- Books Name
- class 8 th Mathematics Book
- Publication
- ReginaTagebücher
- Course
- CBSE Class 8
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Rational Numbers
Properties of rational number
Introduction to rational numbers,
Rational Numbers
A number is called Rational if it can be expressed in the form p/ q where p and q are integers (q> 0). It includes all natural, whole number, and integers.
Case1/2, 4/3, 5/7, 1 etc.
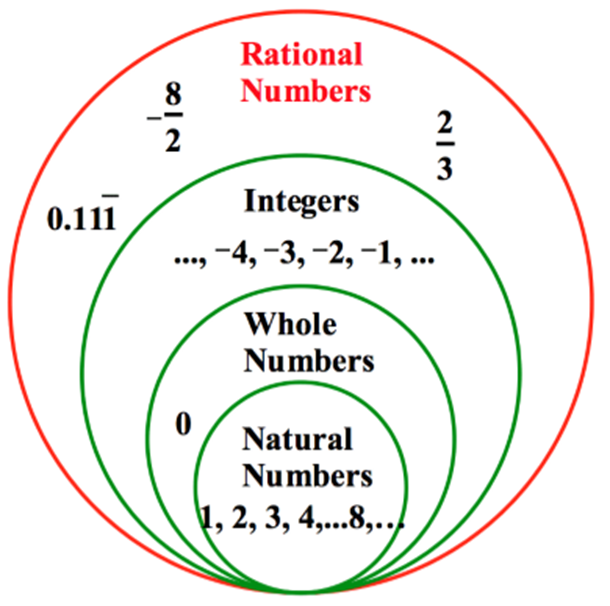
Natural Numbers - All the positive integers from 1, 2, 3,, ∞.
Whole Numbers - All the natural numbers including zero are called Whole Numbers.
Integers - All negative and positive numbers including zero are called Integers.
Closure property,
Closure- Rational numbers are closed under addition, subtraction and multiplication. For eg.- If p and q are any two rational numbers, then and the sum, difference and product of these rational numbers is also a rational number. This is known as the closure law
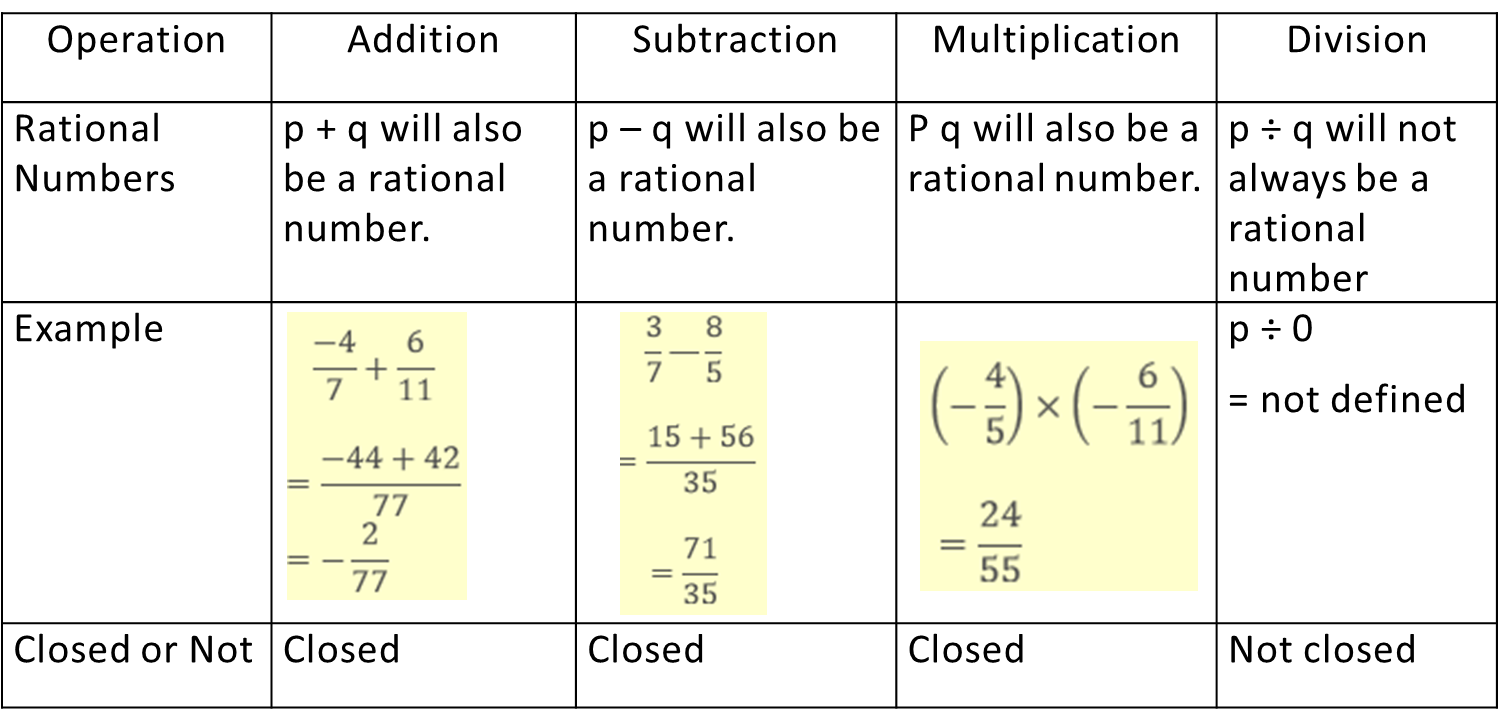
Commutative property,
Commutativity- Rational numbers are commutative under addition and multiplication. If p and q are two rational numbers, then:
Commutative law under addition says- p + q = q + p.
