1. Practical Geometry
- Books Name
- class 8 th Mathematics Book
- Publication
- ReginaTagebücher
- Course
- CBSE Class 8
- Subject
- Mathmatics
Practical Geometry
What is quadrilateral,
A four-sided closed two-dimensional shape is called a quadrilateral.
Types of quadrilateral
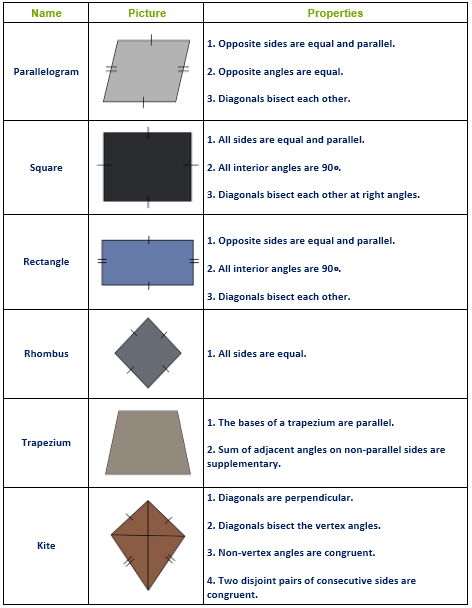
When the lengths of four sides and a diagonal are given
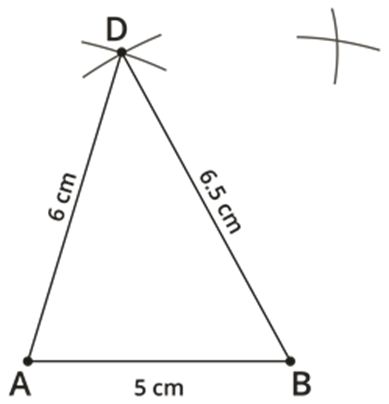
Construct a quadrilateral ABCD, where AB=5 cm, BC=6 cm, CD=4 cm, AD=6 cm and BD=6.5 cm.
Rough diagram:
Let us first draw the rough quadrilateral, which will help us to draw a fair quadrilateral.
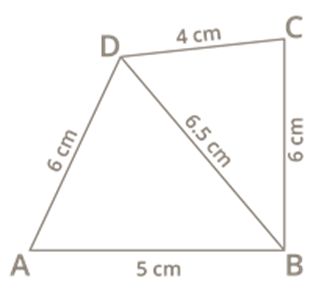
Fair diagram:
Step 1: Draw a line segment AB=5 cm.
![]()
Step 2: Given AD=6 cm and BD=6.5 cm. Take 6 cm as radius and draw an arc from point A. Then, take 6.5 cm as another radius and draw an arc from point B, which cuts the previously drawn arc.
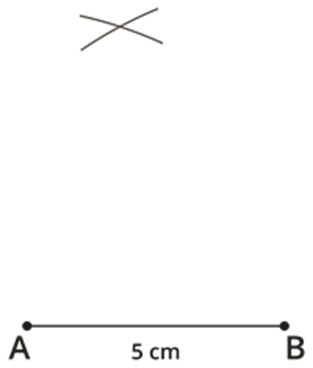
Step 3: Mark the two arcs meeting point as D, then join AD and BD.
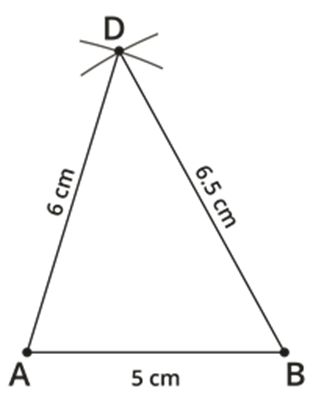
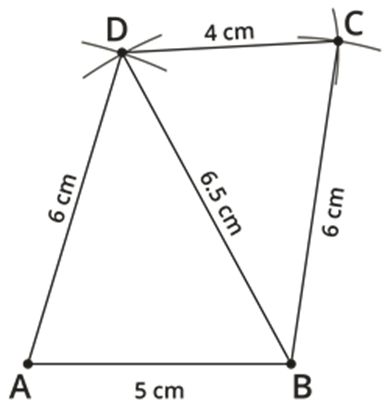
Step 4: Also, given that BC=6 cm and CD=4 cm. Take 6 cm as radius and draw an arc from point B. Then, take 4 cm as another radius and draw an arc from (D), which cuts the previously drawn arc.
