- Books Name
- Class-8 Science Book
- Publication
- PathSet Publications
- Course
- CBSE Class 8
- Subject
- Science
Case Study - The Taj Mahal
Causes of Air Pollution
- Air pollution from Natural Sources: sometimes forest fires or volcanic eruptions can lead to the release of an excess of smoke and dust into the atmosphere.
- Burning of fossil fuels: coal and petroleum used in industries and vehicles when burnt release harmful substances in the air such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides and sulphur dioxide.
- Exhaust from factories: many industries release harmful substances like carbon dioxide, hydrocarbons and other harmful chemicals in the air which decrease its quality.
- Agricultural activities: usage of insecticides, fertilizers and pesticides lead to the release of chemicals in the air. Agricultural activities also lead to the release of ammonia into the atmosphere which is extremely hazardous for us.
- Pollution due to households: paints, cleaning products, air conditioners, refrigerators and other appliances used in houses also contribute to air pollution. The air conditioners and refrigerators release chlorofluorocarbons that damage the ozone layer of the earth. The burning of wood and cow dung cakes in rural areas also leads to air pollution.
- Mining activities: mining results in the release of a large amount of dust and chemicals into the air.
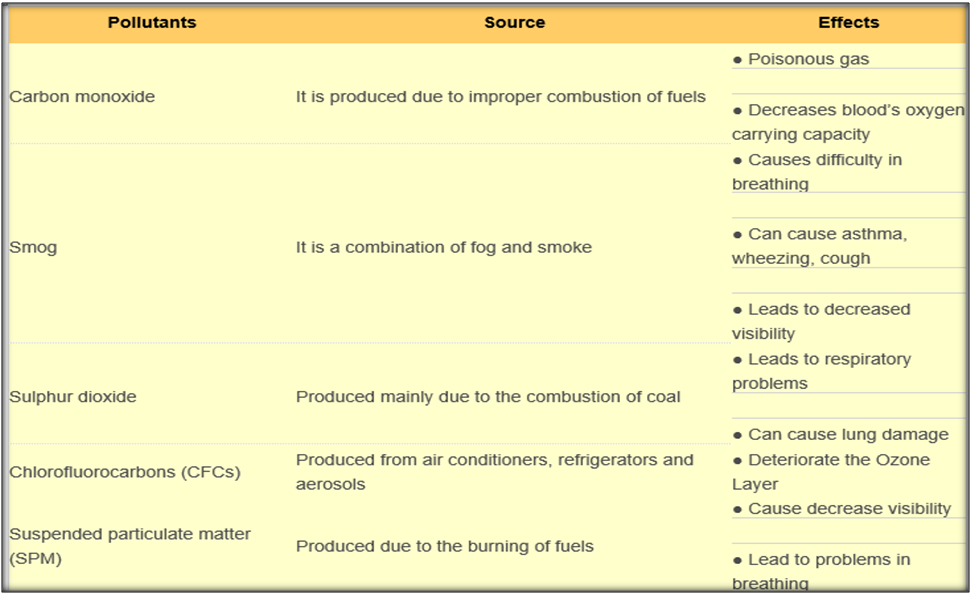
Effects of Pollutants on the Environment
Air pollution and the case study of the Taj Mahal
We know that air pollution can severely affect the environment. One great example of the harmful effects of air pollution can be viewed in the Taj Mahal, the most famous and beautiful tourist attraction in India.
The air pollution in that region has led to the decolorization of the white marble of the Taj Mahal.
Causes of air pollution in Agra and effects on the Taj Mahal
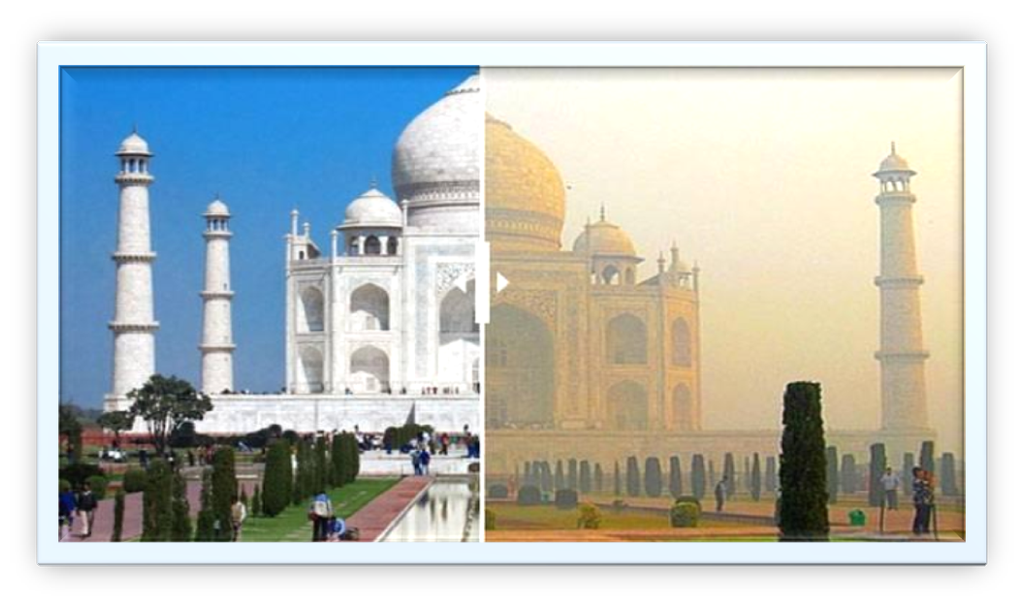

- The main sources of pollutants in the air around the Taj Mahal are the industries around Agra.
- The Mathura oil refinery and other industries including automobiles, rubber processing and chemicals are releasing harmful substances into the air.
- The major pollutants are Nitrogen dioxide and Sulphur Dioxide. These pollutants lead to acid rain in the Agra region.
- When Nitrogen dioxide combines with water it forms nitric acid and when Sulphur Dioxide combines with water it forms sulphuric acid.
- The rainwater which falls on the Taj Mahal leads to the decay of the marble. This is also called ‘marble cancer’.
- The Mathura oil refinery is a major source of suspended particulate matter (SPM) in the air around the Taj Mahal which is making the white marble look yellow in colour.
Steps were taken to reduce air pollution in the area near the Taj Mahal
- The industries are switching to clean fuels such as CNG and LPG to prevent air pollution and protect the monument.
- Also, unleaded petrol should be used in automobiles to prevent harmful smoke from the vehicles near the Taj Mahal area.

 PathSet Publications
PathSet Publications