Commutative law under multiplication says p x q = q x p.
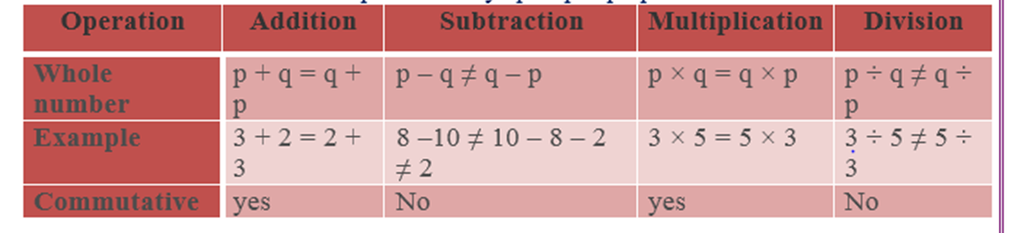
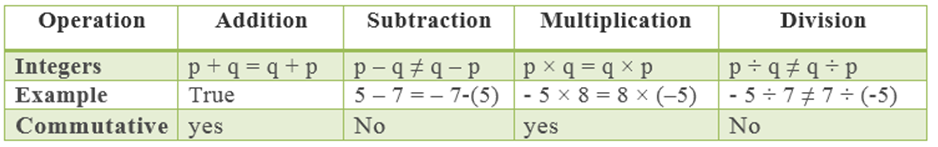
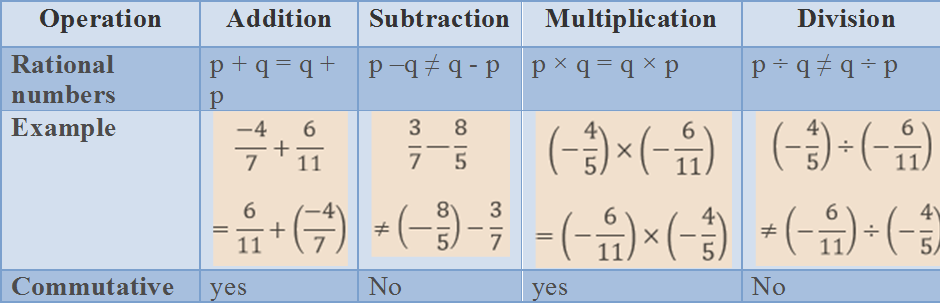
Note- Rational numbers, integers and whole numbers are commutative under addition and multiplication. Rational numbers, integers and whole numbers are non commutative under subtraction and division.
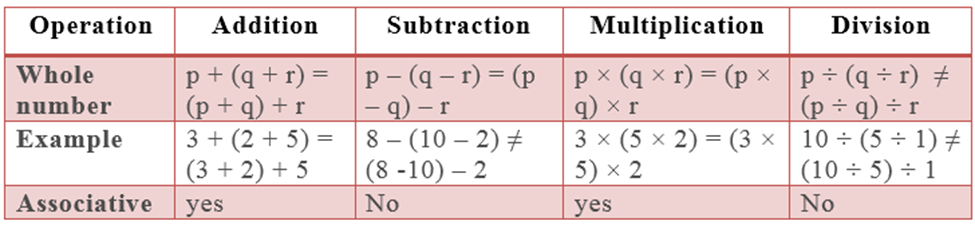
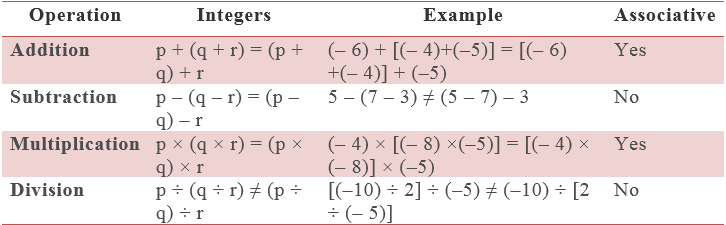
Associativity property,
▪ Associativity- Rational numbers are associative under addition and multiplication. If a, b, c are rational numbers, then:
Associative property under addition: p + (q + r) = (p + q) + r
Associative property under multiplication: p(qr) = (pq)r
The role of 0 and 1
Role of zero and one- 0 is the additive identity for rational numbers. 1 is the multiplicative identity for rational numbers.
Zero is the additive identity for whole numbers, integers and rational numbers.


▪ Multiplicative inverse- If the product of two rational numbers is 1, then they are called multiplicative inverse of each other.
Eg. 4/9 * 9/4 = 1

 Carrier Point
Carrier Point
 Success Academy
Success Academy
 ReginaTagebücher
ReginaTagebücher