Step 5: Mark the two arcs meeting point as C, then join BC and CD. We obtained the required quadrilateral ABCD.
When two diagonals and three sides are given
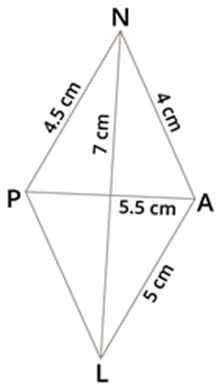
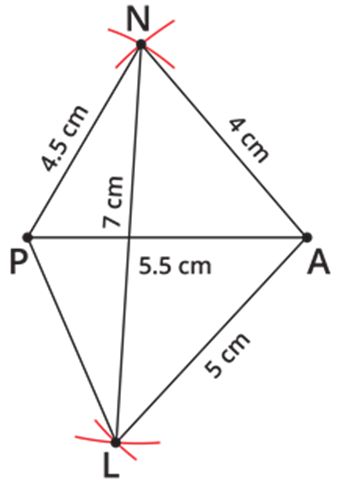
Draw a quadrilateral PLAN, where LA=5 cm, PN=4.5 cm, AN=4 cm, diagonal PA=5.5 cm and the diagonal LN=7 cm.
Rough diagram:
Let us first draw the rough quadrilateral, which will help us to draw a fair quadrilateral.
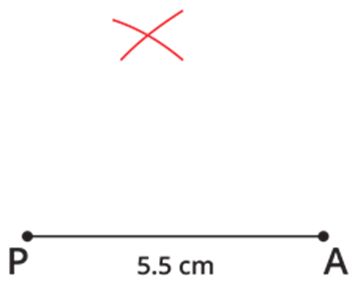
Step 1: Draw a line segment PA=5.5 cm.
![]()
Step 2: Given that PN=4.5 cm and AN=4 cm. Take 4.5 cm as radius and draw an arc from point P. Then, take 4 cm as another radius and draw an arc from point A, which cuts the previously drawn arc.
Step 3: Mark the two arcs meeting point as N, then join PN and AN.
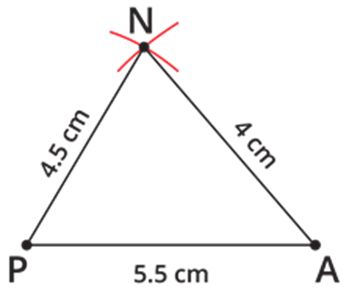
Step 4: Also, given that LA=5 cm and LN=7 cm. Take 5 cm as radius and draw an arc from point A. Then, take 7 cm as another radius and draw an arc from N, which cuts the previously drawn arc.
Step 5: Mark the two arcs meeting point as L, then join NL, AL and PL. We obtained the required quadrilateral PLAN.
When two adjacent sides and three angles are known
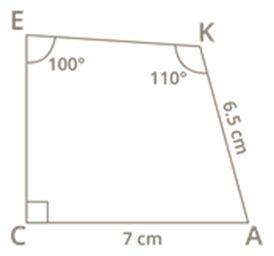
Construct a quadrilateral CAKE where CA=7 cm, AK=6.5 cm, ∠C=90∘, ∠K=110∘, ∠E=100∘.
Let us first draw the rough quadrilateral, which will help us to draw a fair quadrilateral.
