicellular organisms, the cells show division of labor as a particular set of cells is involved in performing a specific body function.
- In a unicellular organism, a single cell performs all the basic functions of life but in multicellular organisms, there is a division of labor.

 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