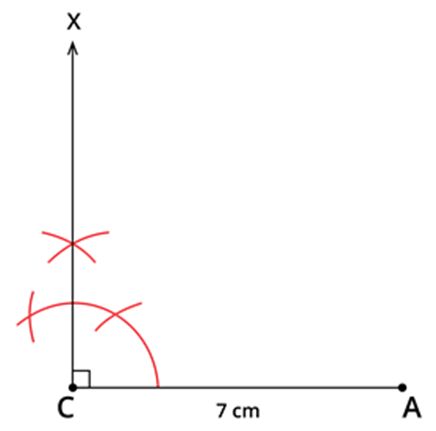
Step 1: Draw a line segment CA=7 cm.
![]()
Step 2: Construct ∠ACX=90∘ using ruler and compass.
Step 3: We know that sum of all the angles of a quadrilateral is 360∘.
∠C+∠A+∠K+∠E=360∘
90∘+∠A+110∘+100∘=360∘
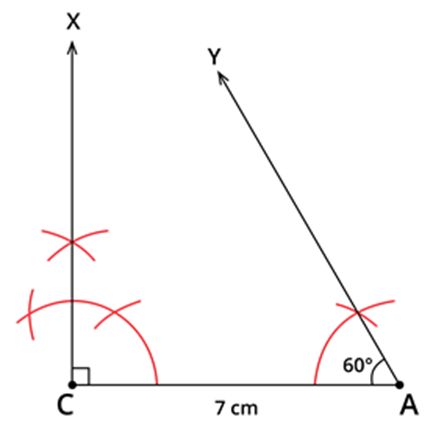
So, ∠A=60∘
Construct ∠CAY=60∘ using ruler and compass.
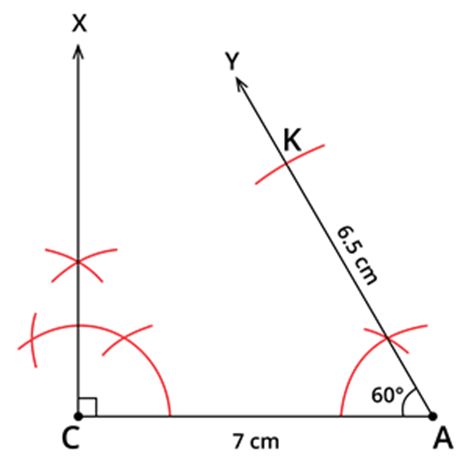
Step 4: With A as centre and 6.5 cm as radius, draw an arc, cutting AY at K.
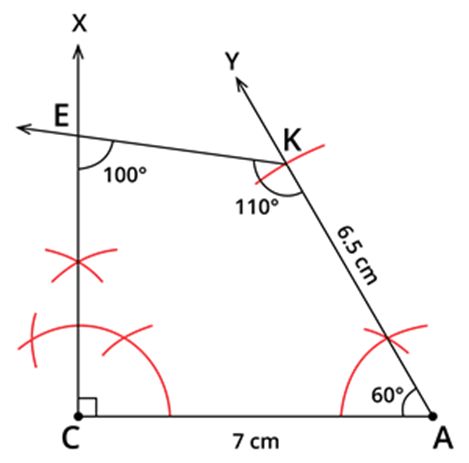
Step 5: With K as centre, make an angle of 110∘, cutting CX at E, then join EK.
Thus, the quadrilateral CAKE is obtained.
When three sides and two included angles are given
Example:
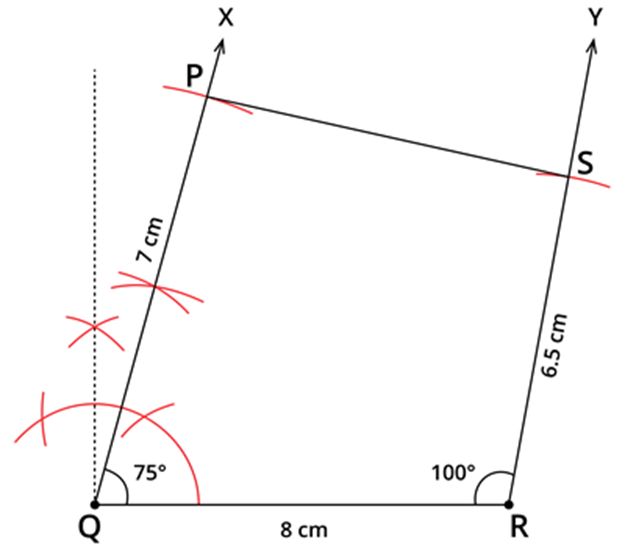
Draw a quadrilateral PQRS, where PQ=7 cm, QR=8 cm, RS=6.5 cm and ∠Q=75∘ and ∠R=100∘.
Let us first draw the rough quadrilateral, which will help us to draw a fair quadrilateral.
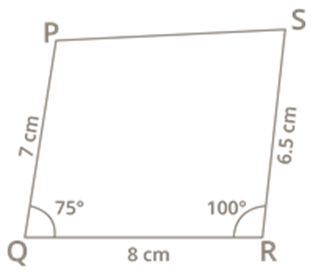
Step 1: Draw a line segment QR=8 cm.
![]()
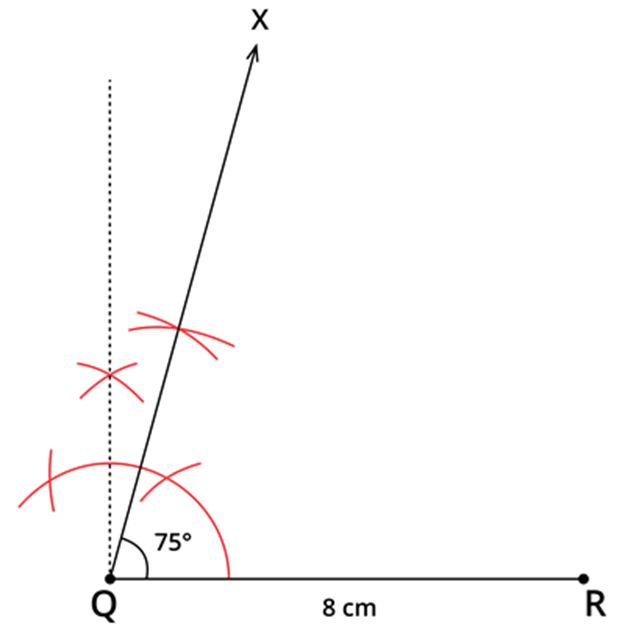
Step 2: Construct ∠RQX=75∘ using ruler and compass.
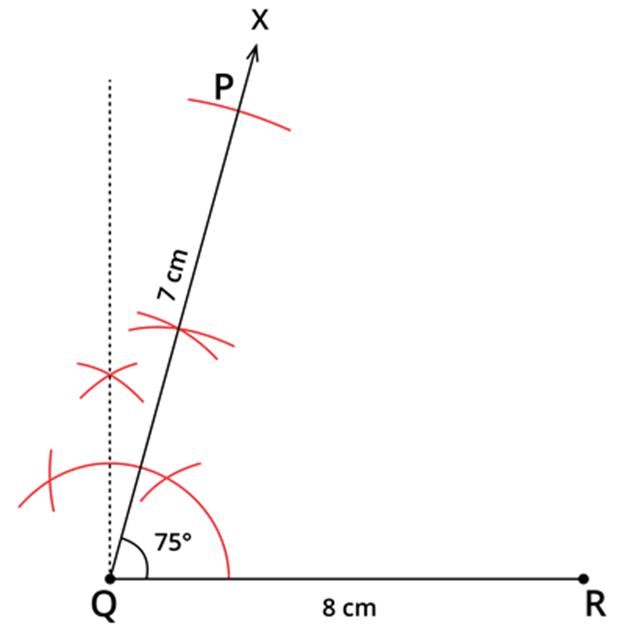
Step 3: With Q as centre and 7 cm as radius, draw an arc, cutting QX at P.
Step 4: Construct ∠QRY=100∘ using protractor.
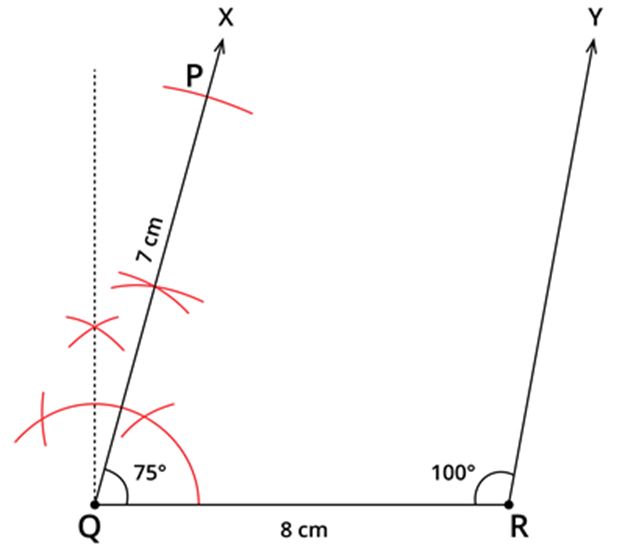
Step 5: With R as centre and 6.5 cm as radius, draw an arc cutting RY at S. Now, join PS. Thus, the quadrilateral PQRS is obtained.
Some Special Cases
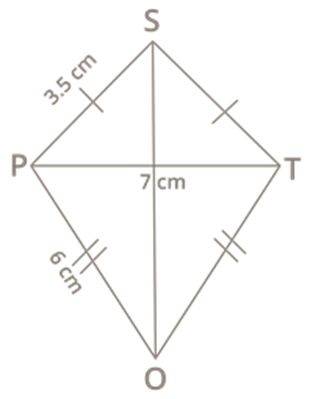
Construct the kite STOP if TP=7 cm, SP=4 cm and OP=6 cm.
Rough diagram:
Let us first draw the rough quadrilateral, which will help us to draw a fair quadrilateral.
Fair diagram:
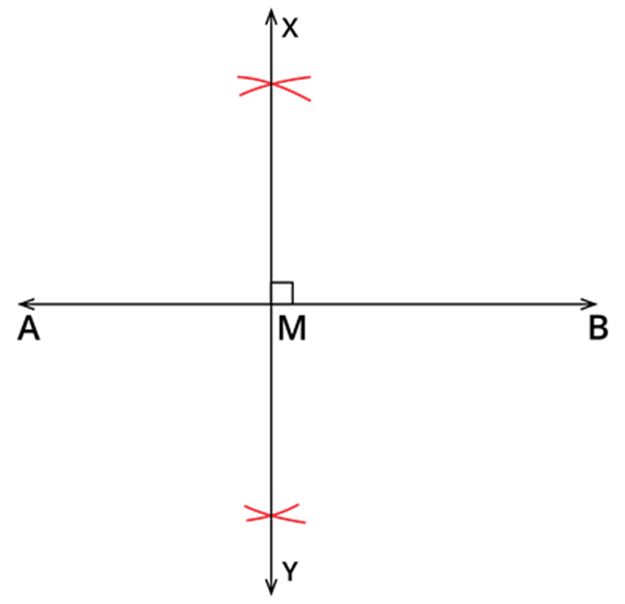
Step 1: Draw a line segment AB with any length.
![]()
Step 2: Draw a perpendicular bisector XY of AB. The intersection of XY and AB is marked as M.
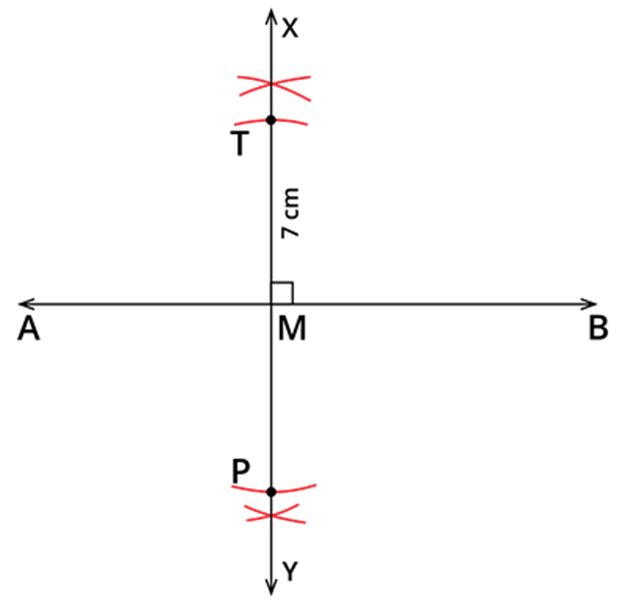
Step 3: Given that TP=7 cm. With M as centre and 72=3.5 cm as radius, draw an arc above AB, which cuts MX at T. Similarly, with the same radius and centre, draw an arc below AB, which cuts MY at P.
Step 4: Given that SP=4 cm. Take 4 cm as radius and P as centre, draw an arc, which cuts AB at S. Join SP and ST.
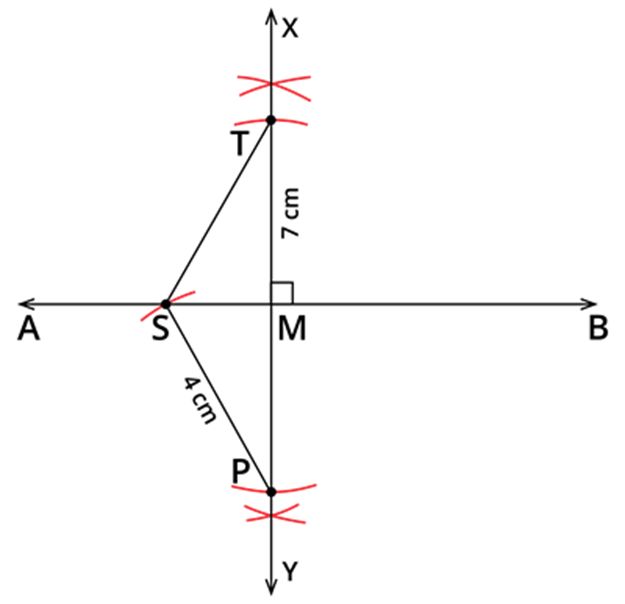
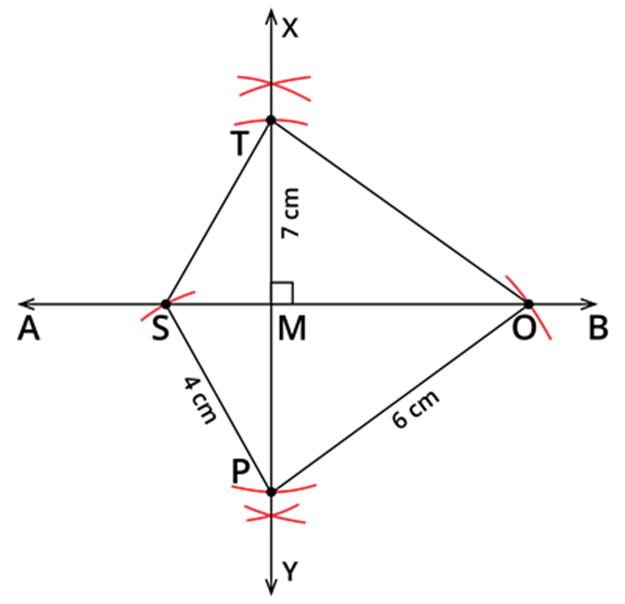
Step 5: Also, given that OP=6 cm. Take 6 cm as radius and P as centre, draw an arc, which cuts AB at O. Join OP and OT. We obtained a required kite STOP.

 ReginaTagebücher
ReginaTagebücher
